Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Oncol. Aug 24, 2023; 14(8): 285-296
Published online Aug 24, 2023. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i8.285
Published online Aug 24, 2023. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i8.285
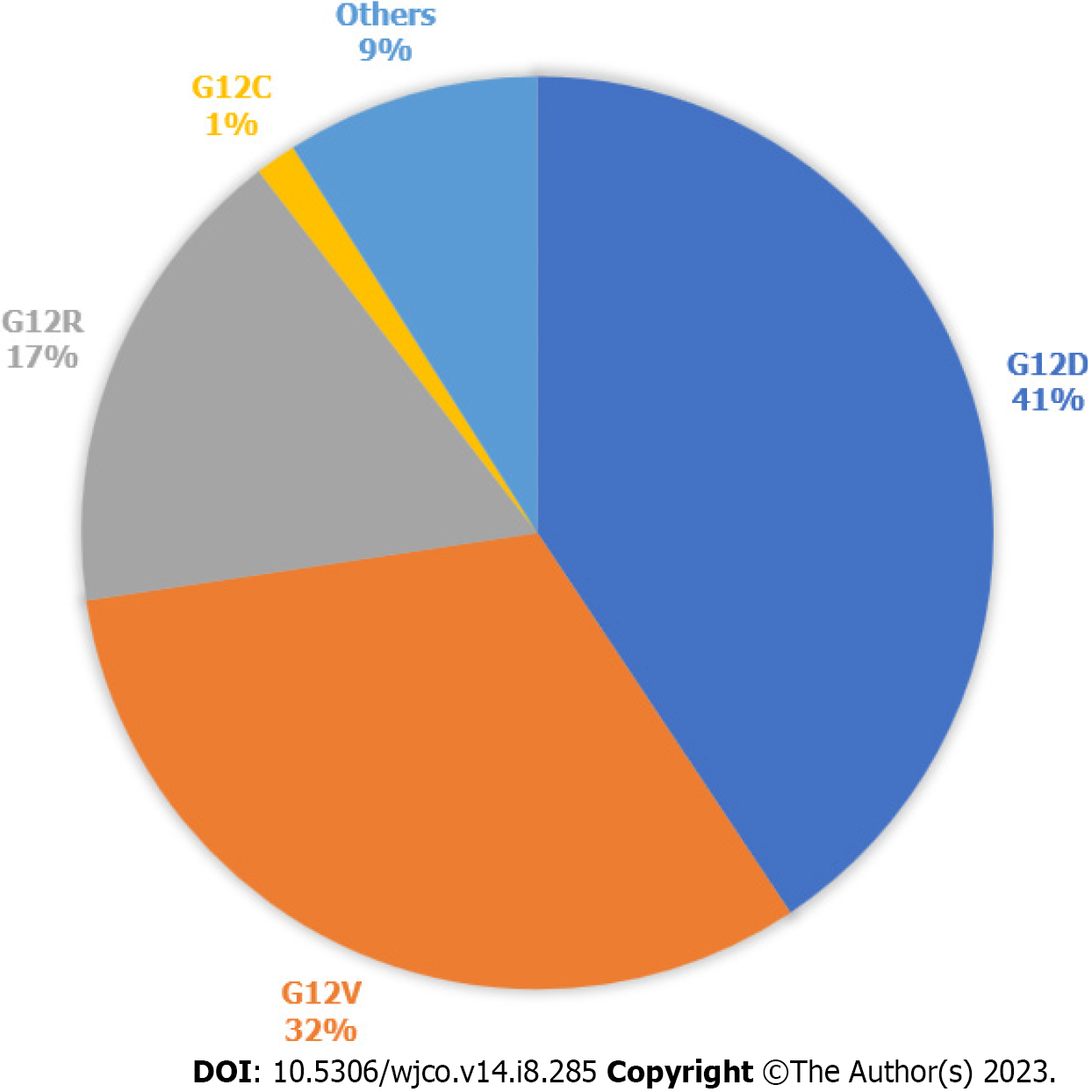
Figure 1 Kirsten rat sarcoma virus mutations in pancreatic cancer.
Types of Kirsten rat sarcoma virus (KRAS) mutations seen in pancreatic cancer, according to data publicly available on cBioPortal. 812 samples with altered KRAS collected from 5 pancreatic cancer studies. Others are A11T, A146T, A18V, G12A, G12I, G12L, G12S, G13C, G13D, G13H, G13P, G13R, L23V, Q61H, Q61K, Q61R.
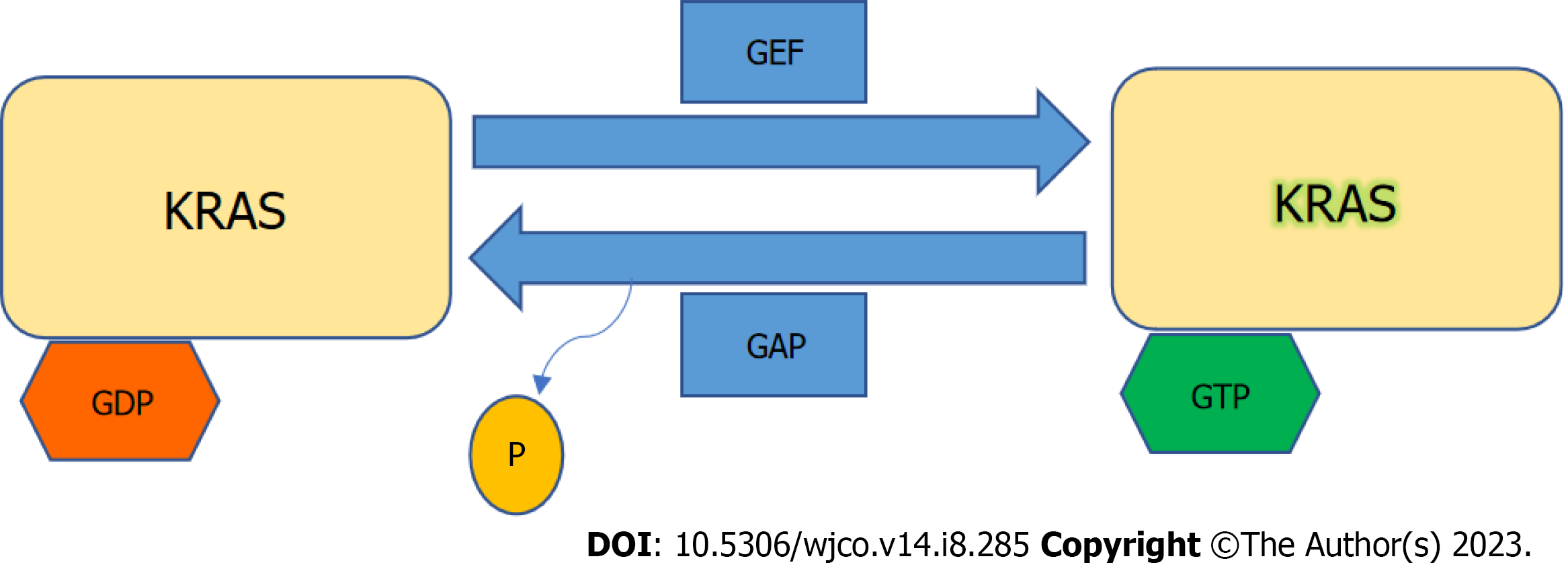
Figure 2 Kirsten rat sarcoma virus activation.
Kirsten rat sarcoma virus is activated when guanine nucleotide exchange factor displaces guanosine diphosphate from nucleotide binding site allowing guanosine triphosphate (GTP) binding and inactivated upon GTP hydrolysis by intrinsic GTP-bound regulatory protein phosphatases (GTPase) activity enhanced by GTPase activating protein. GTP: Guanosine triphosphate; GAP: GTPase activating protein; GDP: Guanosine diphosphate; GEF: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor; KRAS: Kirsten rat sarcoma virus.
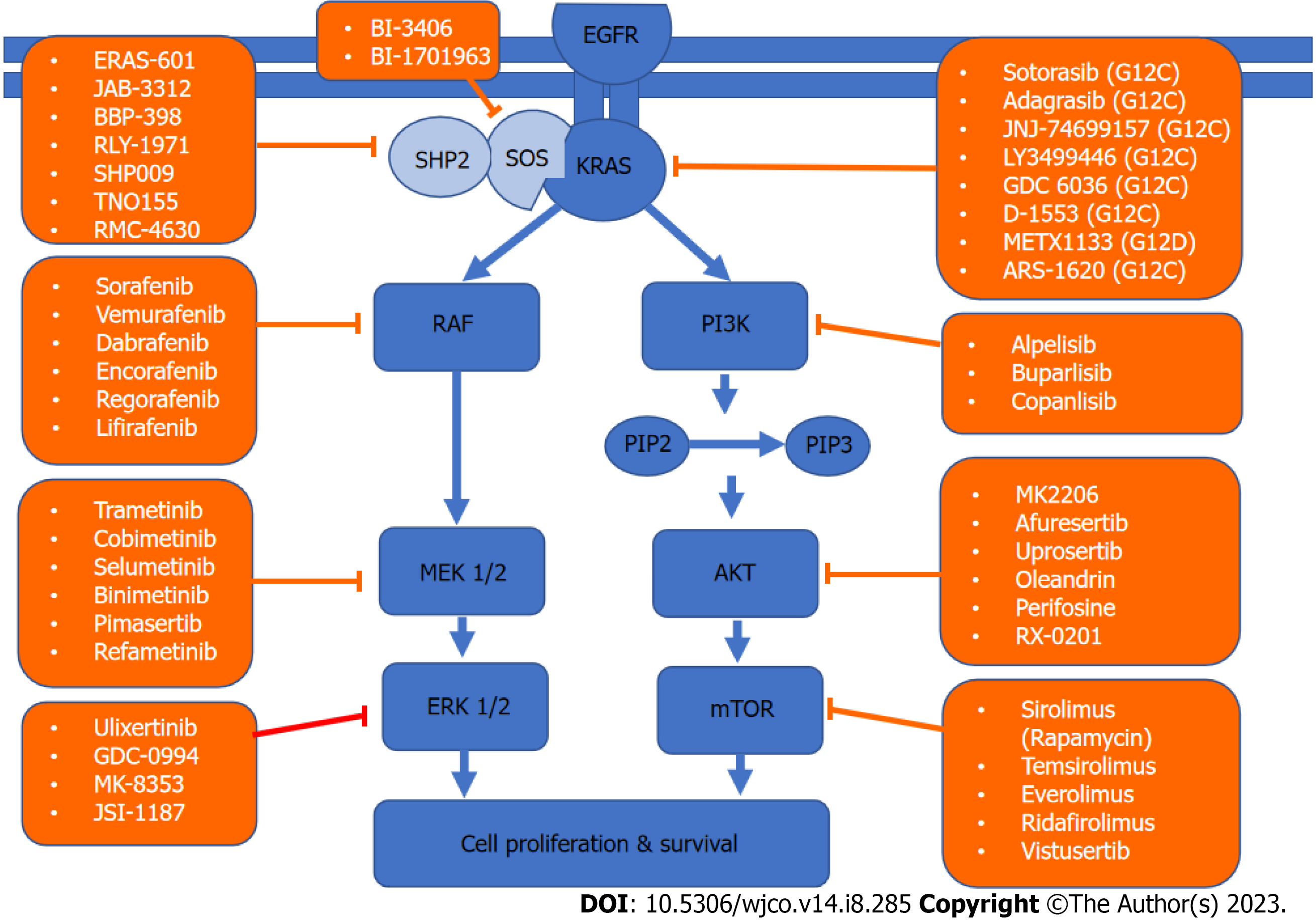
Figure 3 Kirsten rat sarcoma virus signaling network and targeted therapy.
A schematic of the two major Kirsten rat sarcoma virus pathways driving cell survival and drugs that target them. KRAS: Kirsten rat sarcoma virus; AKT: Protein kinase; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; PIP: Prolactin-induced protein; ERK: Extracellular regulated protein kinases; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular regulated protein kinases; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RAF: Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; SHP2: Src homology-2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2; SOS: Son of sevenless.
- Citation: Elhariri A, Alhaj A, Ahn D, Sonbol MB, Bekaii-Saab T, Wu C, Rutenberg MS, Stauffer J, Starr J, Majeed U, Jones J, Borad M, Babiker H. Targeting KRAS in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Progress in demystifying the holy grail. World J Clin Oncol 2023; 14(8): 285-296
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v14/i8/285.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v14.i8.285