Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Mar 24, 2024; 15(3): 434-446
Published online Mar 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i3.434
Published online Mar 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i3.434
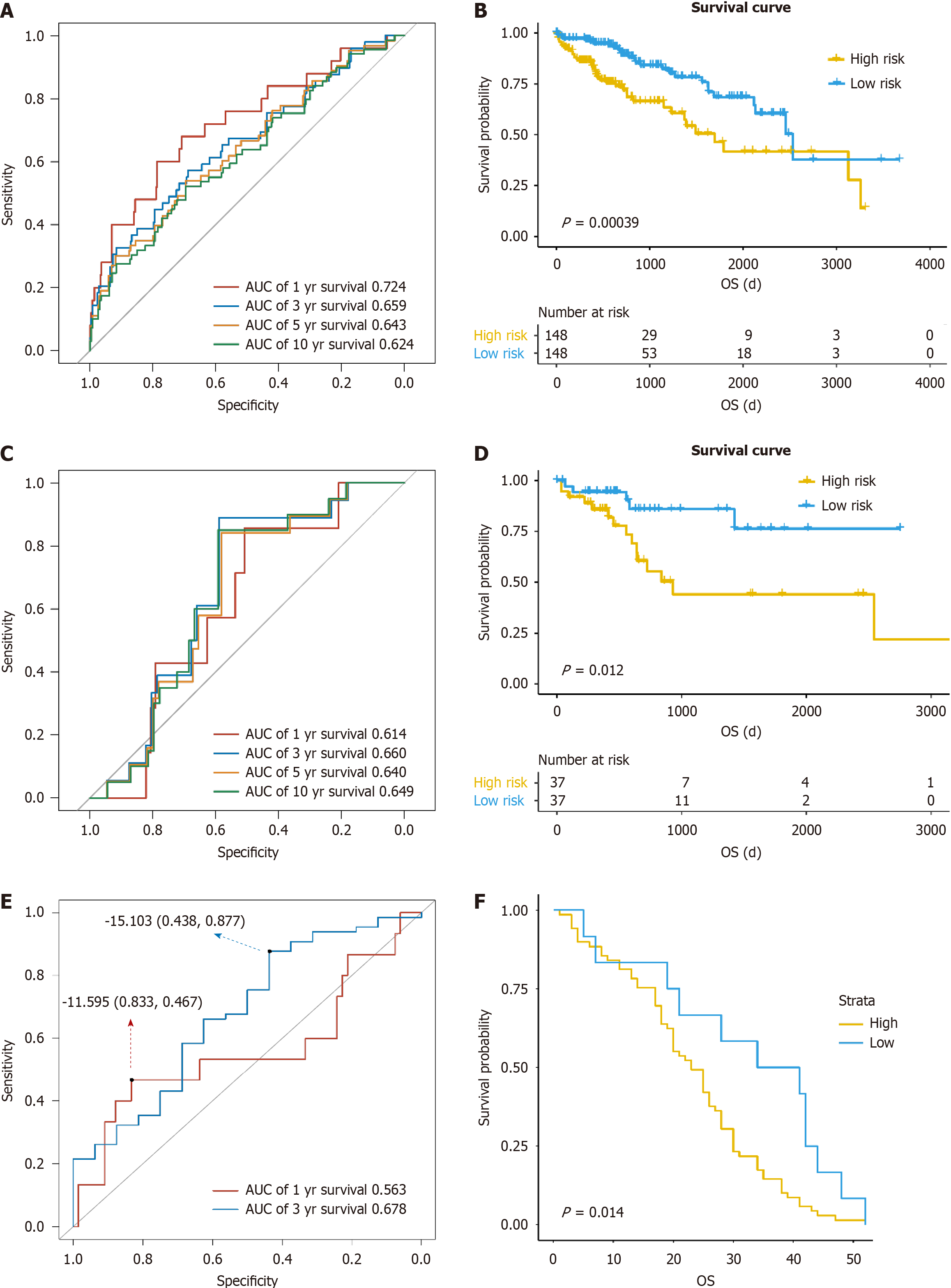
Figure 1 Prognosis predictive model for liver cancer.
A: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the model in training group; B: Survival curve of high- and low-risk patients with liver cancer in training group; C: ROC curve of the model in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) validation group; D: Survival curve of high- and low-risk patients with liver cancer in TCGA validation group; E: ROC curve of the model in gene expression comprehensive (GEO) validation group; F: Survival curve of high- and low-risk patients with liver cancer in GEO validation group. AUC: Area under the curve; OS: Overall survival.
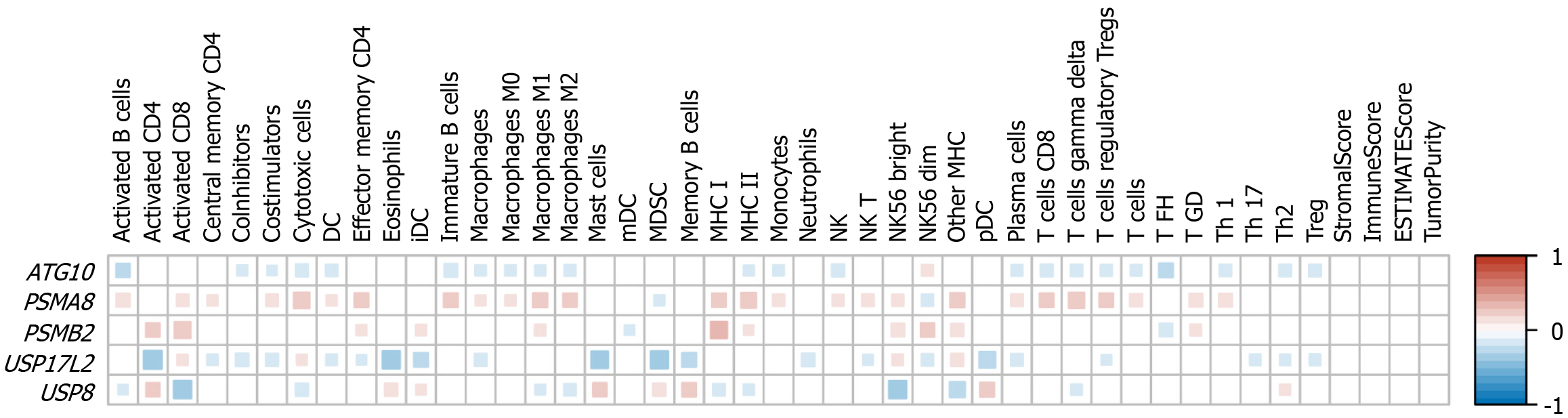
Figure 2 Immunocyte infiltration between cases with high and low expression levels of ATG10, PSMA8, PSMB2, USP17L2, and USP8.
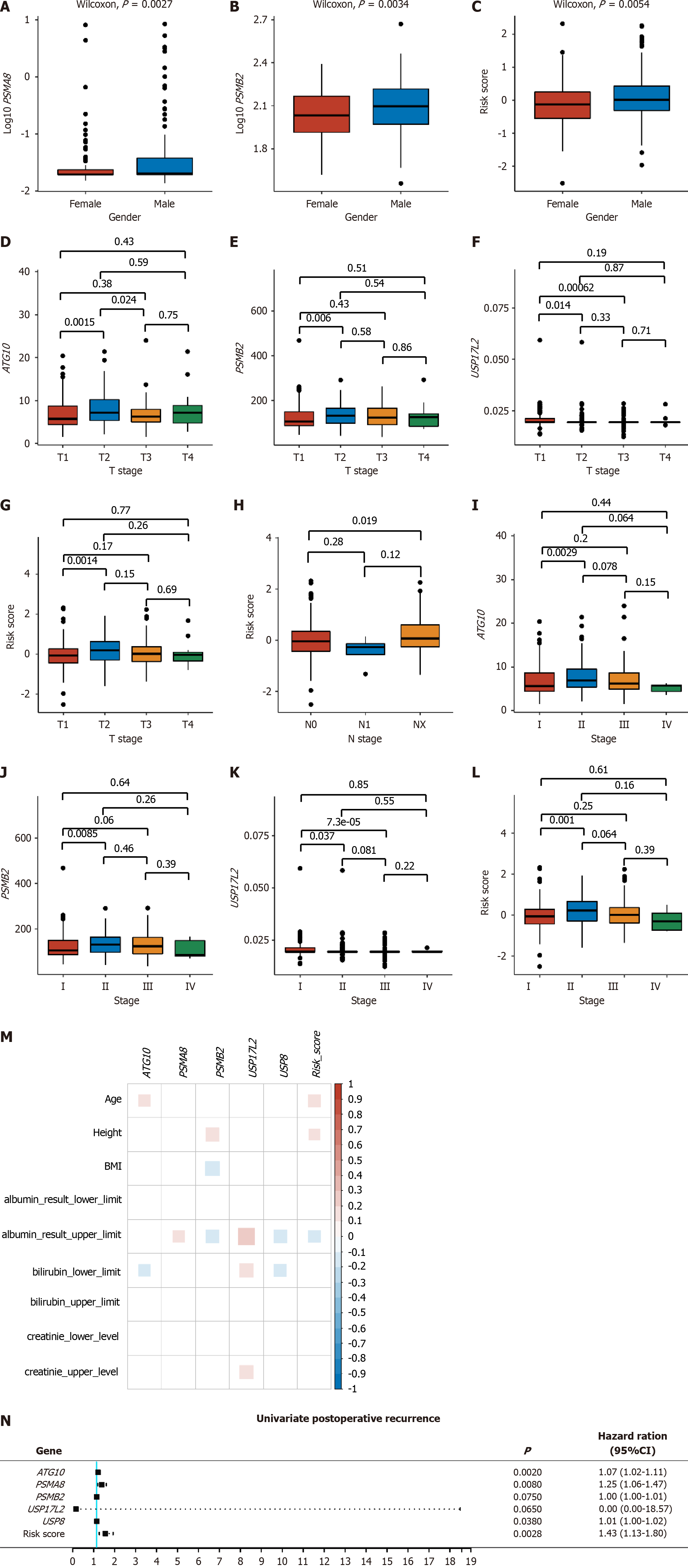
Figure 3 Correlation of expression levels of ATG10, PSMA8, PSMB2, USP17L2, and USP8 and risk score with clinical parameters.
A-C: Gene expression and risk score between genders; D-G: Gene expression and risk score among T stages; H: Risk score among N stages; I-L: Gene expression and risk score among clinical stages; M: Correlation of gene expression levels and risk score with biochemical indexes; N: Correlation of gene expression levels and risk score with postoperative recurrence in liver cancer, with a hazard ratio (HR) > 1 referring to a positive correlation and HR < 1 referring to a negative correlation. P < 0.05 indicated statistical significance. HR: Hazard ratio.
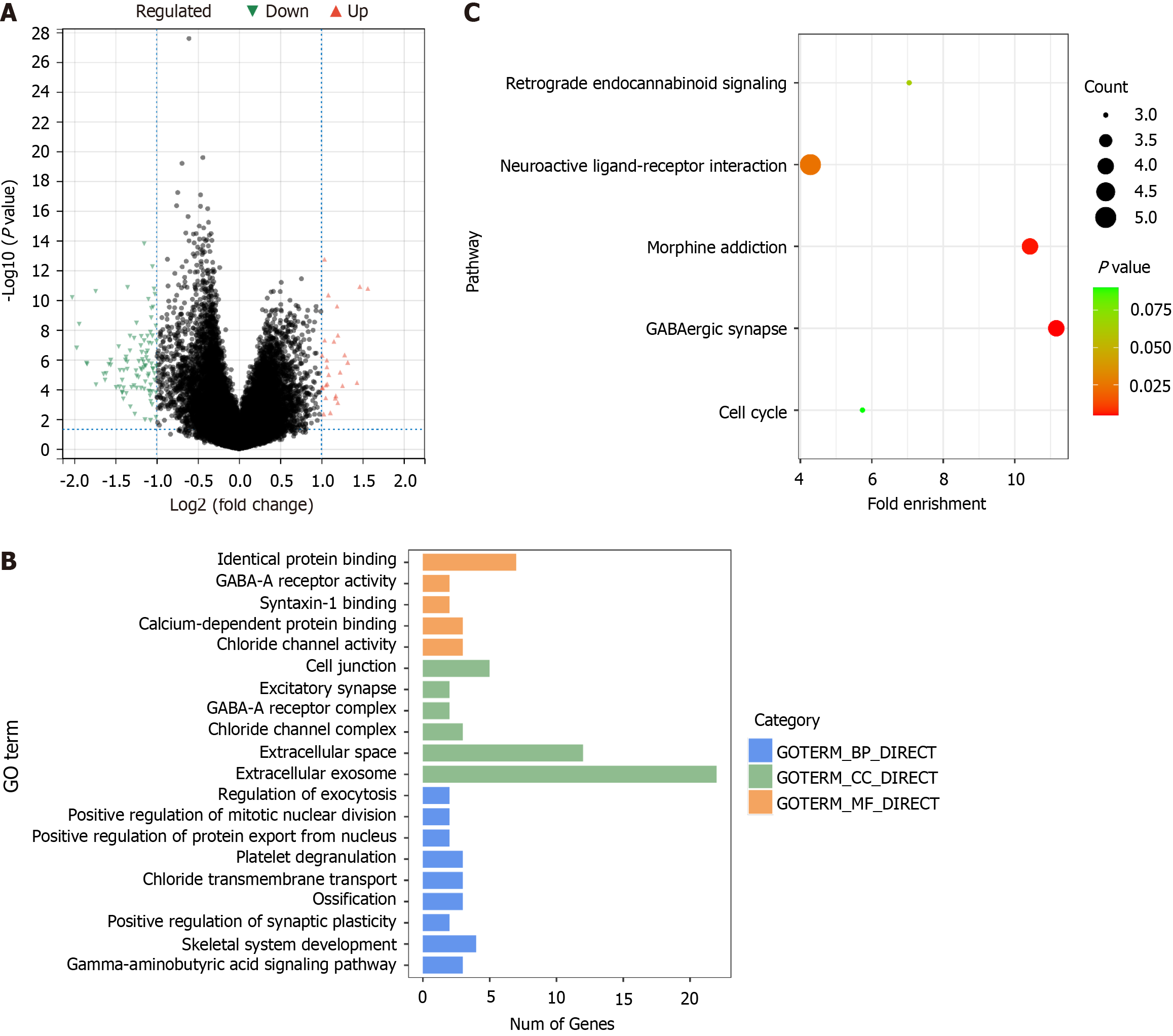
Figure 4 Enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes between liver cancer and normal samples.
A: Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (DEGs); B: Gene ontology terms enriched by DEGs; C: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways enriched by DEGs. GO: Gene ontology; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; DEGs: Differentially expressed genes.
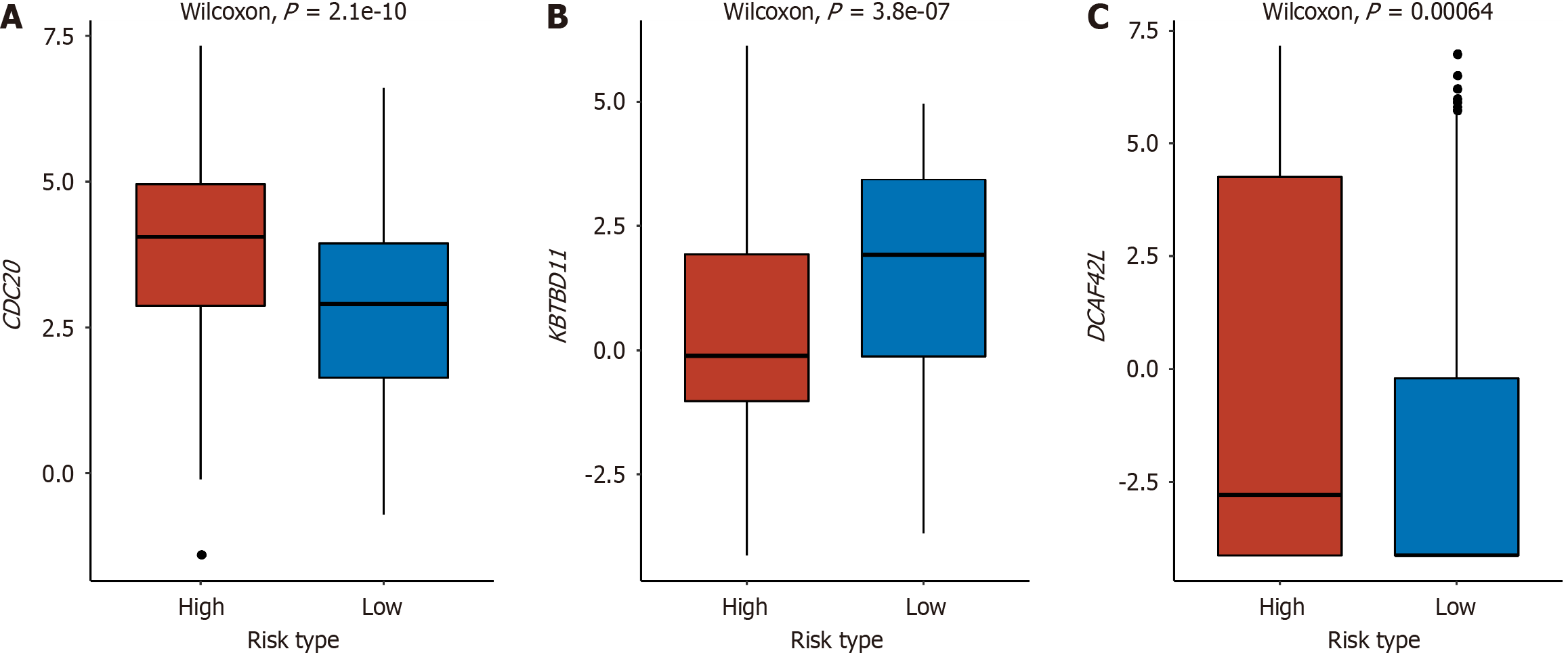
Figure 5 Differentially expressed genes in E3 gene set between high- and low-risk groups.
A-C: CDC20 (A), KBTBD11 (B), and DCAF4L2 (C) in E3 gene sets were significantly different between high- and low-risk groups.
- Citation: Li H, Ma YP, Wang HL, Tian CJ, Guo YX, Zhang HB, Liu XM, Liu PF. Establishment of a prognosis predictive model for liver cancer based on expression of genes involved in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(3): 434-446
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i3/434.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i3.434