Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Oncol. Feb 24, 2020; 11(2): 83-90
Published online Feb 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i2.83
Published online Feb 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i2.83
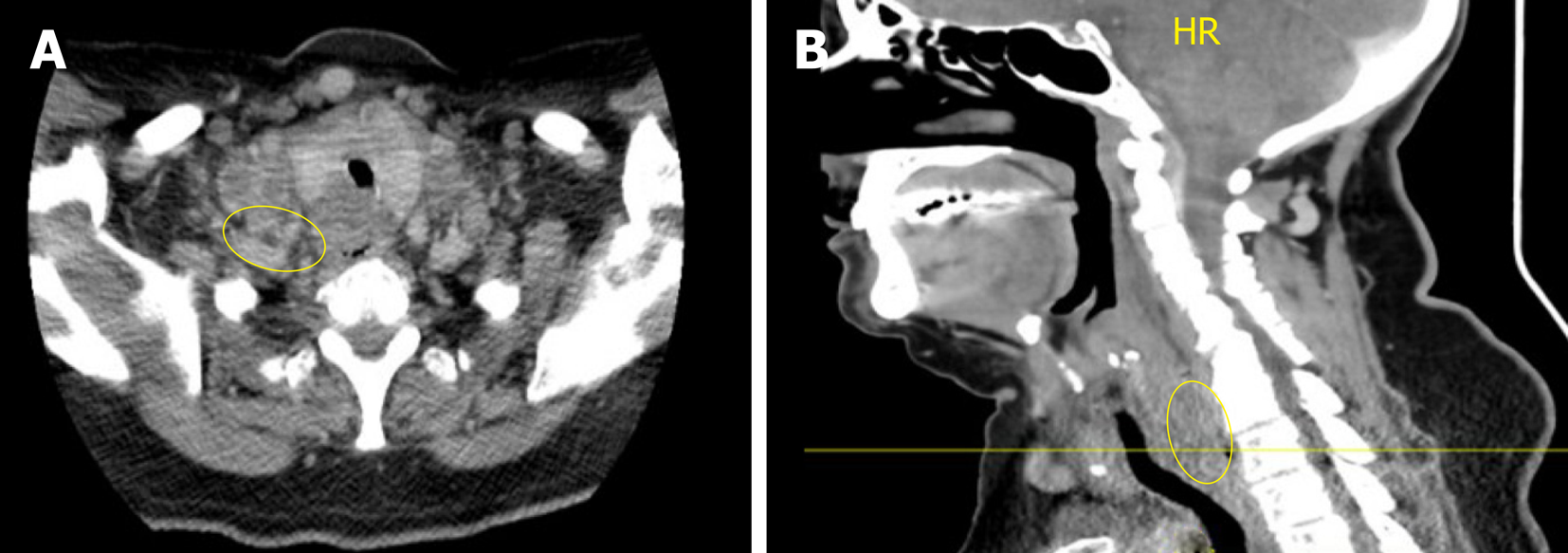
Figure 1 Computed tomography of the neck and chest.
A: Axial view; B: Sagittal View. Heterogeneous and partially necrotic mass like enhancement dorsal to the larynx and upper trachea which appears to dorsally displace the visible portions of the esophagus. The mass measures approximately 3 cm transverse by 1.8 cm anterior-posteriorly, and extends craniocaudally into the superior mediastinum. There is Widespread metastatic and necrotic adenopathy involving cervical lymph nodes.
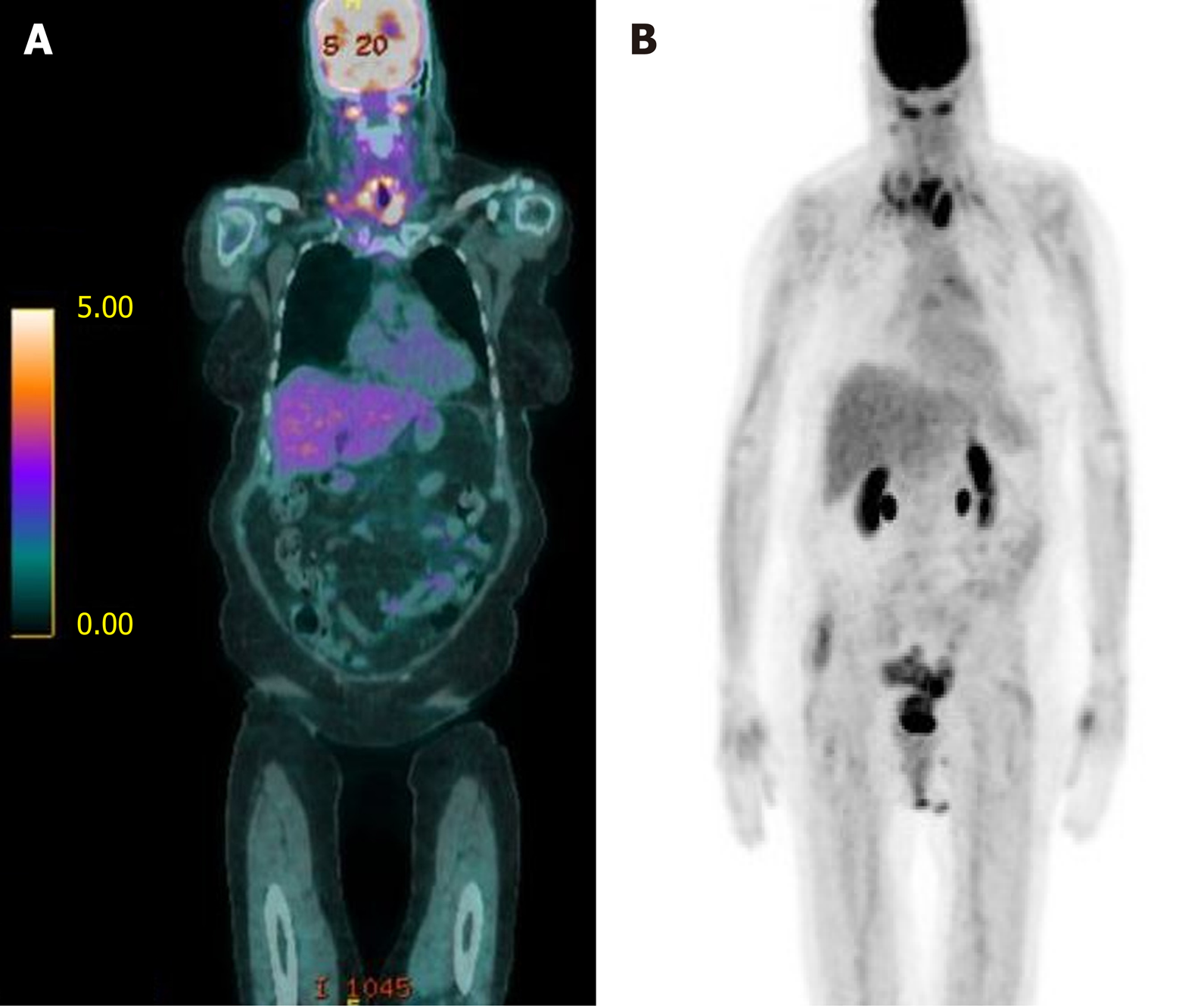
Figure 2 Bilateral lower cervical (SUV 5.
1) and mediastinal (SUV 3.9) adenopathy consistent with metastatic disease. A: Fused coronal positron emission tomography (PET)/ computed tomography (CT) imaging demonstrating an upper esophageal mass (SUV 6.7) as well as bilateral lower cervical adenopathy consistent w/ metastatic disease (SUV 5.1). A few mediastinal lymph nodes are FDG-avid, suspicious for metastatic disease (max SUV 3.9); B: Coronal PET/CT scout with similar uptake noted. PET: Positron Emission Tomography; CT: Computed Tomography.
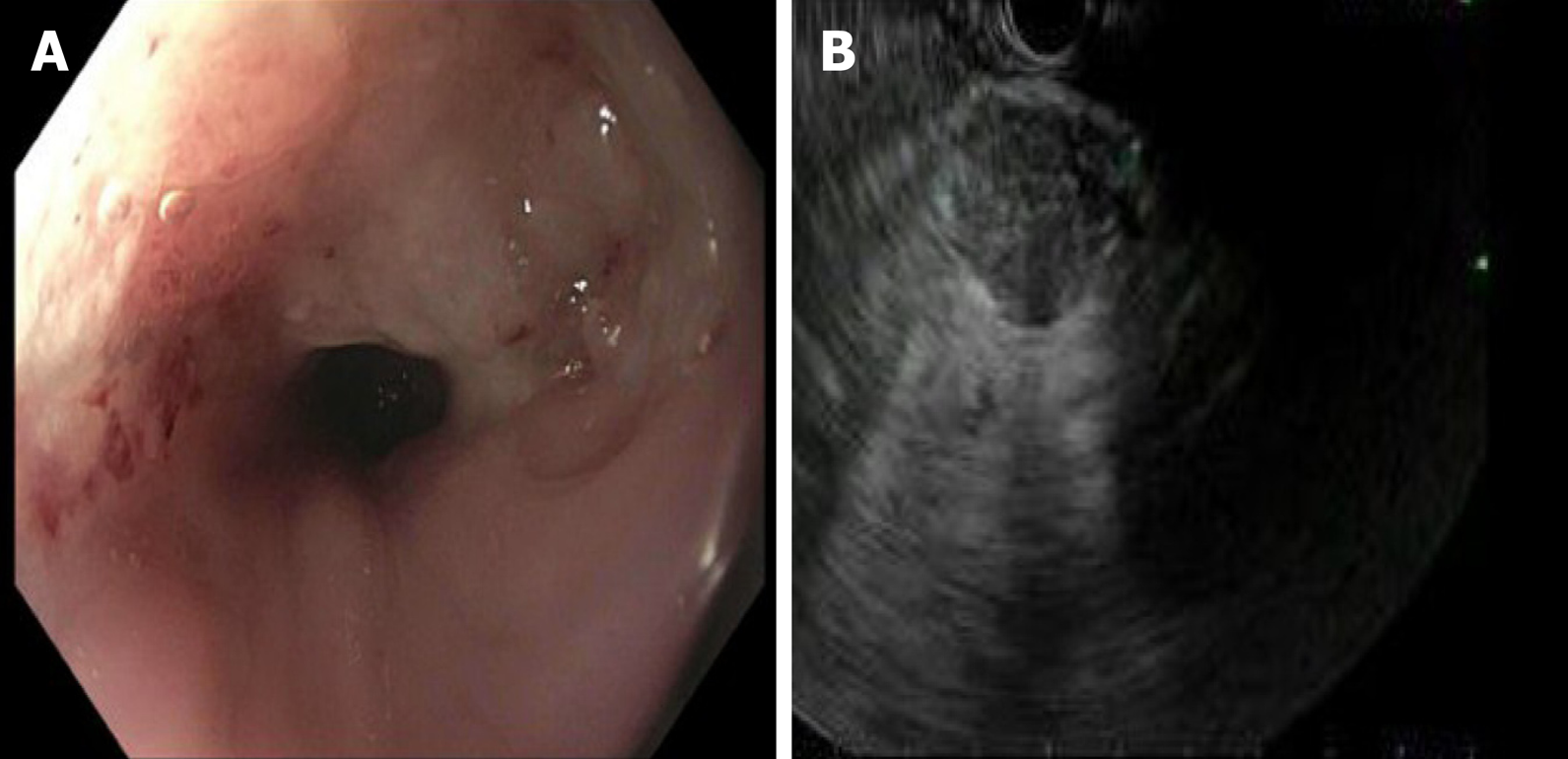
Figure 3 Upper endoscopy which demonstrated a mass in the upper third of the esophagus.
A: Upper endoscopy with a non-obstructing non-circumferential submucosal mass in the upper third of the esophagus; B: Endoscopy ultrasonography demonstrating 2.5 cm × 2.4 cm heterogenous, hypoechoic solid mass with irregular outer borders in the body of the pancreas.
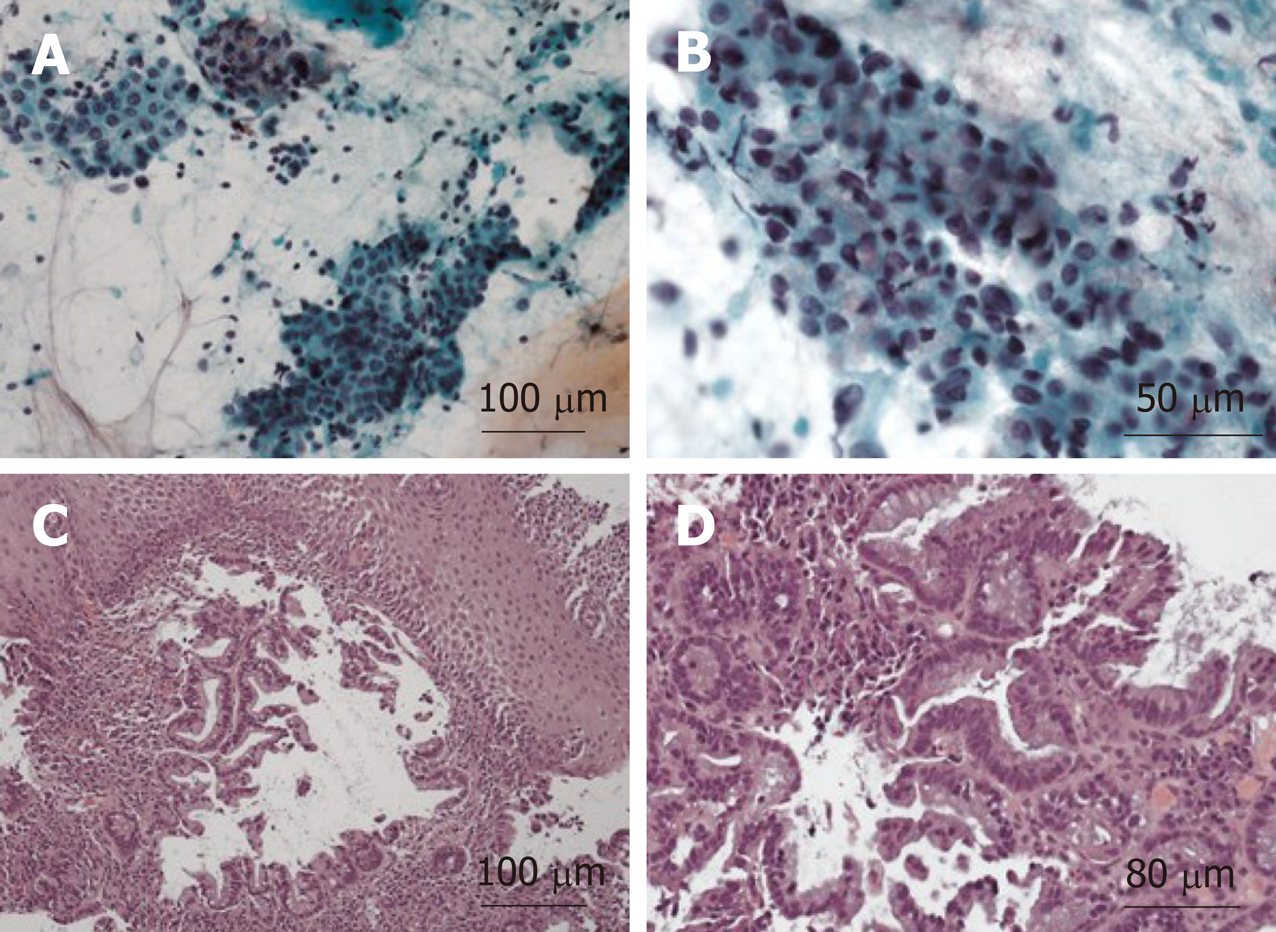
Figure 4 Histologic preparation of right cervical lymph node core needle biopsy.
A: Immunohistochemical stain for Caudal Type Homeobox 2 positive stain, 10 × magnifications; B: Immunohistochemical stain for thyroid transcription factor 1 weakly positive stain, 40 × magnification; C: Loss of lymph node architecture with several glands present on a background of fibrous stroma, 10 × magnification; D: Higher power view demonstrating cytologic atypia and abundant mucin, 20 × magnification.
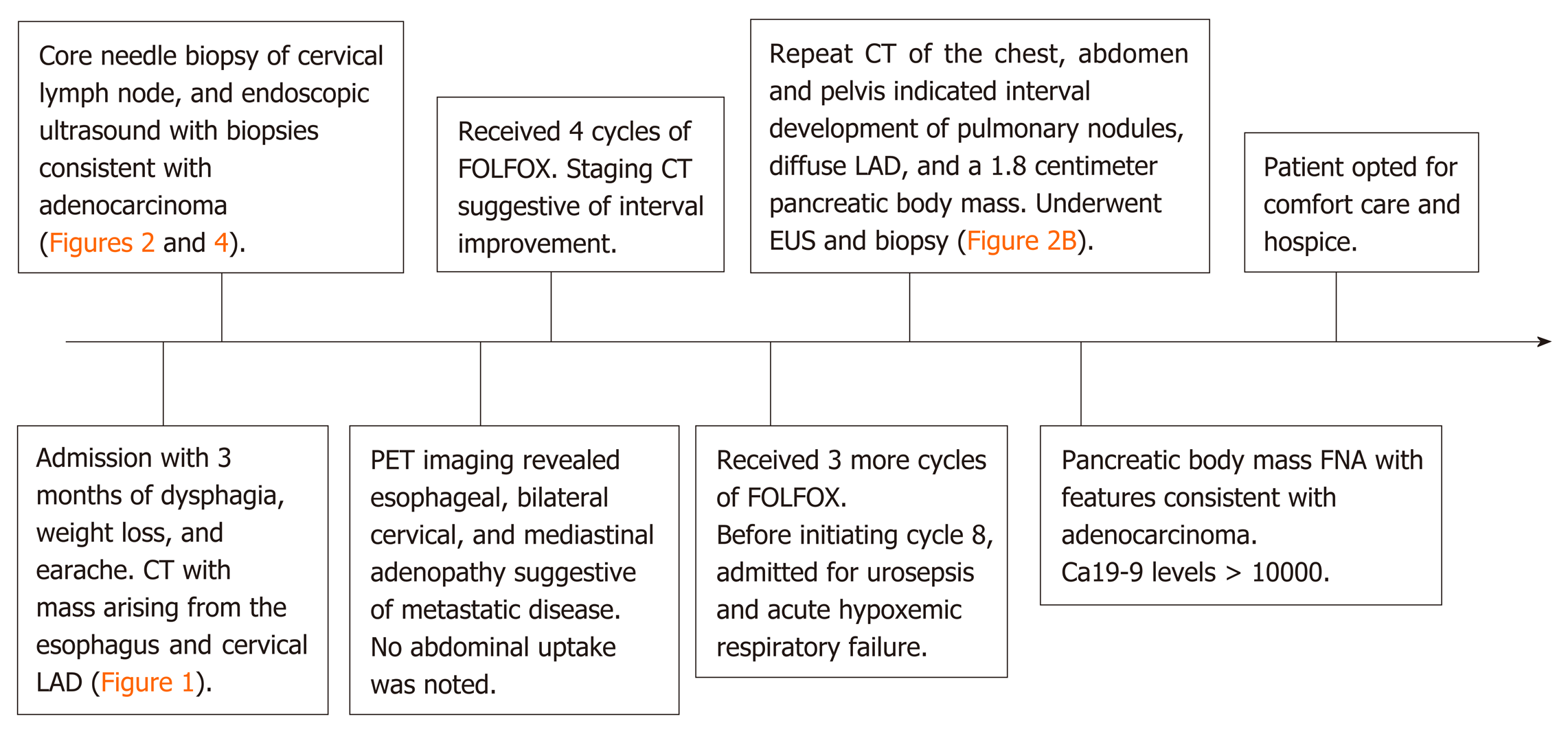
Figure 5 Timeline summary of events.
CT: Computed Tomography; LAD: Lymphadenopathy; PET: Positron Emission Tomography; FOLFOX: Folinic acid, fluorouracil, oxaliplatin; EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound; FNA: Fine Needle Aspiration.
- Citation: Burns EA, Kasparian S, Khan U, Abdelrahim M. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma with early esophageal metastasis: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Oncol 2020; 11(2): 83-90
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v11/i2/83.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v11.i2.83