Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Radiol. Apr 28, 2017; 9(4): 191-198
Published online Apr 28, 2017. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v9.i4.191
Published online Apr 28, 2017. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v9.i4.191
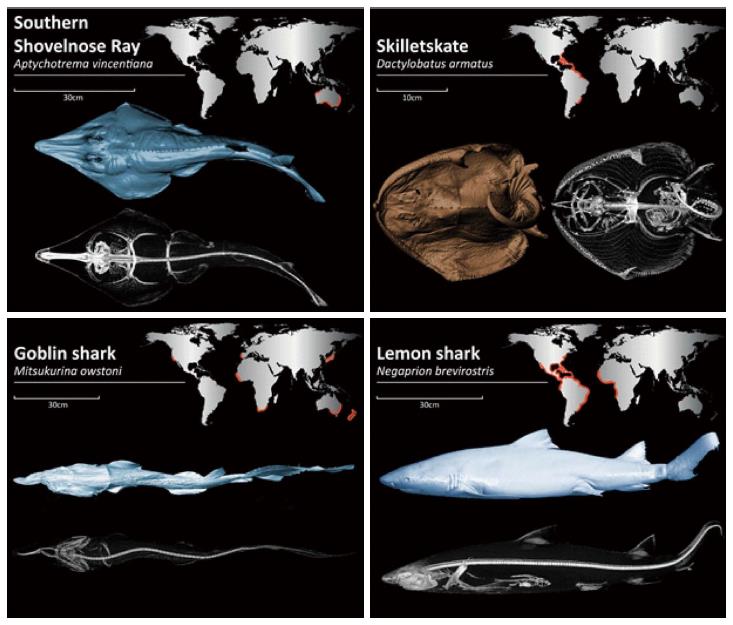
Figure 1 Three-dimensional reconstructions and global distribution, represented by orange highlights, of the four representative species in our study.
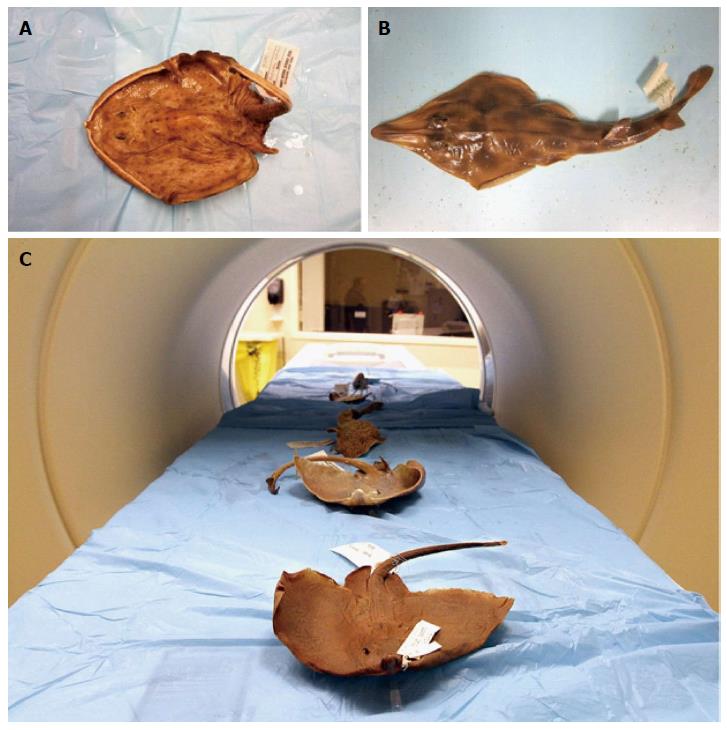
Figure 2 Formalin-preserved specimens positioned in the computed tomography scanner.
A: Skilletskate (Dactylobatus armatus); B: Southern Shovelnose ray (Aptychotrema vincentiana); C: The processes of the scan.
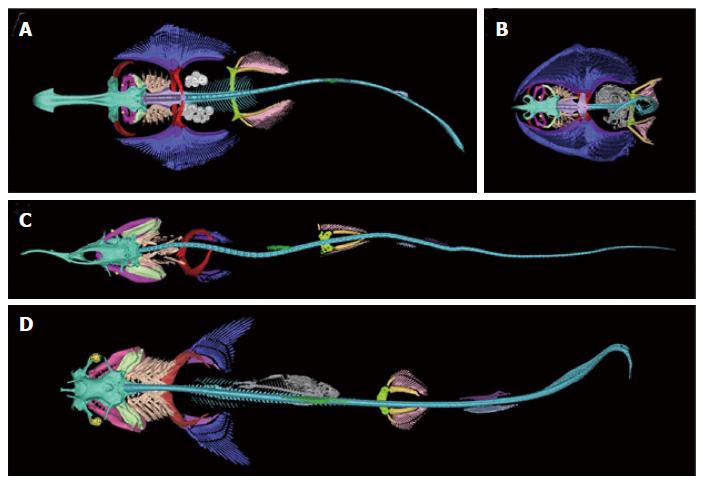
Figure 3 Dorsal view of three-dimensional reconstructions of the skeleton.
A: Shovelnose ray (Aptychotrema vincentiana); B: Skilletskate (Dactylobatus armatus); C: Lemon shark (Negaprion brevirostris); D: Goblin Shark (Mitsukurina owstoni). Skeletal element color coding: turquoise, chondrocranium; maroon, antorbitals; magenta, jaws (palatoquadrate, meckel's cartilage, and labial cartilage); orange, spiracular cartilage; yellow, eye cup and lens; pale green, hyoid arch (hyomandibular, ceratohyal, and basihyal); peach, gill arches (pharyngobranchials, epibranchials, ceratobranchials, hypobranchials, basibranchial, and branchial rays); violet, synarcual; cyan, vertebral column; red, scapulocoracoid; purple, pectoral basal cartilages; blue, pectoral radials; gray, ingested fish (flounder and teleost vertebral column); white, eggs; green, anterior dorsal fin; skyblue, posterior dorsal fin; deep purple, anal fin; greenyellow, puboischiadic bar; gold, pelvic basal cartilages; pink, pelvic radials.
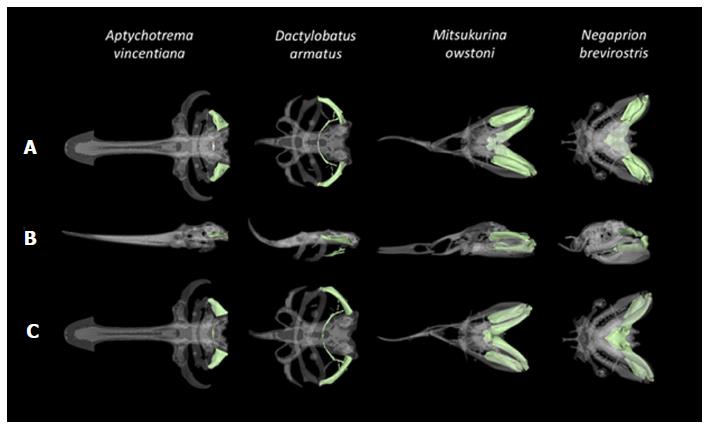
Figure 4 Close-up dorsal, lateral, and ventral views of the cranial skeleton of four elasmobranchs.
A: Shovelnose ray (Aptychotrema vincentiana); B: The Skilletskate (Dactylobatus armatus); C: The Goblin Shark (Mitsukurina owstoni) and the Lemon shark (Negaprion brevirostris), reconstructed in 3D with the hyoid arch highlighted in pale green.
- Citation: McQuiston AD, Crawford C, Schoepf UJ, Varga-Szemes A, Canstein C, Renker M, De Cecco CN, Baumann S, Naylor GJP. Segmentations of the cartilaginous skeletons of chondrichthyan fishes by the use of state-of-the-art computed tomography. World J Radiol 2017; 9(4): 191-198
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v9/i4/191.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v9.i4.191