Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Oncol. Aug 24, 2021; 12(8): 702-711
Published online Aug 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i8.702
Published online Aug 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i8.702
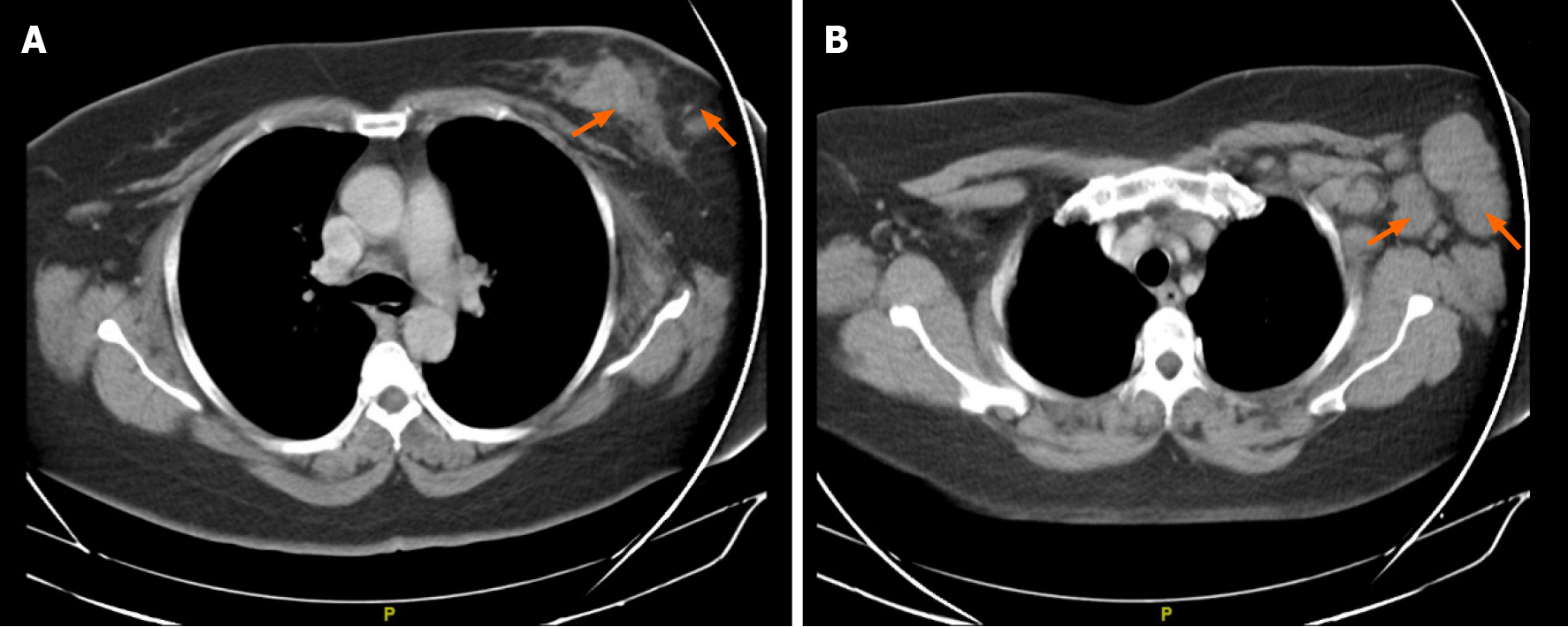
Figure 1 Chest computer tomography scan used as part of staging.
A: Left breast with heterogeneous area on the left side suggestive of a 38 mm malignant neoformative neoplasm; B: Associated with ipsilateral nodal involvement.
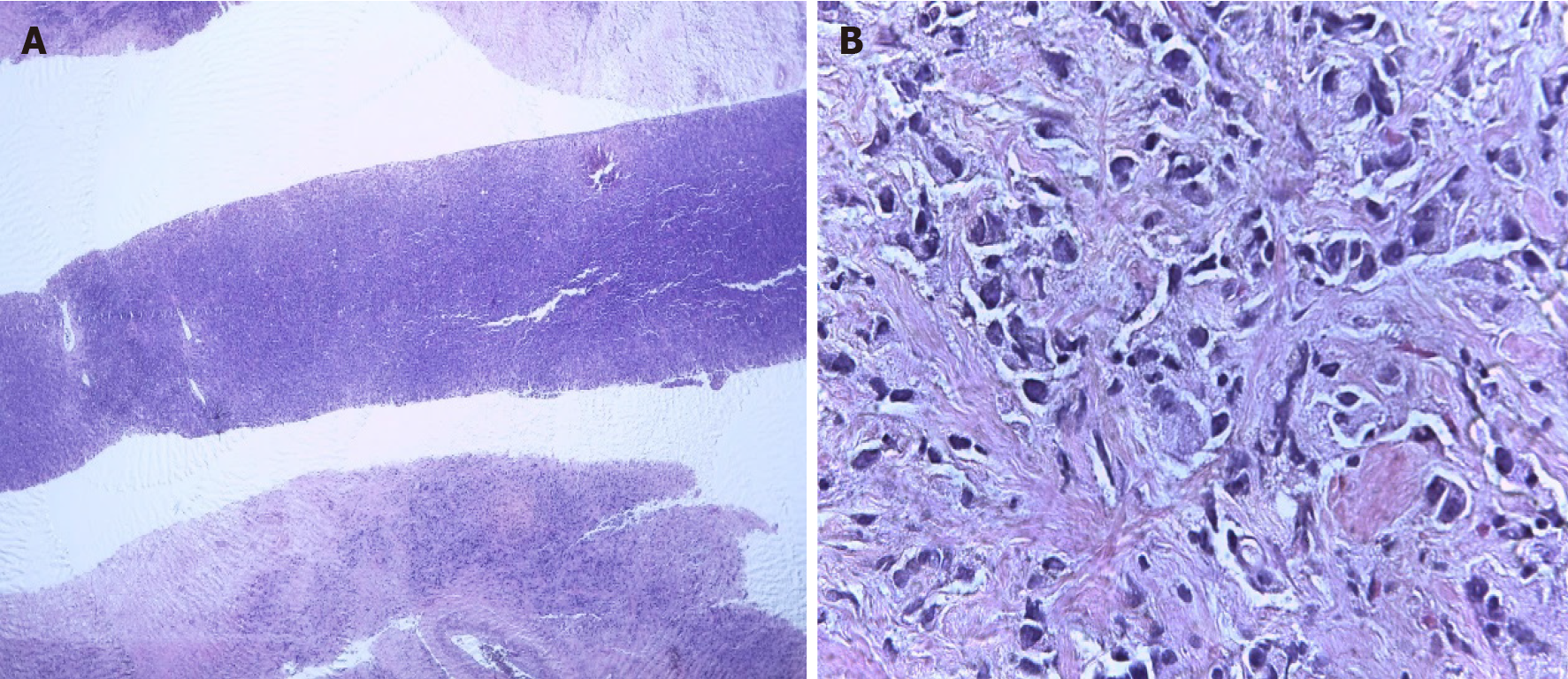
Figure 2 Core biopsy of the left breast.
A: R12 tumor sample; B: Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
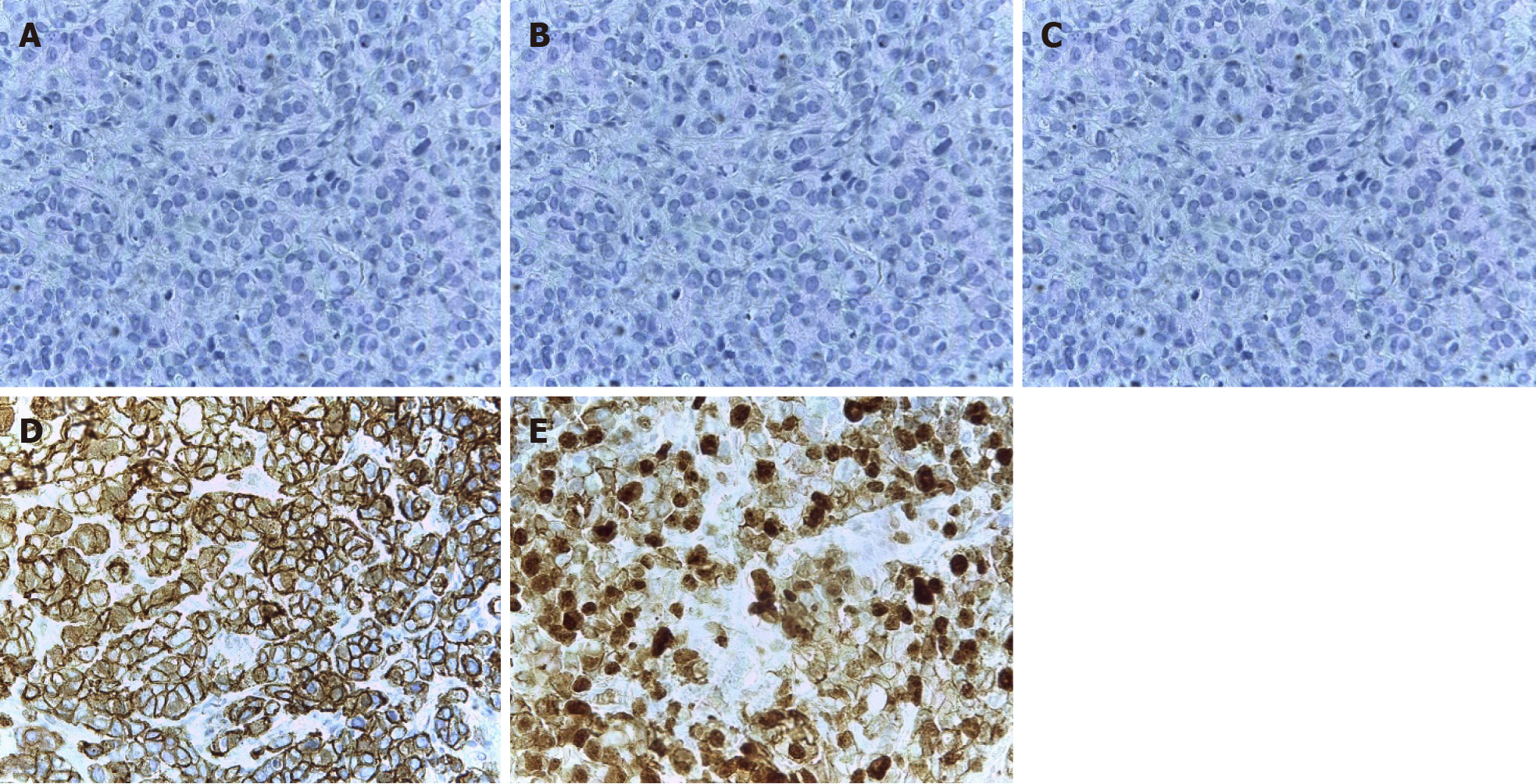
Figure 3 Immunohistochemistry of the R12 left breast.
A: Estrogen receptor: Negative; B: Progesterone receptor: Negative; C: CerbB2: Negative; D: E-cadherin: Positive; E: Ki67: 60%.
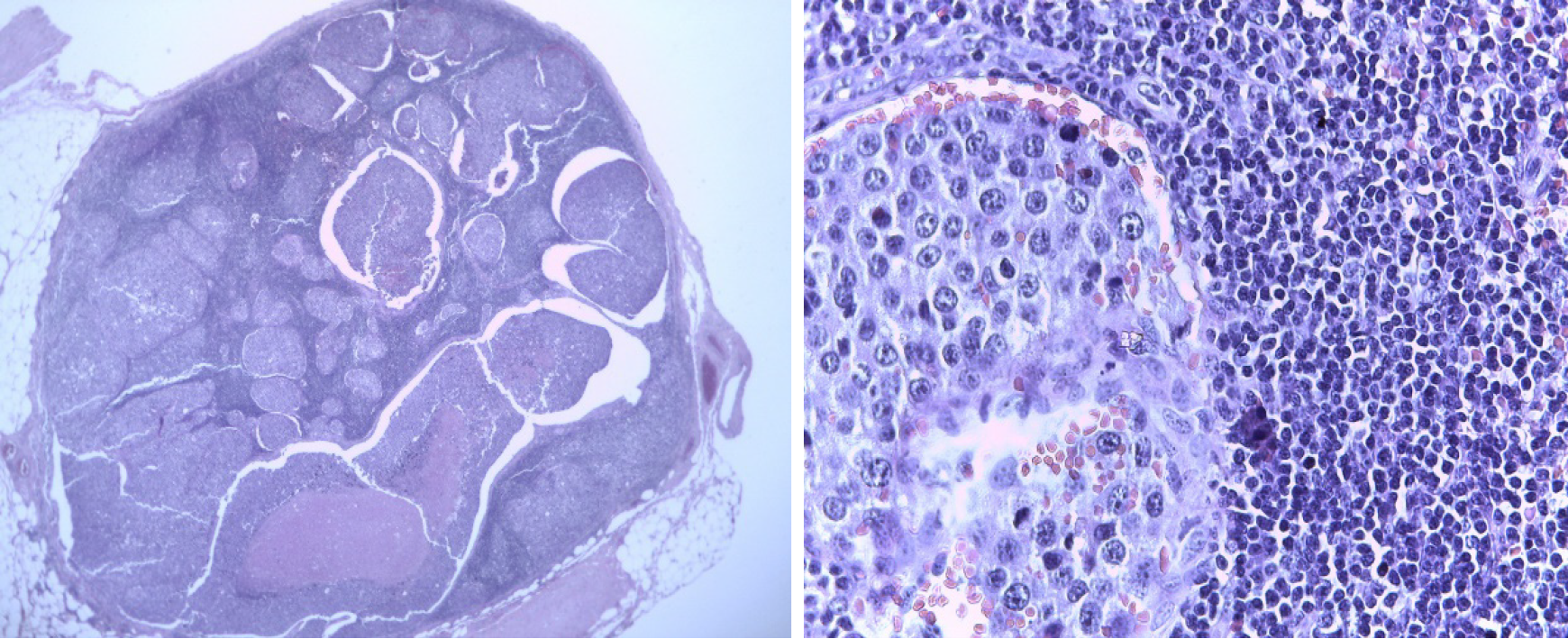
Figure 4 Surgical piece: R12 left breast tumor.
Figure 5 Surgical piece: Left axillary node.
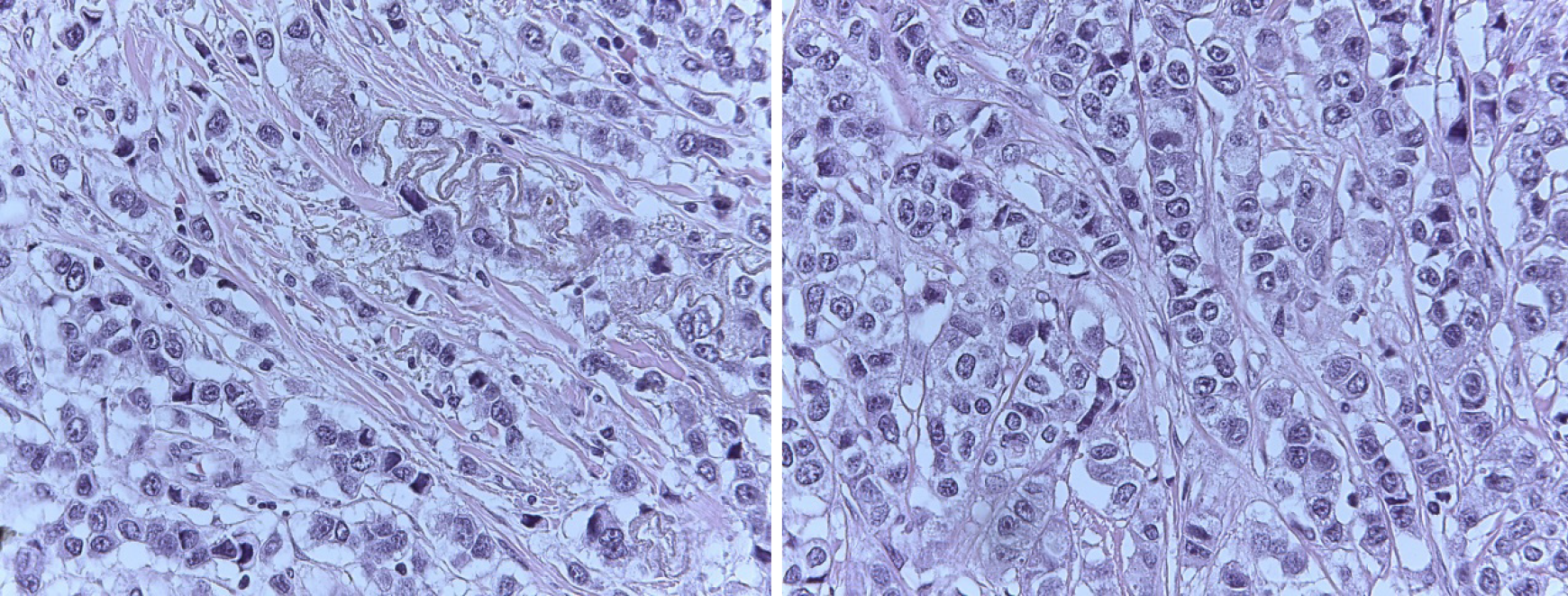
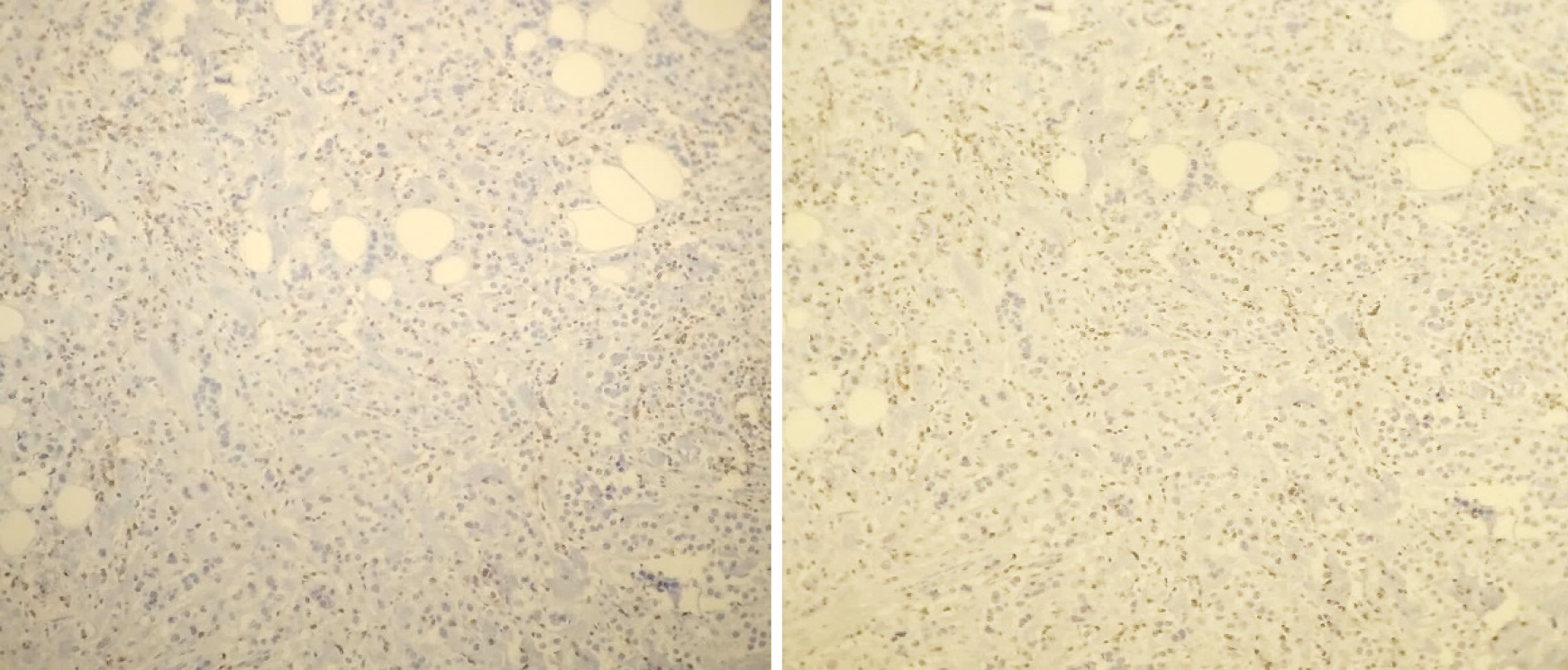
Figure 6 Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in residual tissue (post-neoadjuvant scenario): Less than 10%.
Figure 7 CD8 staining (× 10 magnification): 40%.
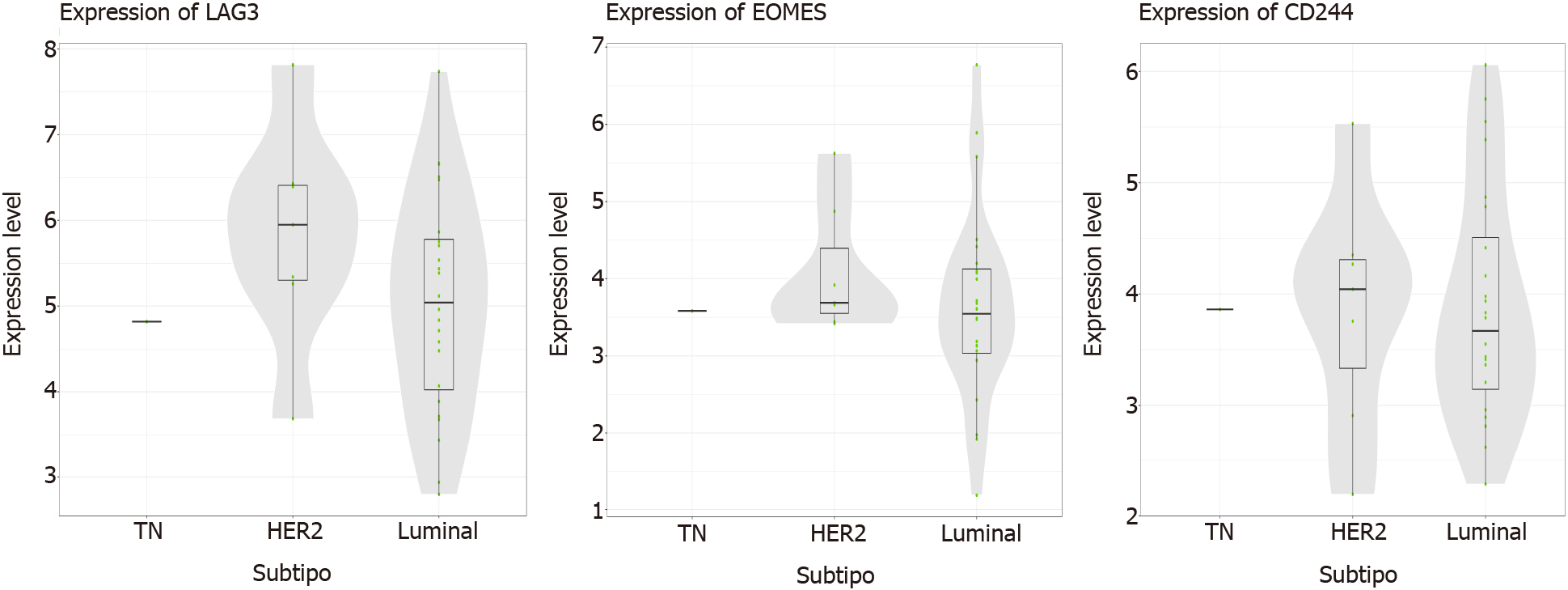
Figure 8 List of genes determining the presence of anergic CD8 cells (“exhausted”): “high” result, from the nCounter® PanCancer Immune Profiling Panel platform.
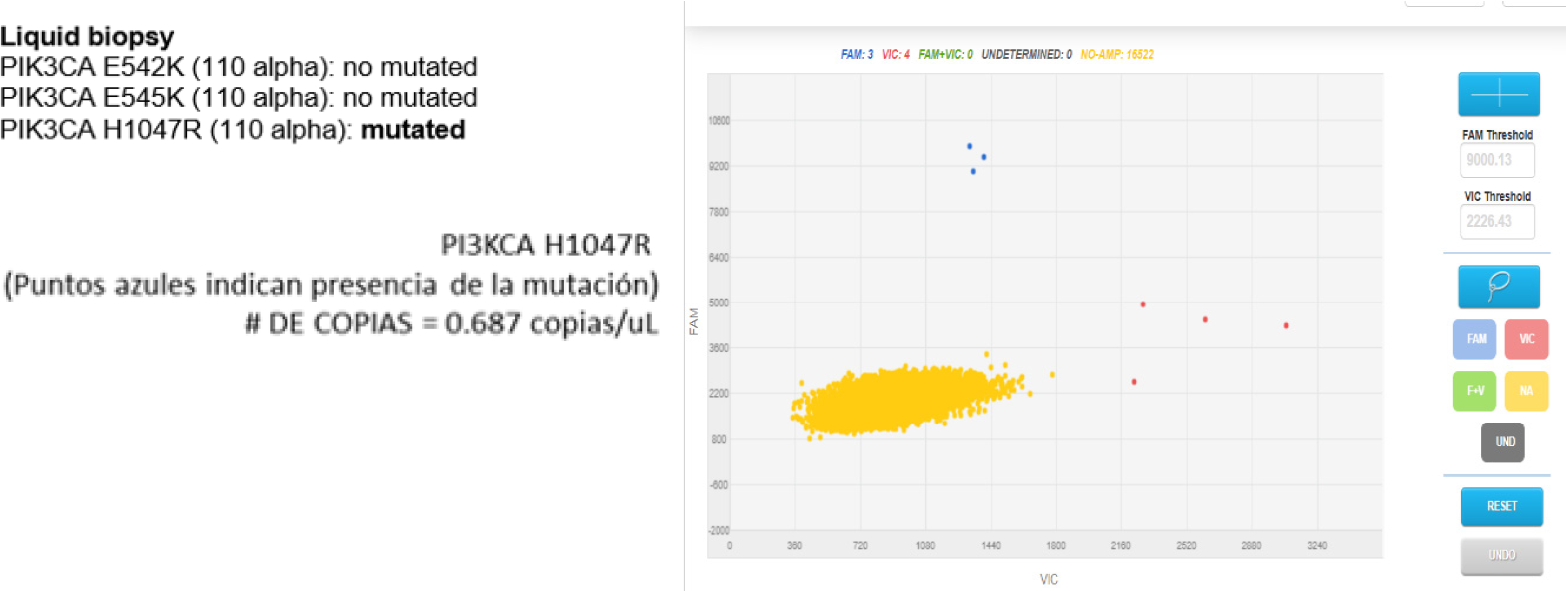
Figure 9 Liquid biopsy, PIK3CA 110 alpha result: Mutated.
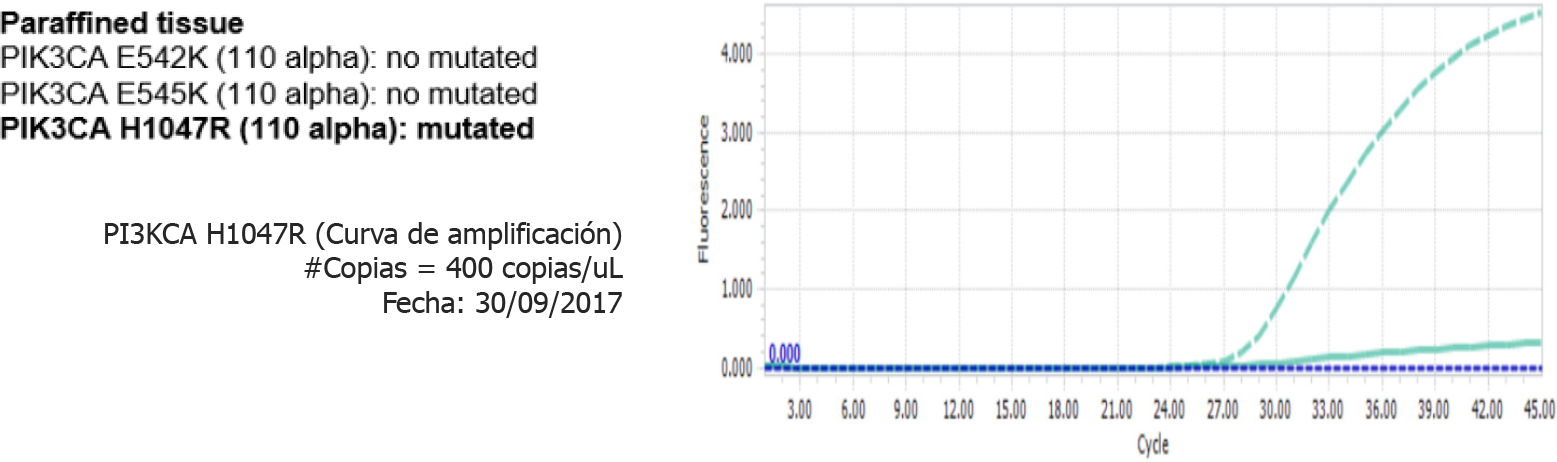
Figure 10 Paraffined tissue, PIK3CA 110 alpha result: Mutated.
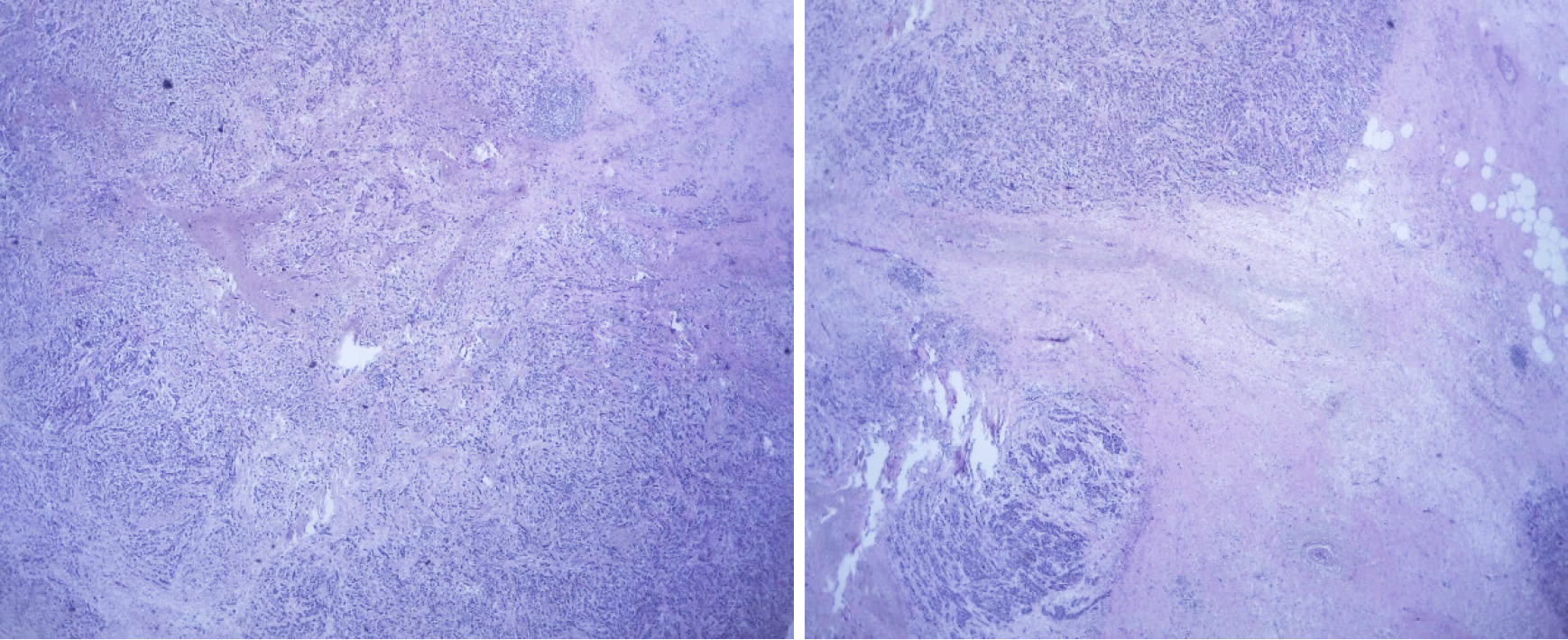
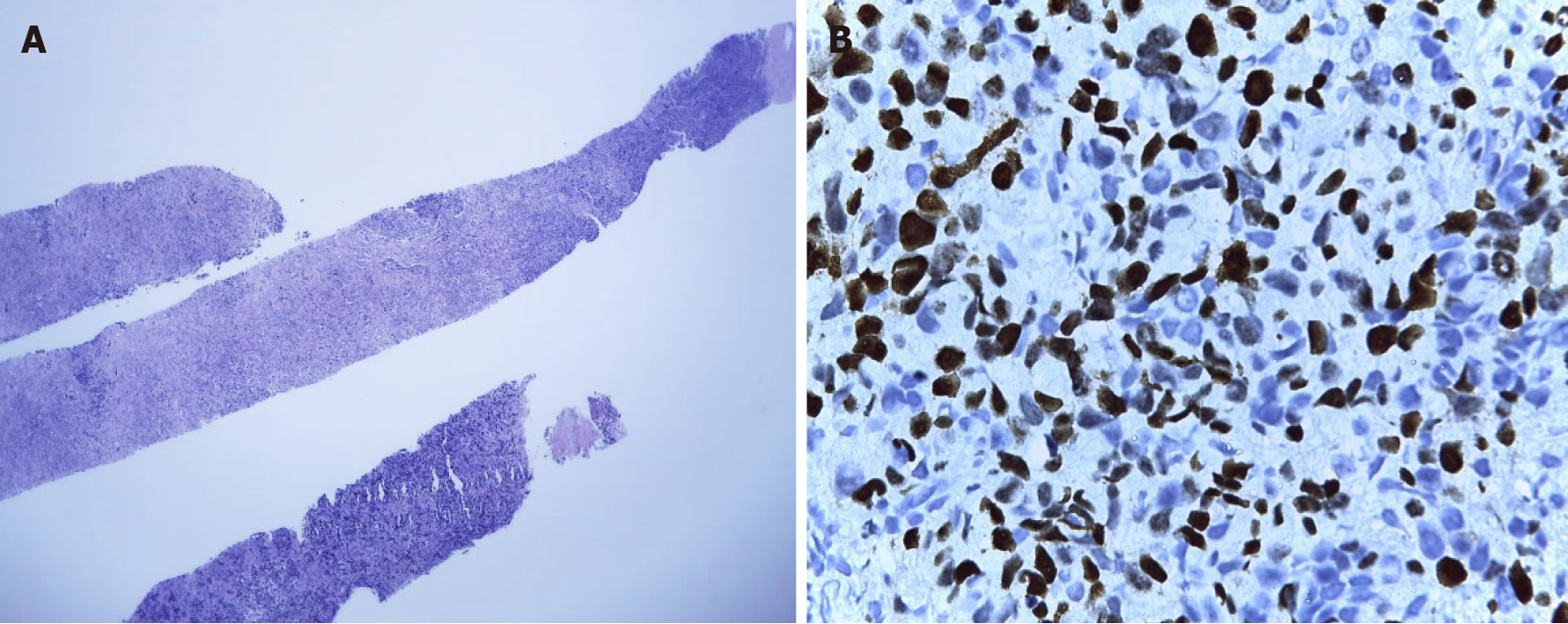
Figure 11 Biopsy of the left axillary node.
A: Compatible with metastases of infiltrating primary breast carcinoma; B: Immunohistochemistry in relation to triple-negative breast cancer tumor (ki67: 60%-70%).
- Citation: Valencia GA, Rioja P, Morante Z, Araujo JM, Vallejos HD, Guerra H, Gomez HL. PIK3CA mutation in non-metastatic triple-negative breast cancer as a potential biomarker of early relapse: A case report. World J Clin Oncol 2021; 12(8): 702-711
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v12/i8/702.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v12.i8.702