Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. May 15, 2016; 7(2): 199-210
Published online May 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i2.199
Published online May 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i2.199
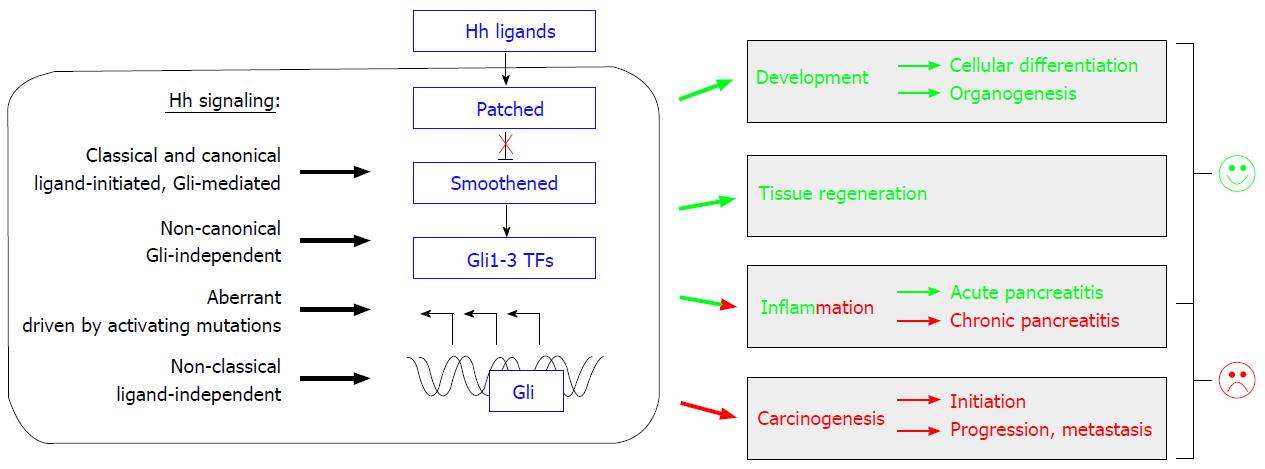
Figure 1 Overview of the Hedgehog signaling cascade and different activation modes (for details see ref.
[7]). As described in detail in chapters II to IV, the Hh pathway exerts positive and negative (labeled with green and red color, respectively) functions during development, regeneration, inflammation and cancerogenesis in the pancreas. Hh: Hedgehog; TF: Transcription factors.
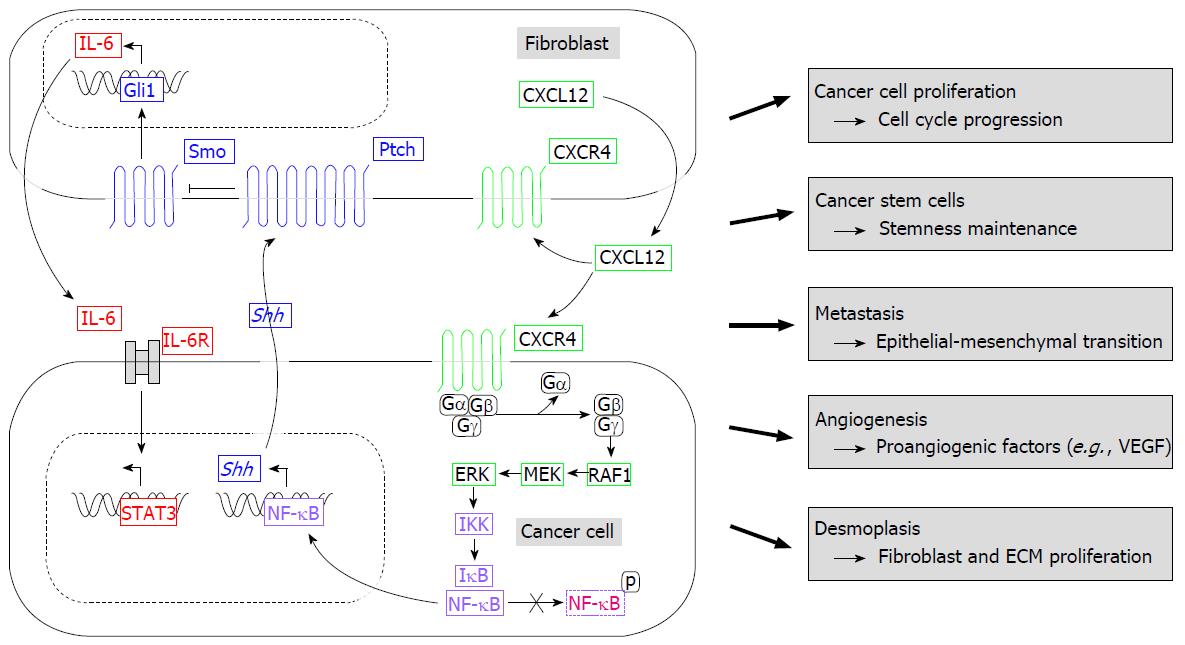
Figure 2 Illustrated summary of Hedgehog pathway and its effetcs at different stages in the formation and progression of ductal pancreatic carcinoma.
Stromal cells secrete CXCL12 that binds to its receptor CXCR4 of ductal pancreatic cancer (DPC) cells (paracrine) and of stromal cells themselves (autocrine) resulting in Shh expression. Shh, secreted by DPC cells, binds in a paracrine manner Smo on stromal cells of the tumor microenvironment ending up in IL-6 secretion, which is known to regulate the progression of precursor lesions and tumor formation. For details see chapter IV. Based on[63,77,85]. CXCL12/CXCR4: CXC-motif-chemokine 12/CXC chemokine receptor type 4; ECM: Extracellular matrix; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinases; Hh: Hedgehog; IκB: Inhibitor of kappa B; IKK: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase; IL-6: Interleukin-6; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB; Ptch: Patched; RAF1: V-Raf-1 murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1; Shh: Sonic Hh; Smo: Smoothened; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Klieser E, Swierczynski S, Mayr C, Jäger T, Schmidt J, Neureiter D, Kiesslich T, Illig R. Differential role of Hedgehog signaling in human pancreatic (patho-) physiology: An up to date review. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016; 7(2): 199-210
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v7/i2/199.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v7.i2.199