Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Orthop. Nov 18, 2020; 11(11): 475-482
Published online Nov 18, 2020. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v11.i11.475
Published online Nov 18, 2020. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v11.i11.475
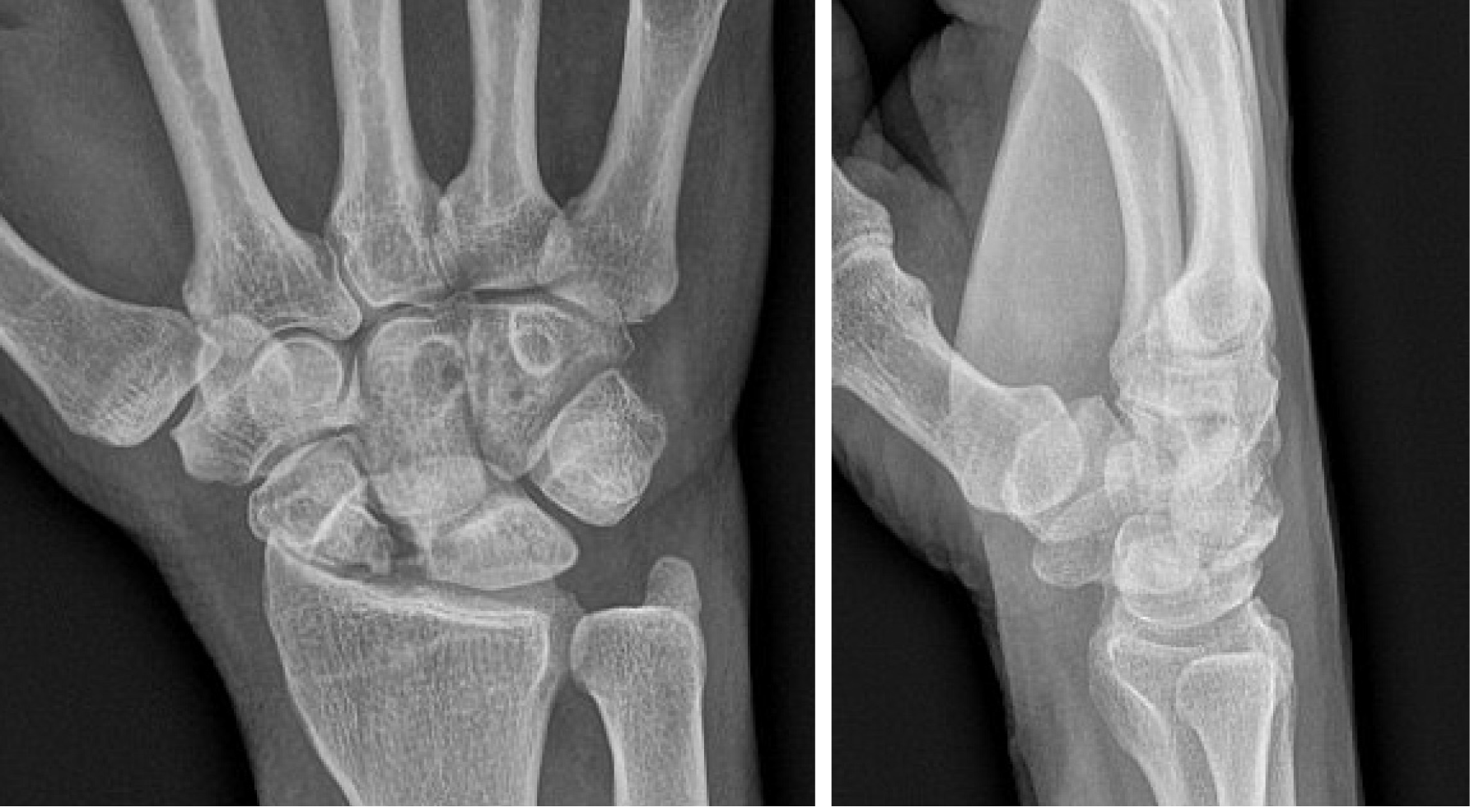
Figure 1 Plain PA and lateral radiographs demonstrating a post-traumatic deformity of a proximal right scaphoid with moderate to severe radiocarpal joint narrowing as well as dorsal intercalated segmental instability.
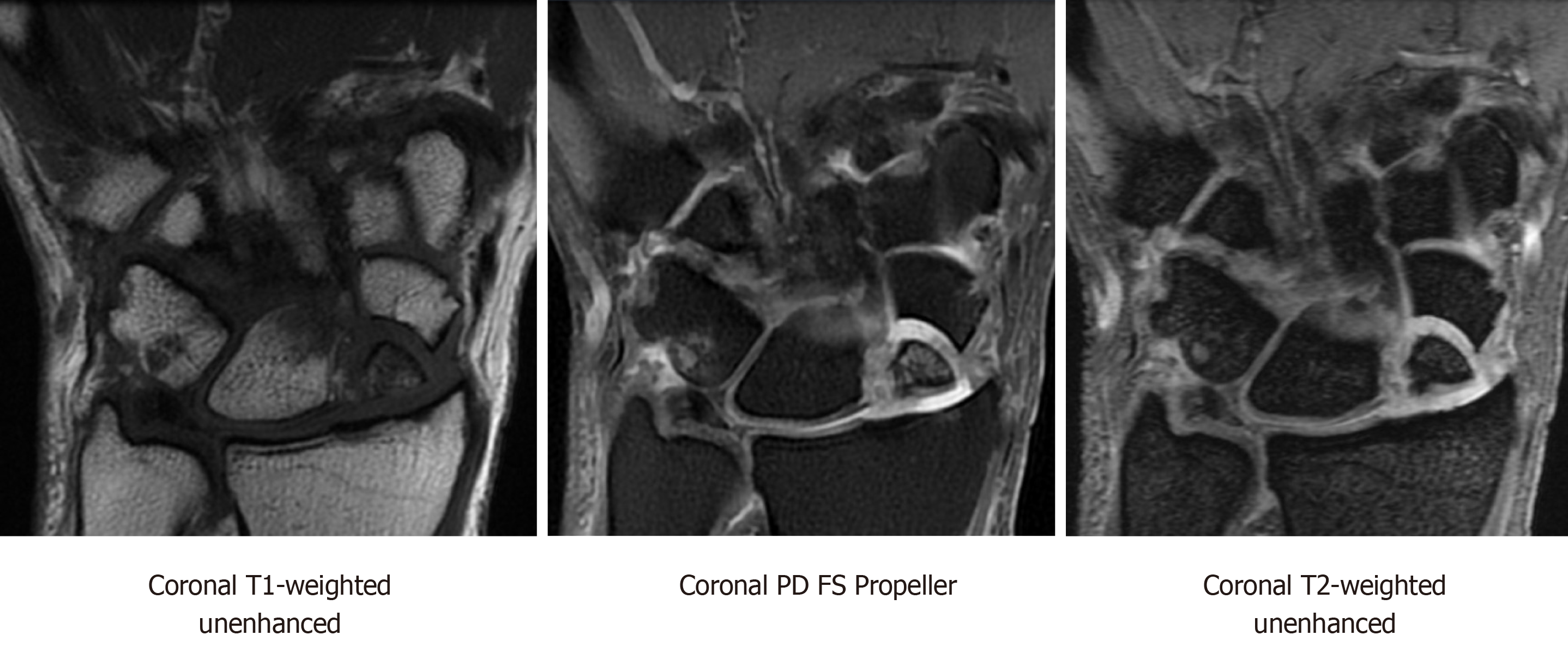
Figure 2 Coronal magnetic resonance imaging T1-weighted unenhanced, coronal proton density fat-saturation propeller, and coronal T2-weighted sequences showing scaphoid nonunion advanced collapse with chronic ununited comminuted scaphoid fracture involving the proximal pole and mid waist.
There are several displaced and necrotic proximal pole fragments, and severe chondrosis at the radioscaphoid articulation. PD: Proton density; FS: Fat-saturation.
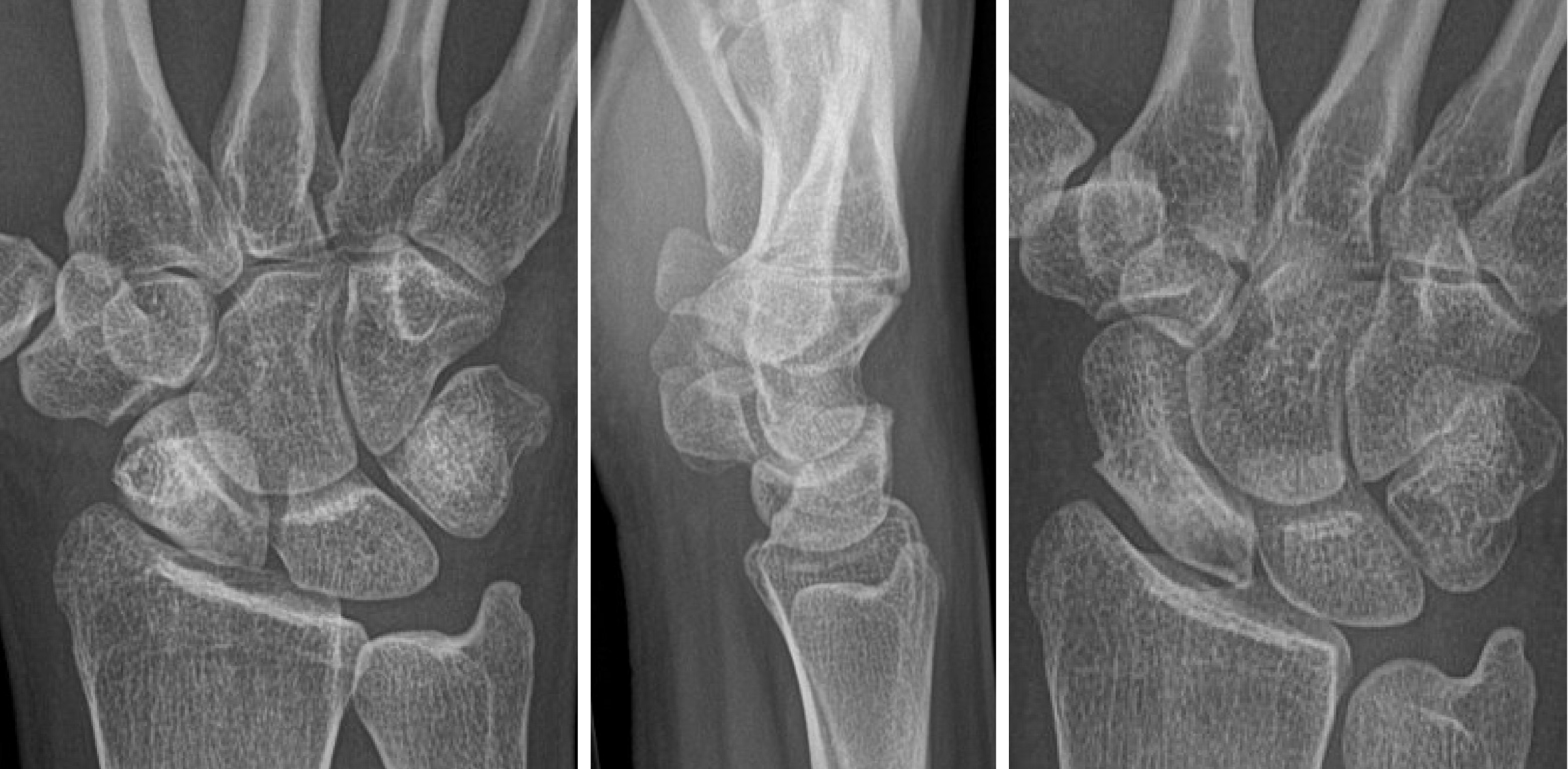
Figure 3 Plain PA, lateral and navicular view radiographs demonstrating sclerosis of the scaphoid at the waist and resorption of the proximal pole.
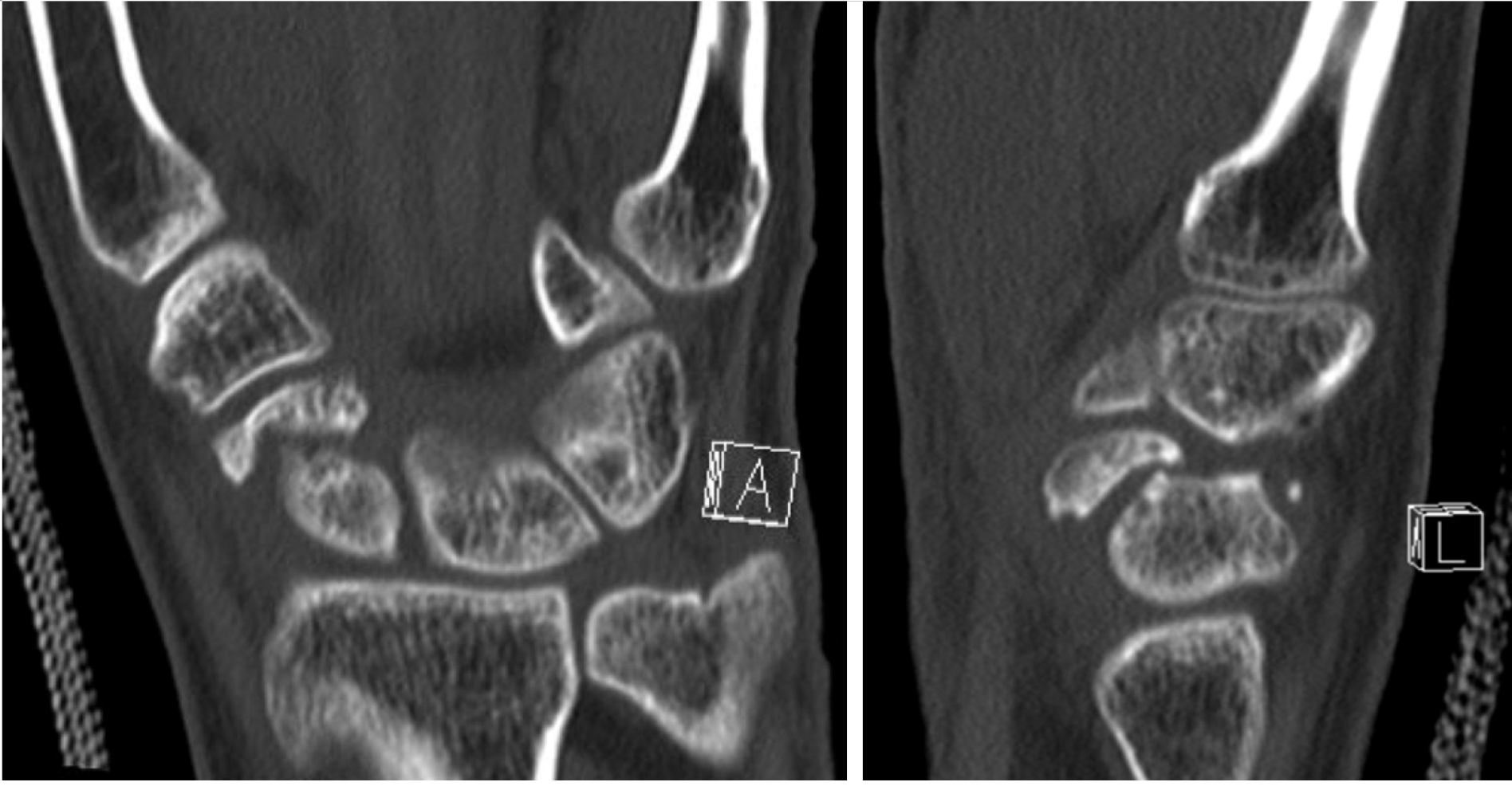
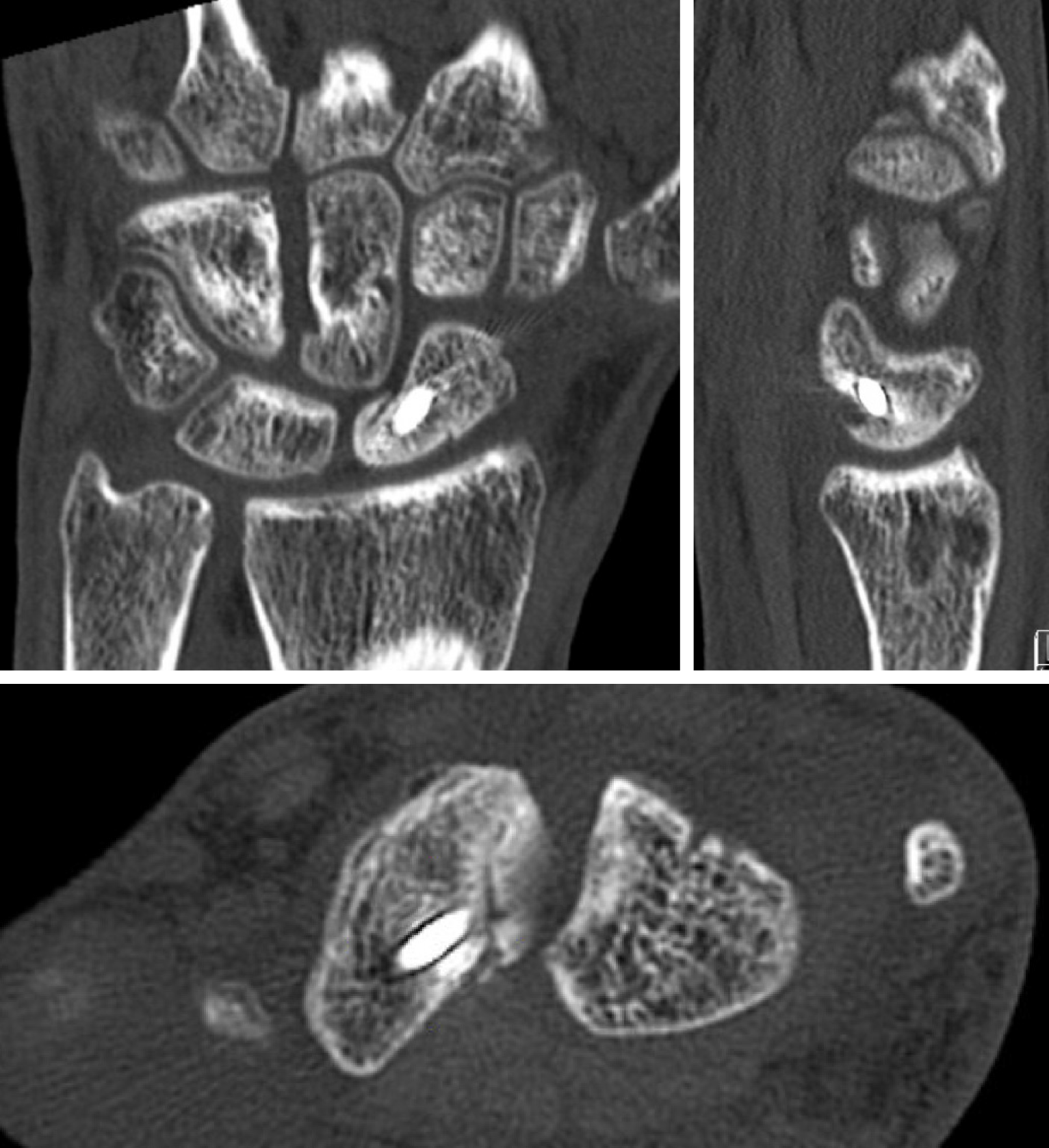
Figure 4 Coronal and sagittal unenhanced computed tomography image demonstrating a chronic fracture involving the distal scaphoid with moderate humpback deformity and dorsal intercalated segmental instability.
Figure 5 Coronal, sagittal, and axial unenhanced computed tomography images status post treatment of scaphoid nonunion with vascularized bone graft from the distal radius and single threaded screw.
There is evidence of bony bridging and integration of the graft.
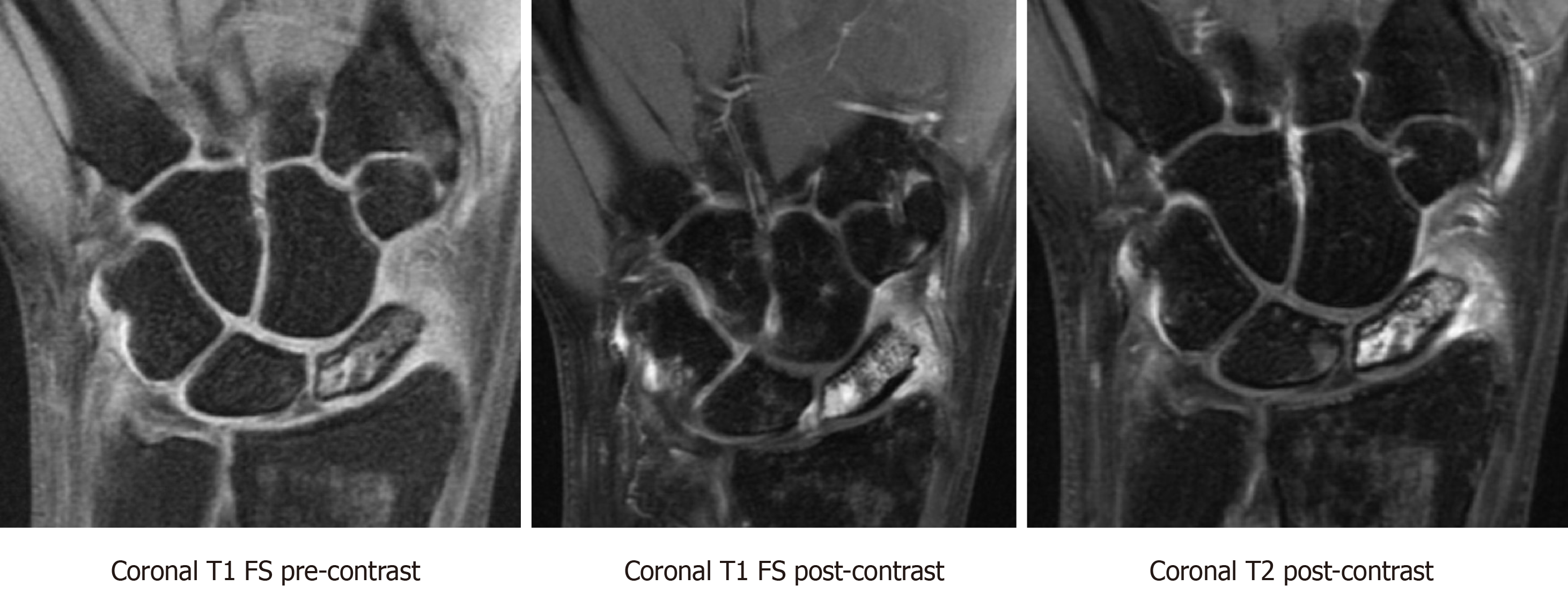
Figure 6 T1-weighted fat saturated pre-contrast, T1-weighted fat saturated post-contrast, and T2-weighted post-contrast sequences showing preserved vascularity in a proximal pole scaphoid fracture.
There is a hypointense fracture line and diffuse marrow edema throughout the scaphoid. There is also hypointense T1 signal and hyperintense T2 signal with corresponding hyperenhancement on post-contrast imaging at the proximal pole, most intense in the proximal pole in keeping with preserved vascularity. FS: Fat saturated.
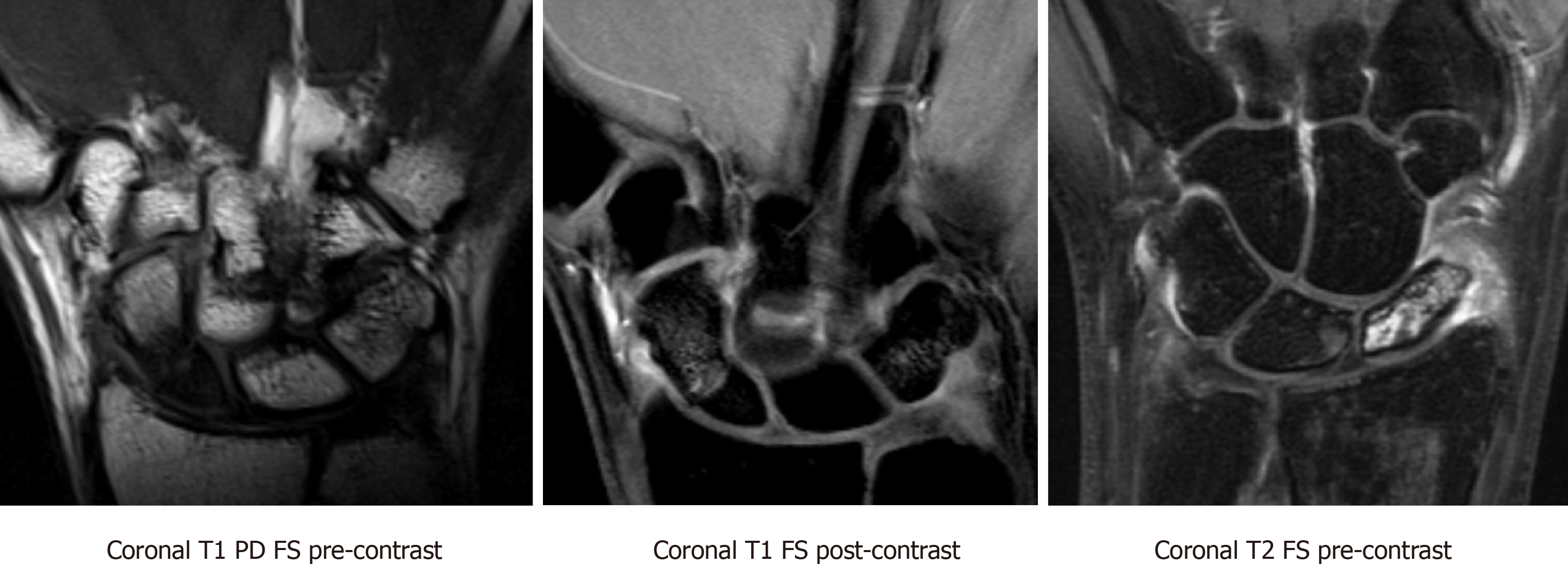
Figure 7 Coronal T1-weighted proton density fat saturation pre-contrast, Coronal T1-weighted fat saturation post-contrast, and coronal T2-weighted fat saturation pre-contrast magnetic resonance imaging sequences demonstrating nondisplaced ununited fracture of the proximal pole of the scaphoid.
There is T1 hypointense and heterogeneous T2 signal within the proximal pole fracture fragment. The proximal pole fracture fragment demonstrates no significant contrast enhancement on the postcontrast images, compatible with avascular necrosis. PD: Proton density; FS: Fat saturation.
- Citation: Cheema HS, Cheema AN. Radiographic evaluation of vascularity in scaphoid nonunions: A review. World J Orthop 2020; 11(11): 475-482
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v11/i11/475.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v11.i11.475