Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 15, 2017; 8(4): 161-175
Published online Nov 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i4.161
Published online Nov 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i4.161
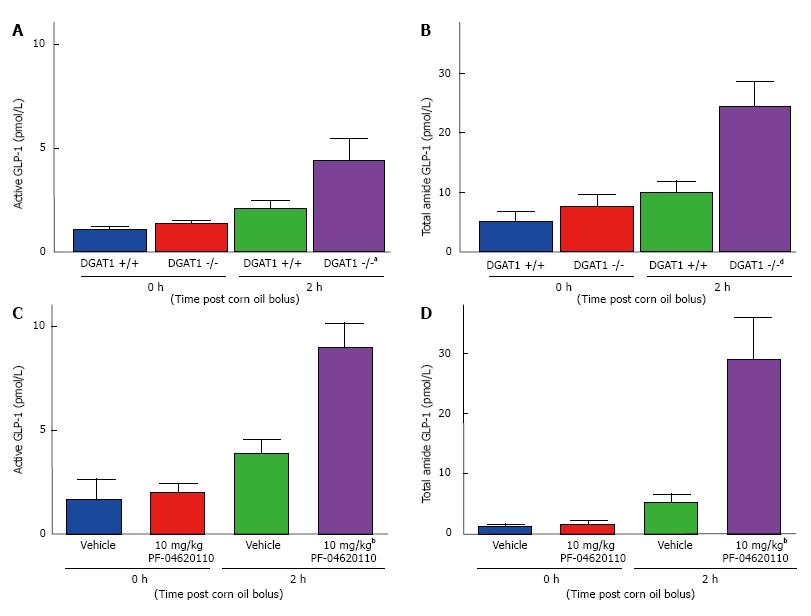
Figure 1 Diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 knockout and acute administration of a diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 inhibitor, PF-04620110 increases postprandial plasma glucagon like peptide-1 levels in mice.
Fasted male DGAT1 knockout (-/-), wildtype (+/+) and C57BL/6J mice were administered either vehicle or 10 mg/kg of PF-04620110 by oral gavage (n = 8 per group). Thirty minutes post compound administration mice received a bolus of corn oil (challenge). Blood was collected just prior to bolus (time 0) and at 2 h afterwards for determination of active/total GLP-1 concentrations. (A) Active GLP-1 (pmol/L) and (B) total GLP-1 in DGAT1 -/- and +/+ mice following challenge. (C) Active GLP-1 (pmol/L) and total GLP-1 (D) in C57BL/6J mice treated with vehicle or PF-04620110 following challenge. DGAT1 -/- compared to DGAT1 +/+ and vehicle compared to PF-04620110 treatment at 2 h timepoint (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.001 Student’s t-test). Values are means ± SEM. DGAT: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1; GLP-1: Glucagon like peptide-1.
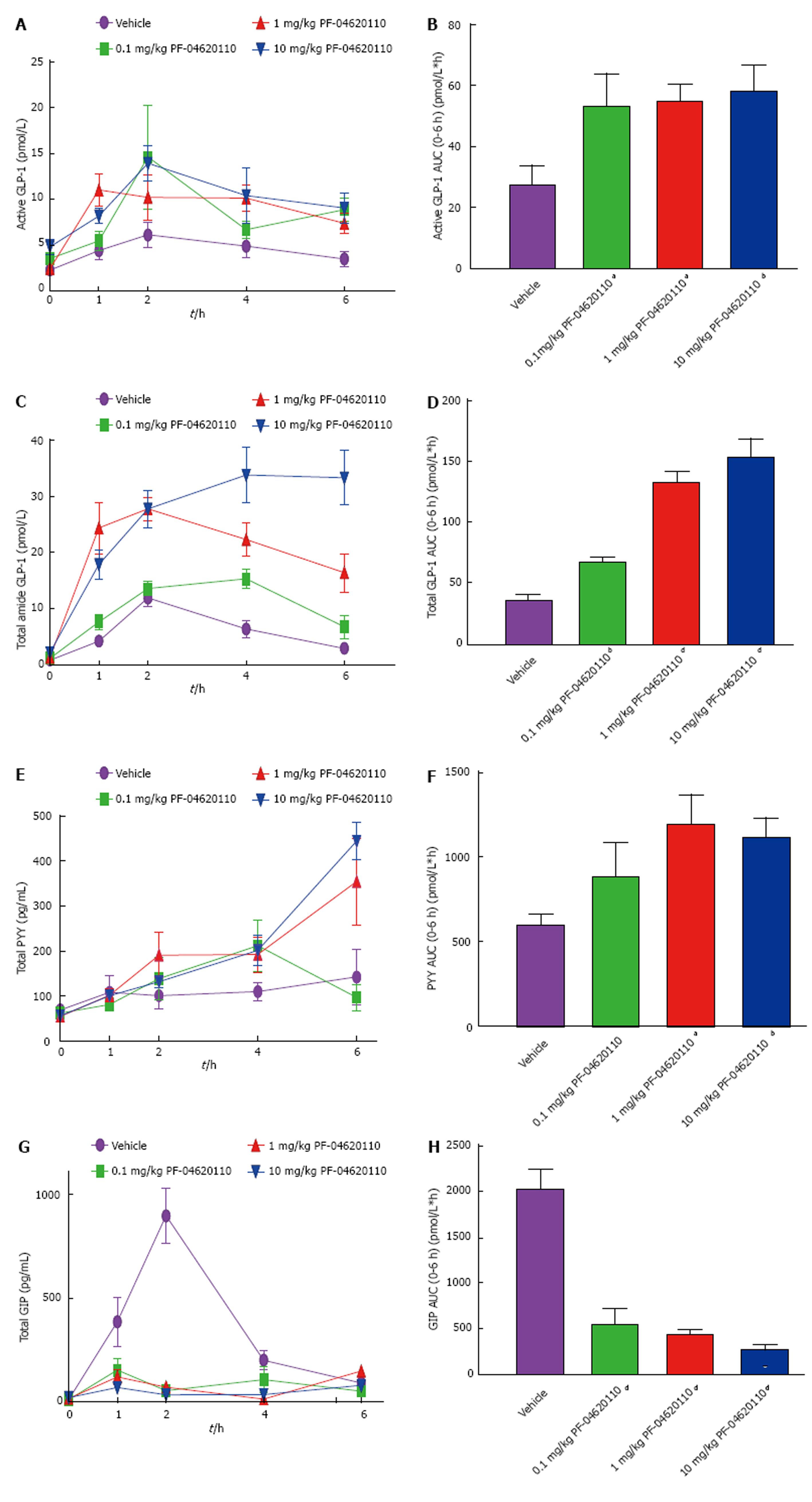
Figure 2 Pharmacological diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 inhibition alters Incretin effect postprandially in a dose responsive manner.
Fasted male C57BL/6J mice were administered vehicle or 10, 1, 0.1 or 0.01 mg/kg of PF-04620110 by oral gavage (n = 8 per group). Thirty minutes post compound administration mice received a bolus of corn oil (challenge). Blood was collected just prior to bolus (time 0) and at 1, 2, 4 and 6 h afterwards for determination of active/total GLP-1, PYY and GIP concentrations. (A) Active GLP-1 (pmol/L), (C) total GLP-1, (E) total PYY (pg/mL) and (G) total GIP (pg/mL) in C57BL/6J mice treated with vehicle or PF-04620110 following challenge. AUC values for (B) active GLP-1, (D) total GLP-1, (F) total PYY and (H) total GIP. Diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 (DGAT1) inhibitor treatment compared to vehicle (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.001 ANOVA). Values are means ± SEM. GLP-1: Glucagon like peptide-1; GIP: Glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.
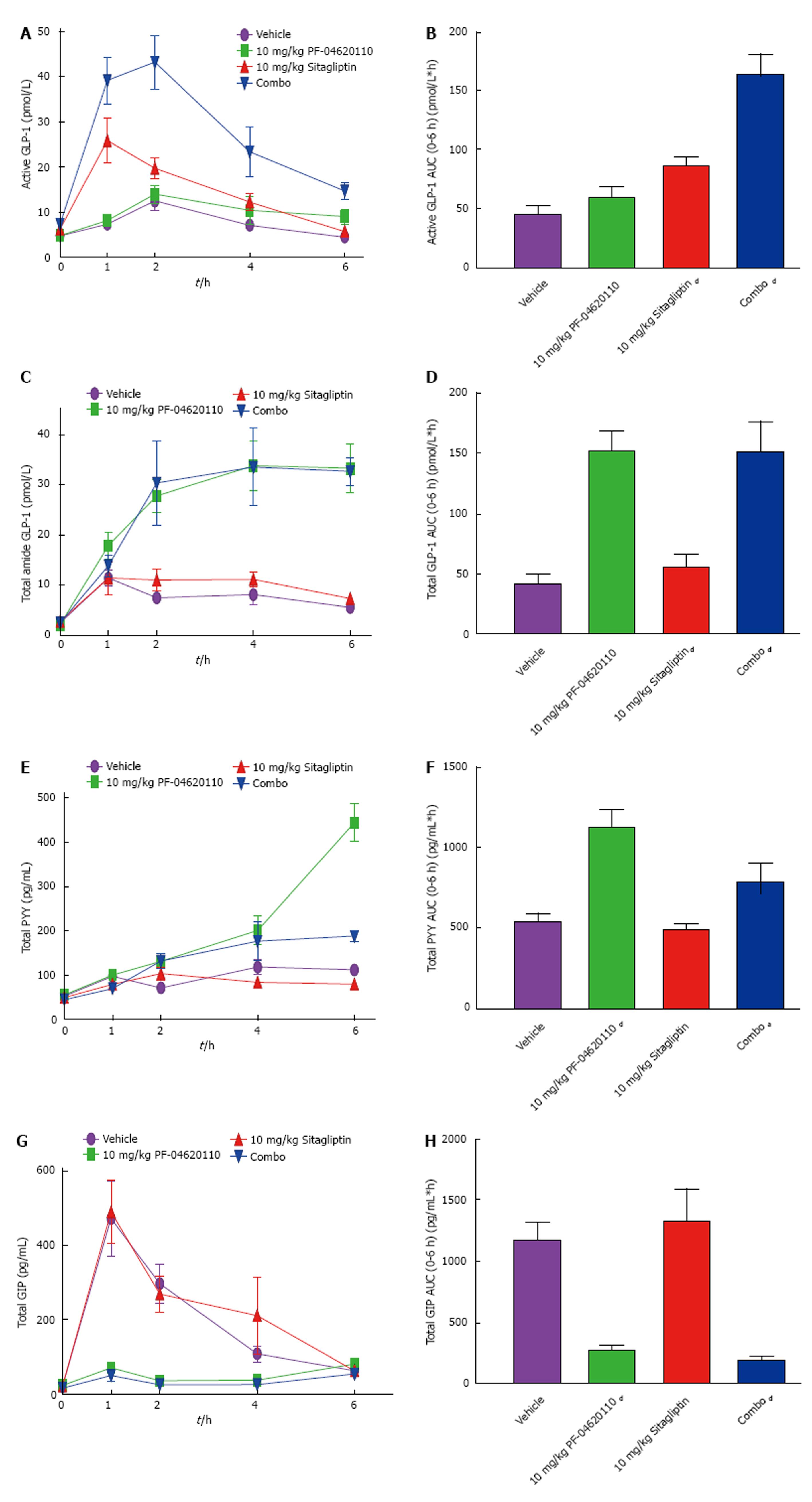
Figure 3 Incretin effect enhanced postprandially over time with combination pharmacological DPP-IV and diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 inhibition.
Fasted male C57BL/6J mice were administered vehicle, 10 mg/kg of PF-04620110 or Sitagliptin by oral gavage (n = 8 per group). Thirty minutes post compound administration mice received a bolus of corn oil (challenge). Blood was collected just prior to bolus (time 0) and at 1, 2, 4 and 6 h afterwards for determination of active/total GLP-1, PYY and GIP concentrations. (A) Active GLP-1 (pmol/L), (C) total GLP-1, (E) total PYY (pg/mL) and (G) total GIP (pg/mL) in C57BL/6J mice treated with vehicle or PF-04620110 following challenge. AUC values for (B) active GLP-1, (D) total GLP-1, (F) total PYY and (H) total GIP. DGAT1 inhibitor treatment compared to vehicle (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.001 ANOVA). Values are means ± SEM. DGAT: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1; GLP-1: Glucagon like peptide-1; PYY: Peptide tyrosine-tyrosine.
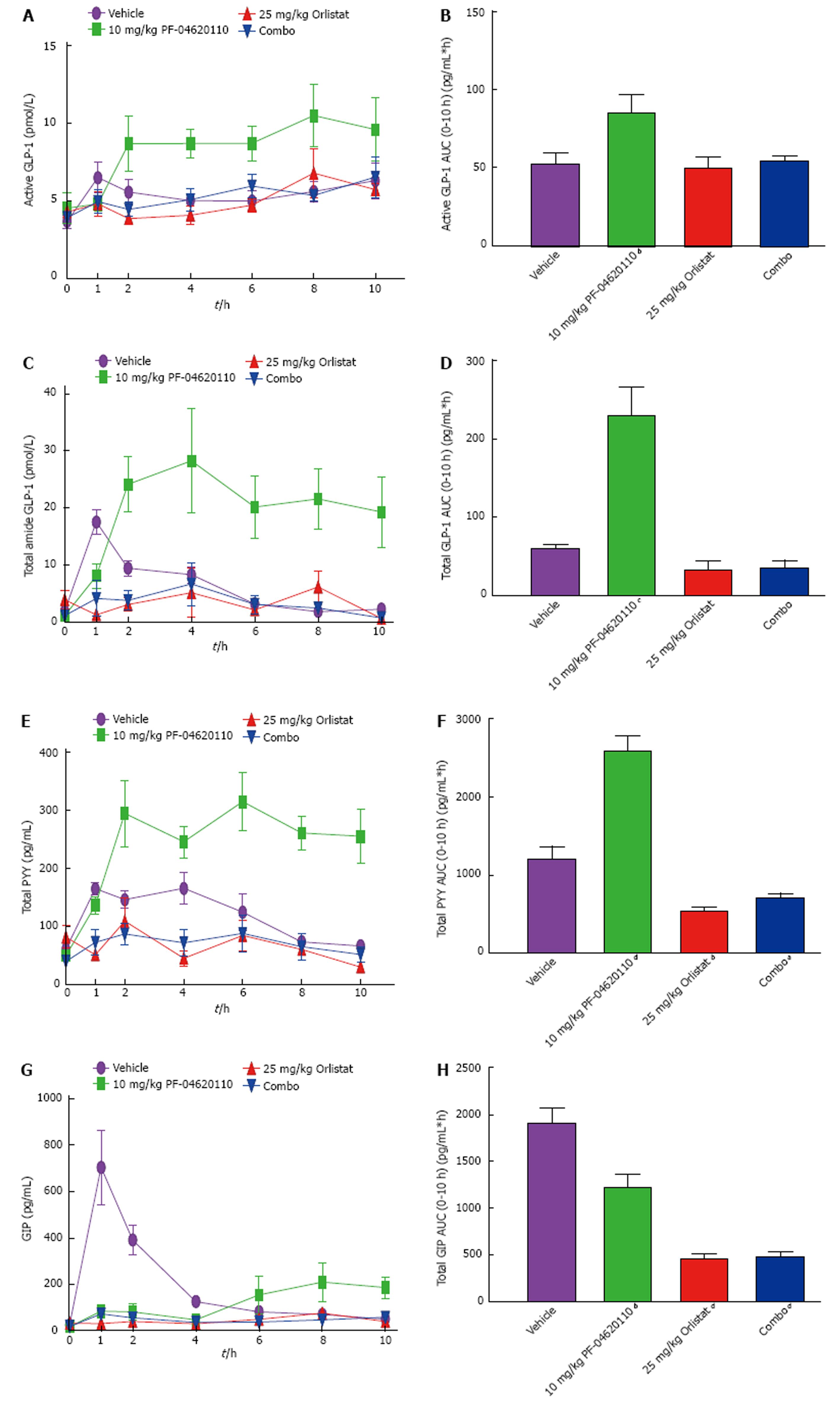
Figure 4 Incretin effect suppressed postprandially over time with combination orlistat and pharmacological diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 inhibition.
Fasted male C57BL/6J mice were administered vehicle, 10 mg/kg of PF-04620110 or orlistat (xenical) by oral gavage (n = 8 per group). Thirty minutes post compound administration mice received a bolus of corn oil (challenge). Blood was collected just prior to bolus (time 0) and at 1, 2, 4 and 6 h afterwards for determination of active/total GLP-1, PYY and GIP concentrations. (A) Active GLP-1 (pmol/L), (C) total GLP-1, (E) total PYY (pg/mL) and (G) total GIP (pg/mL) in C57BL/6J mice treated with vehicle or PF-04620110 following challenge. AUC values for (B) active GLP-1, (D) total GLP-1, (F) total PYY and (H) total GIP. DGAT1 inhibitor treatment compared to vehicle (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.001 ANOVA). Values are means ± SEM. DGAT: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1; GLP-1: Glucagon like peptide-1; PYY: Peptide tyrosine-tyrosine.
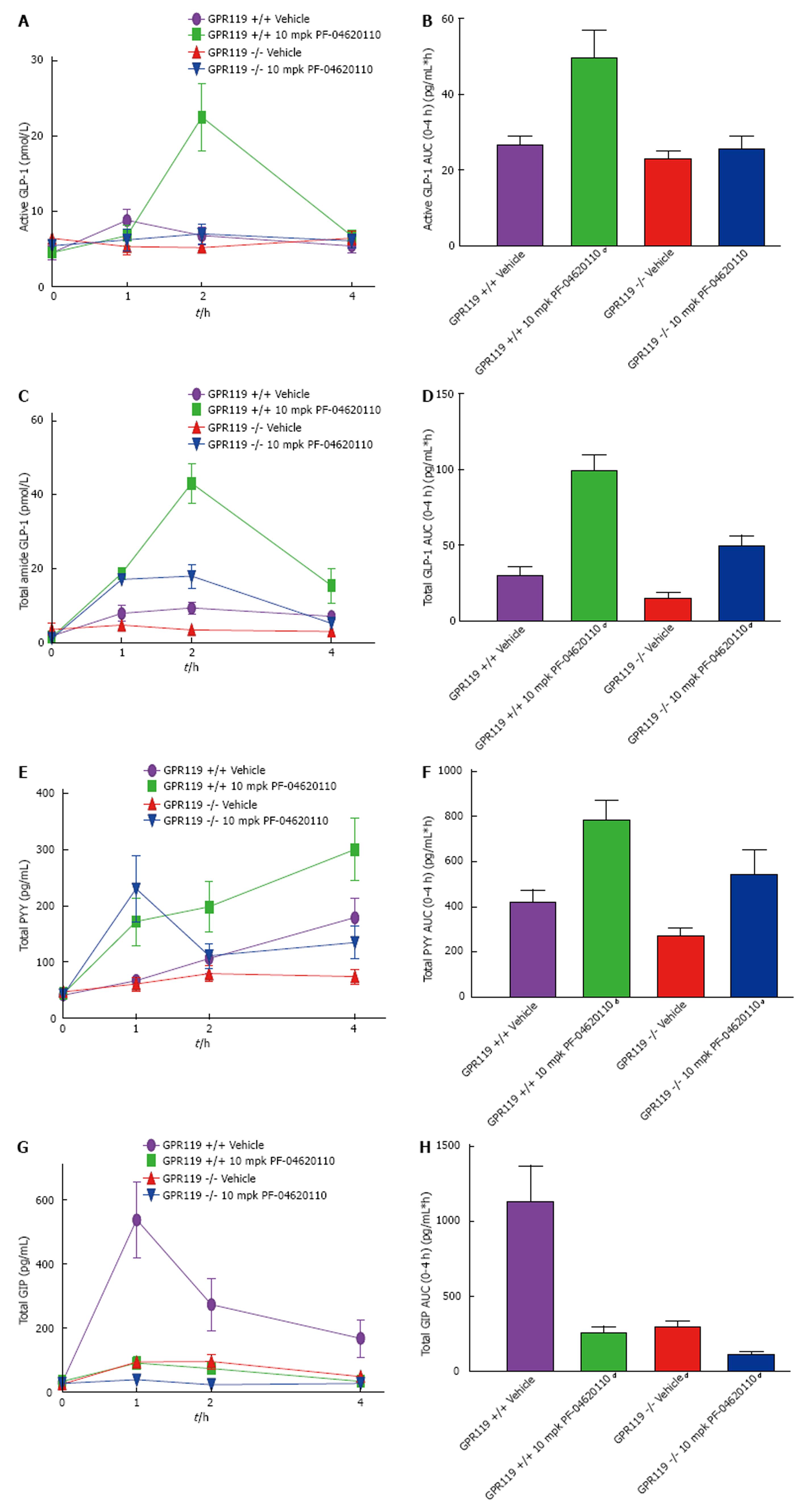
Figure 5 Incretin effect suppressed postprandially over time with pharmacological diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 inhibition in GPR119 -/- mice.
Fasted male GPR119 -/- and +/+ mice were administered vehicle or 10 mg/kg of PF-04620110 by oral gavage (n = 8 per group). Thirty minutes post compound administration mice received a bolus of corn oil (challenge). Blood was collected just prior to bolus (time 0) and at 1, 2, 4 and 6 h afterwards for determination of active/total GLP-1, PYY and GIP concentrations. (A) Active GLP-1 (pmol/L), (C) total GLP-1, (E) total PYY (pg/mL) and (G) total GIP (pg/mL) in C57BL/6J mice treated with vehicle or PF-04620110 following challenge. AUC values for (B) active GLP-1, (D) total GLP-1, (F) total PYY and (H) total GIP. Treatments compared to vehicle +/+ (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.001 ANOVA). Values are means ± SEM. DGAT: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1; GLP-1: glucagon like peptide-1.
- Citation: Maciejewski BS, Manion TB, Steppan CM. Pharmacological inhibition of diacylglycerol acyltransferase-1 and insights into postprandial gut peptide secretion. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2017; 8(4): 161-175
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v8/i4/161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v8.i4.161