Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Orthop. Nov 18, 2016; 7(11): 718-725
Published online Nov 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i11.718
Published online Nov 18, 2016. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i11.718
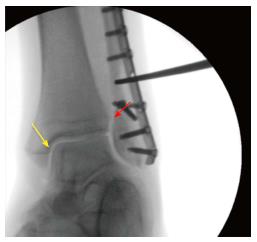
Figure 1 Intra-operative assessment of the syndesmotic integrity in a Weber B fracture with the hook test under fluoroscopy (Mortise view).
In this case, the tibiofibular clear space (red arrow) and the medial clear space (yellow arrow) do not open indicating that the syndesmotic ligaments are intact.
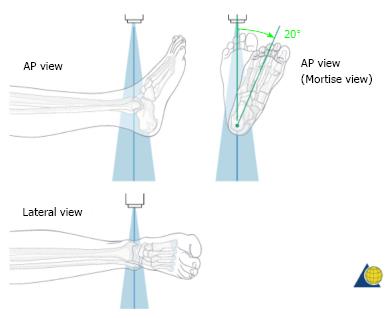
Figure 2 Illustration of the plain radiographs of the ankle (Copyright by AO Foundation, Switzerland).
AP: Anterior-posterior.
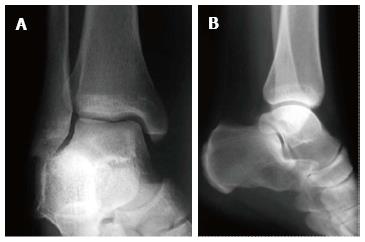
Figure 3 Examples for radiographs of the ankle: Mortise view (A) and lateral view (B).
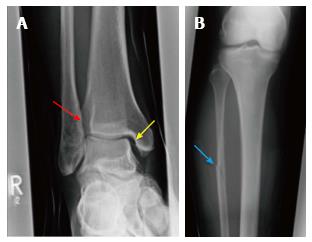
Figure 4 The increased tibiofibular clear space (red arrow) and medial clear space (yellow arrow) are highly suspicious for a syndesmotic lesion (A) and the radiograph of the proximal part of the lower leg is showing a Maisonneuve injury (blue arrow) (B).
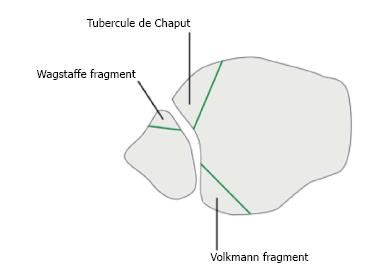
Figure 5 Schematic illustration of the avulsion fractures of the anterior part of the syndesmosis (Tubercule de Chaput, Wagstaffe fragment) and posterior Volkmann fragment (Copyright by AO Foundation, Switzerland).
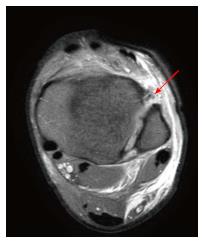
Figure 6 Axial plane of magnetic resonance imaging showing a full thickness tear of the anterior part of the syndesmosis (red arrow).
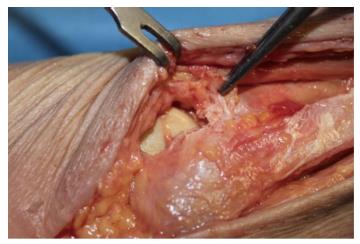
Figure 7 Intraoperative visualization of the anterior part of the syndesmosis; in this patient the anterior part of the syndesmosis is completely disrupted (hold with the pincers).
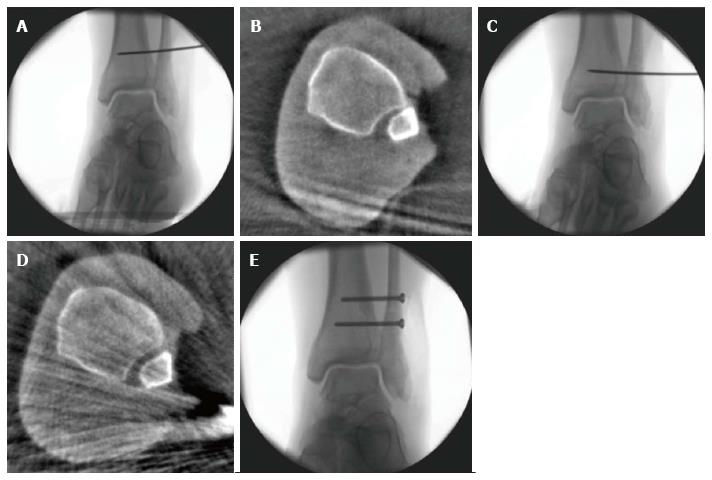
Figure 8 A 25-year-old patient with a Maisonneuve injury.
Assessment of reduction with intra-operative three-dimensional scan (A-E): After closed reduction and temporary fixation with a k-wire (A) the three-dimensional scan shows malreduction of the distal fibula in the incisura (B). Immediate intraoperative revision was performed (C) with repeated intraoperative three-dimensional scan showing correct reduction of the distal fibula. With k-wire in place, two syndesmotic screws have been placed to stabilize the ankle diastase (E).
- Citation: Schnetzke M, Vetter SY, Beisemann N, Swartman B, Grützner PA, Franke J. Management of syndesmotic injuries: What is the evidence? World J Orthop 2016; 7(11): 718-725
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v7/i11/718.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v7.i11.718