Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. May 24, 2024; 15(5): 603-613
Published online May 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i5.603
Published online May 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i5.603
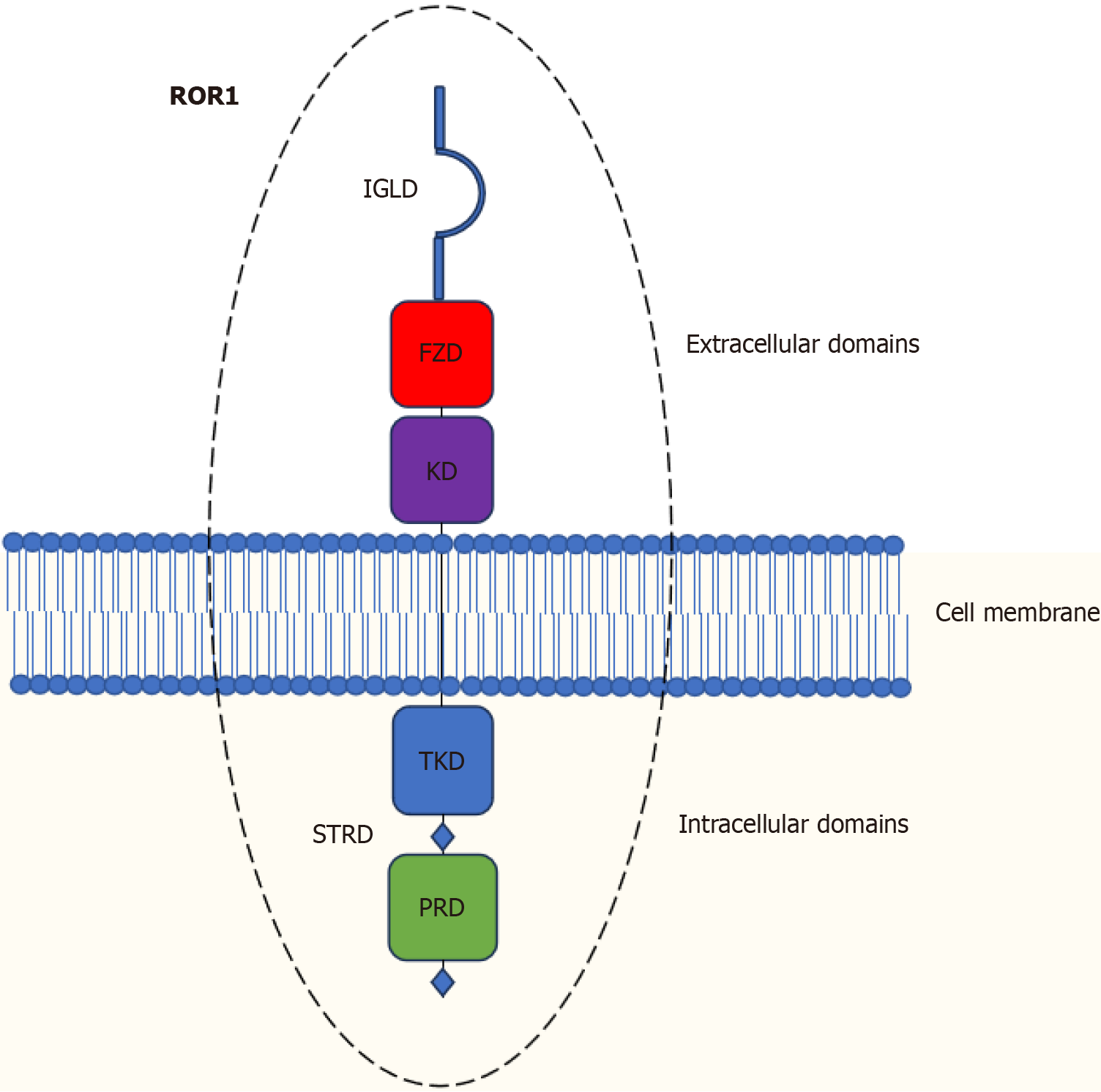
Figure 1 Diagram of the receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 domain structure.
IG: Ig-like domain; FZD: Frizzled domain; KD: Kringle domain; TKD: Tyrosine kinase domain; S/T: Serine/Threonine-rich domain; PRD: Proline-rich domain.
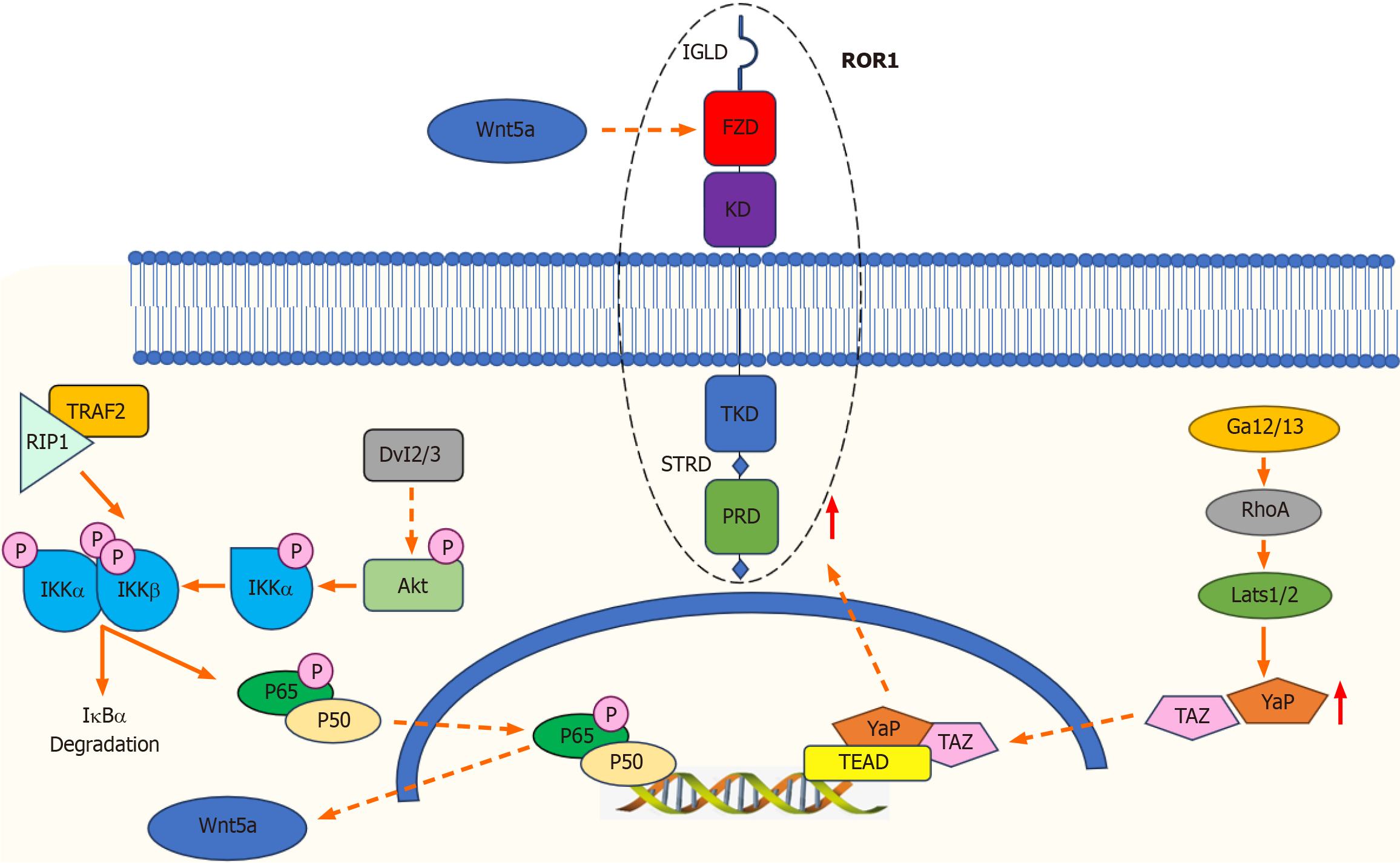
Figure 2 Signaling pathways regulated by receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1.
Dvl2/3: Dishevelled 2/3; Akt: Protein kinase B; Iκκα: IκB kinase α; IκBα: Inhibitor of kappa B α; p65: Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit; RhoA: Ras homolog gene family, member A; Gα12/13: G protein subunit alpha 12/13; Lats1/2: Large tumor suppressor kinase 1/2; YAP/TAZ: Yes-associated protein/Transcriptional co-Activator with PDZ-binding motif. Binding of Wnt5a to receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1) induces Dvl2/3 activation and Akt phosphorylation, leading to phosphorylation of Iκκα, activation of the IκB kinase complex, degradation of IκBα, and p65 phosphorylation. Subsequently, p65 is transferred to the nucleus where it promotes the transcription of specific genes, including Wnt5a, producing an autonomous feedback loop. Binding between Wnt5a and the ROR1/frizzled complex leads to activation of RhoA via Gα12/13. This activation inhibits Lats1/2 activity, leading to the dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation of YAP/TAZ. The binding of YAP/TAZ to transcription enhanced association domain increases the transcription of genes linked to tumorigenesis and stemness while increased levels of YAP/TAZ enhance ROR1 expression.
- Citation: Wu ZL, Wang Y, Jia XY, Wang YG, Wang H. Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1: A novel antitumor target in gastrointestinal cancers. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(5): 603-613
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i5/603.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i5.603