Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Aug 15, 2017; 8(3): 142-149
Published online Aug 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.142
Published online Aug 15, 2017. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.142
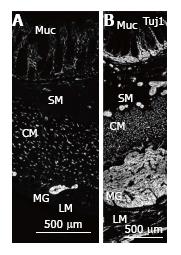
Figure 1 Nerve fibres in normal colon and MEN2B colon.
Tuj1 immunoreactivity showing nerve fibres in full thickness biopsy of the transverse colon cut with circular muscle in cross section. A: Control patient (4-year-old, HSCR normal margin) showing multiple nerve fibres in the mucosa (Muc) within and at the base of the crypts, small ganglia in the submucosa (SM), nerve fibres in cross section in the circular muscle (CM) and myenteric ganglia (MG) between the CM and longitudinal muscle layer (LM); B: MEN2B patient showing greatly increased amount of labelling and increase in size of MG and SM ganglia. The MG is increased in diameter to a thickness similar to the circular muscle. The density and number of nerve fibres in the CM is higher than control. The nerve fibres in the Muc are greatly increased. The SM contains many large ganglia near the CM, near the Muc and in between. Neurons are not distinguishable because this antibody only displays nerve fibres. Note A and B are at the same magnification. CM: Circular mucle; LM: Longitudinal muscle; MG: Myenteric ganglia.
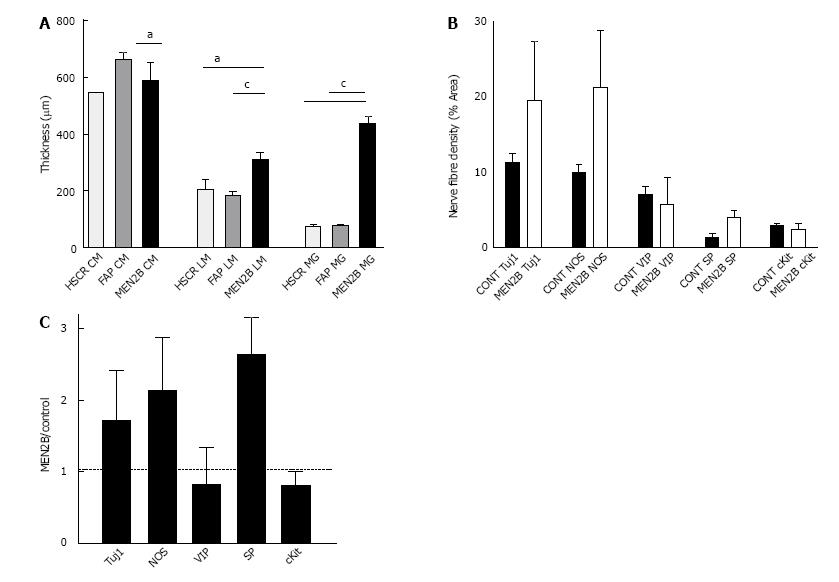
Figure 2 Thickness of muscle layers and ganglia and density of nerve fibres in normal colon and MEN2B colon.
A: Comparison of thickness (mm) of muscle and myenteric ganglia in colon from Control (HSCR and FAP) and MEN2B patient. Graph shows mean and SEM. HSCR n = 6, FAP n = 12, MEN2B n = 24, aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001; B: Nerve fibre and ICC density in circular muscle in transverse colon from Control (HSCR and FAP combined, n = 3) and MEN2B patient (n = 3). Percent area of circular muscle containing immunoreactive pixels; C: Relative nerve fibre and ICC density in the circular muscle in MEN2B patient (n = 3) relative to Control patients (HSCR and FAP combined, n = 3). Labelling with Tuj1, NOS, VIP, SP and cKit (for interstitial cells of Cajal).
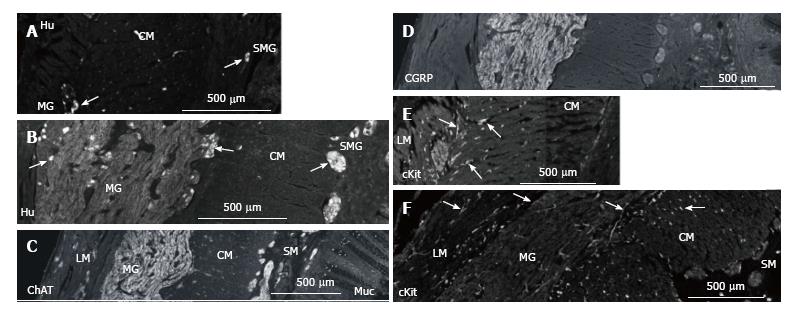
Figure 3 Nerve cells in myenteric and submucosal ganglia in normal colon and MEN2B colon.
A: Hu immunoreactivity showing nerve cell bodies in transverse colon cut with circular muscle in cross section. Control patient (HSCR) showing myenteric ganglia (MG) neurons and submucosal ganglia; B: MEN2B patient at same magnification showing greatly enlarged MG containing 41 neurons and multiple large ganglia in the submucosa (SMG) containing 2-6 neurons. Note most of the increase in size of the MG is due to nerve fibres; C: Choline acetyle transferase (ChAT) immunoreactivity in transverse colon of MEN2B patient. Note many large ganglia in the submucosa (SM); D: Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) immunoreactivity in transverse colon of MEN2B patient. CGRP labels extrinsic sensory nerves. Note most of labelling is in the myenteric ganglia; E: ICC in the muscle in normal colon (HSCR); F: MEN2B colon. cKit-immunoreactivity shows ICC in the muscle and around the MG (arrows) and shows mast cells in the mucosa and submucosa. Mast cells are round cells with no process while ICC are elongate cells with processes. ICC numbers are similar in control and MEN2B. The longitudinal muscle (LM), myenteric ganglia (MG), circular muscle (CM), submucosa (SM), submucosal ganglia (SMG) and mucosa (Muc) are shown from left to right.
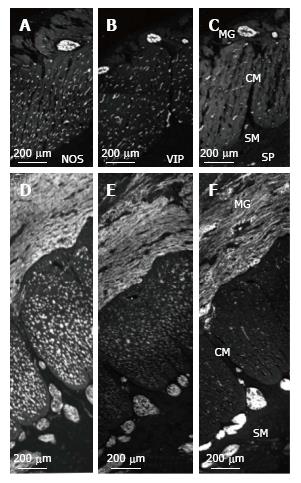
Figure 4 NOS, VIP and SP nerve fibres in myenteric and submucosal ganglia and circular muscle in normal colon and MEN2B colon.
A: NOS-; B: VIP-; C: SP-immunoreactivity in Control (HSCR) patient; D: NOS-; E: VIP-; F: SP-immunoreactivity in MEN2B patient. Note all images are at the same magnification. The enlarged myenteric ganglia (MG) contain many NOS, VIP and SP nerve fibres with NOS at the highest density. The submucosal (SM) ganglia also contain all 3 labels, but SP is most intense and extremely bright in MEN2B. In the circular muscle (CM), NOS is the most abundant and highly increased in MEN2B. Full thickness biopsy of the transverse colon cut with circular muscle in cross section.
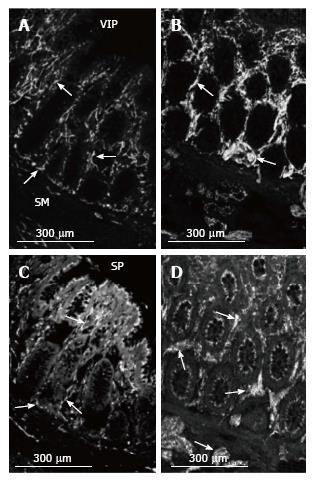
Figure 5 VIP and SP nerve fibres in the mucosa in normal colon and MEN2B colon.
VIP-immunoreactivity in (A) Control (HSCR) and (B) MEN2B patient. Crypts in transverse colon. VIP immunoreactive nerve fibres (arrows) are plentiful at the base and within the arms of the crypts in the control. There is a large increase in the numbers of VIP-IR nerve fibres and brightness of labelling in the crypts. SP-immunoreactivity in (C) Control (HSCR) and (D) MEN2B patient. Background labelling is higher with SP with labelling of epithelial cells. Varicose nerve fibres are visible (arrows) in a similar pattern to VIP. The thickness and brightness of the nerve fibres is greatly increased within the crypts and in the submucosa in MEN2B. Note all images are at the same magnification.
- Citation: Hutson JM, Farmer PJ, Peck CJ, Chow CW, Southwell BR. Multiple endocrine neoplasia 2B: Differential increase in enteric nerve subgroups in muscle and mucosa. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2017; 8(3): 142-149
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v8/i3/142.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.142