Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Oncol. Jun 10, 2018; 9(3): 42-55
Published online Jun 10, 2018. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v9.i3.42
Published online Jun 10, 2018. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v9.i3.42
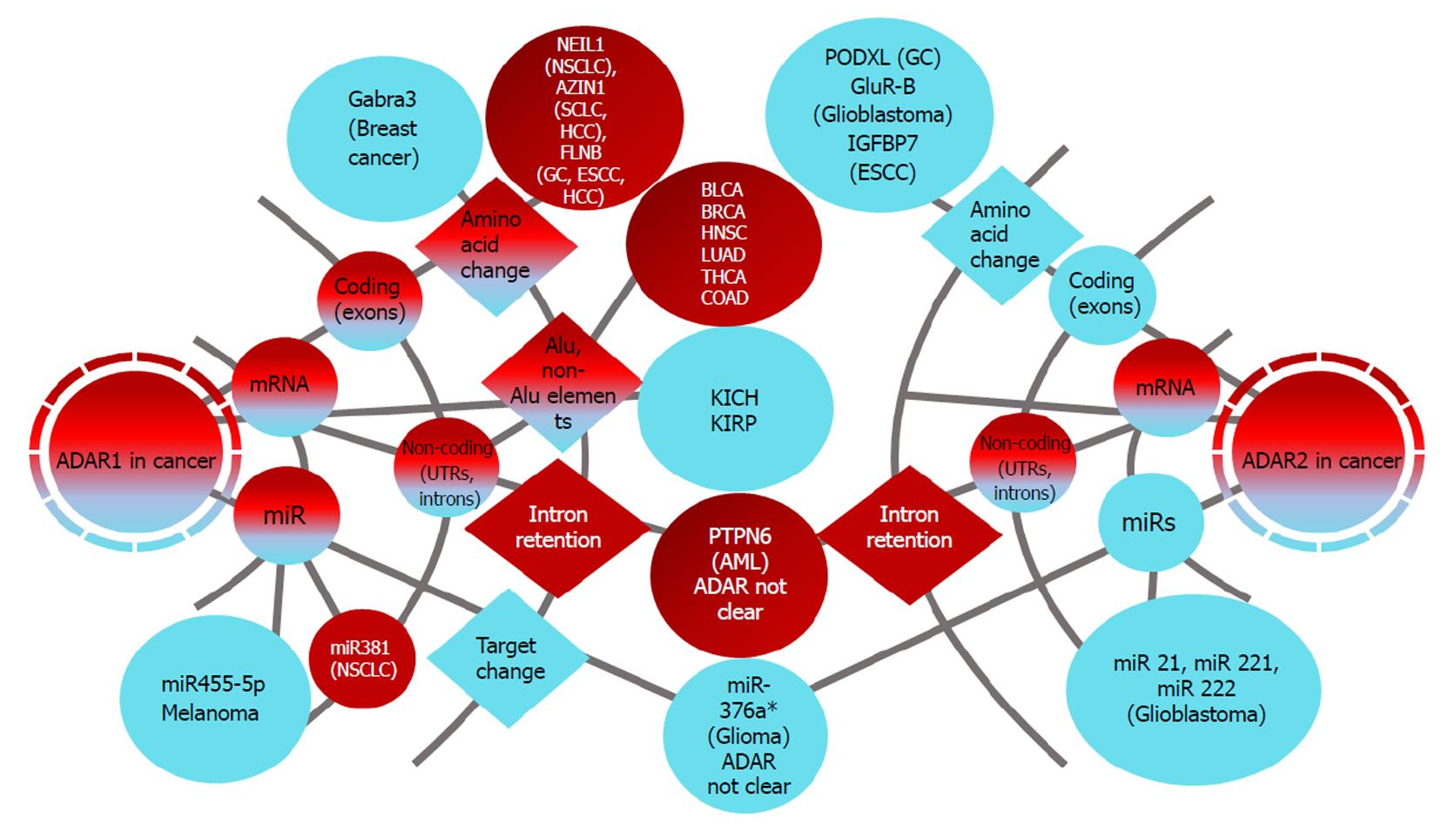
Figure 2 Editing of double-stranded RNA on mRNA and miRNA.
Below, high ADAR1 levels are associated with breast cancer, NSCLC, colon cancer and cervical cancer, while low ADAR1 levels are shown in melanoma. Low levels of ADAR2 are present in glioblastoma. HCC, ESCC and gastric cancer are indicated as ADAR2-low and ADAR1-high cancers. The potential roles of ADAR1 and ADAR2 in cancer are depicted by mind map. Red means high expression/inosine content and blue means low expression/inosine content. In circles are the names of molecules/cancers and in diamonds are the mechanisms. NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ESCC: Esophageal cell carcinoma; GC: Gastric cancer; ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; AML: Acute myeloid leukemia; SCLC: Small cell lung cancer; BLCA: Bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA: Breast invasive carcinoma; COAD: Colon adenocarcinoma; HNSC: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; LUAD: Lung adenocarcinoma; THCA: Carcinoma; KICH: Kidney chromophobe; KIRP: Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; NEIL1: NEI-like protein 1; Gabra3: Alpha-3 subunit of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A; FlnB: Filamin B; PTPN6: Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 6; PODXL: Podocalyxin-like; GluR-B: Glutamate R-B; IGFBP7: Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7.
- Citation: Tusup M, Kundig T, Pascolo S. Epitranscriptomics of cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2018; 9(3): 42-55
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v9/i3/42.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v9.i3.42