Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 15, 2015; 6(4): 150-158
Published online Nov 15, 2015. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.150
Published online Nov 15, 2015. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.150
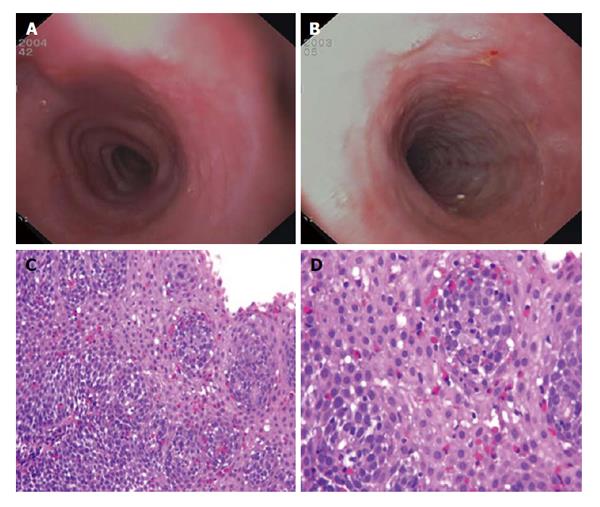
Figure 1 Endoscopic and microscopic findings in eosinophilic esophagitis.
A: Esophageal rings; B: White exudates, longitudinal furrows and mucosal fragility; C and D: Esophageal mucosa infiltrated by several eosinophils (red cells) (C: Original magnification HE 150 ×; D: HE 400 ×).
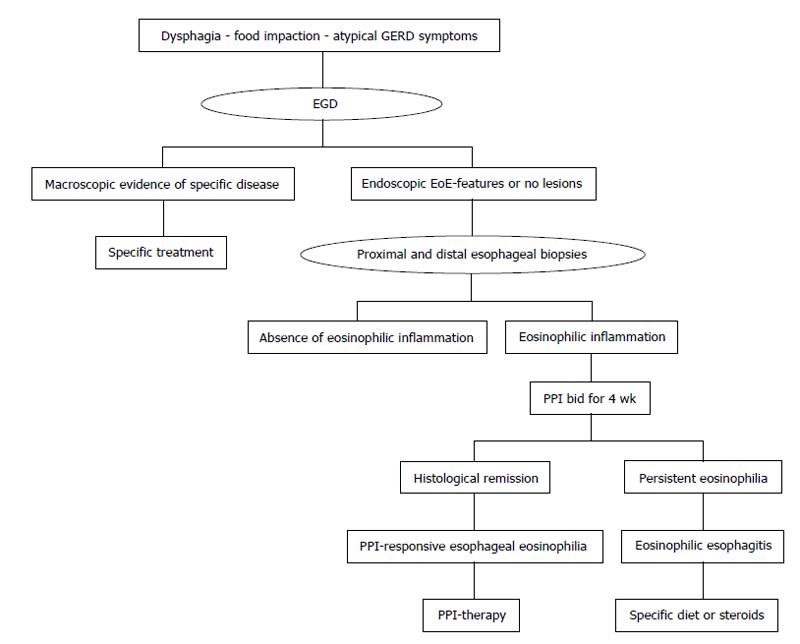
Figure 2 Diagnostic flow-chart of eosinophilic esophagitis.
GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; EoE: Eosinophilic esophagitis; PPI: Proton pump inhibitors; EGD: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
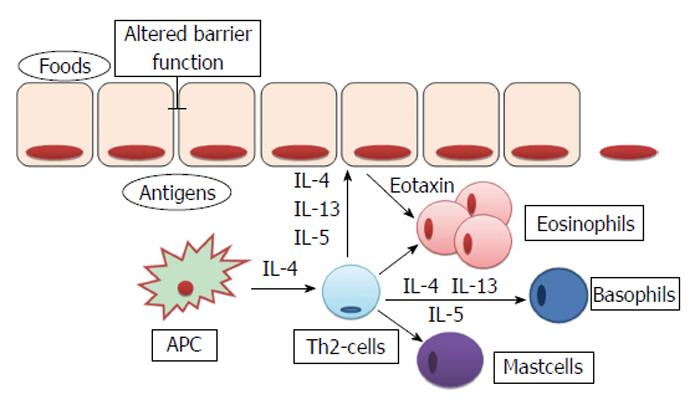
Figure 3 Pathophysiological mechanism involved in eosinophilic infiltration of esophageal mucosa.
IL: Interleukin; APC: Antigen-presenting cell.
- Citation: D’Alessandro A, Esposito D, Pesce M, Cuomo R, De Palma GD, Sarnelli G. Eosinophilic esophagitis: From pathophysiology to treatment. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2015; 6(4): 150-158
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v6/i4/150.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.150