Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
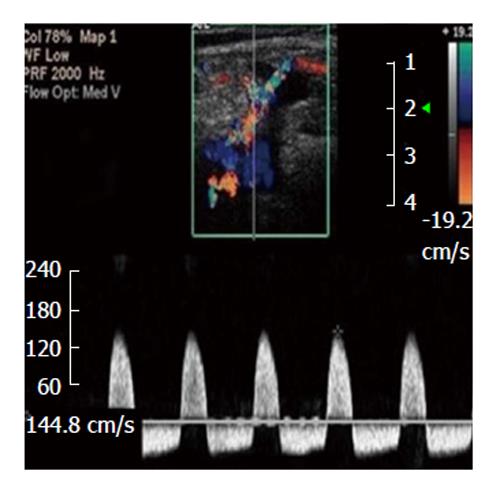
Figure 1 To-and-fro spectral waveform of a pseudoaneurysm; neck wasn't depicted[65].
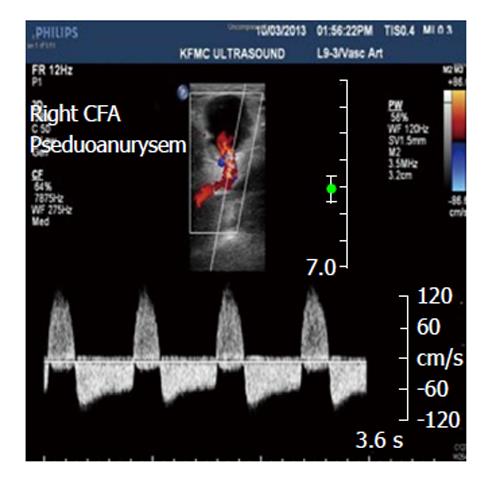
Figure 2 Right common femoral artery pseudoaneurysms associated with the characteristic findings of a pulsatile mass, a palpable thrill, and an audible “to-and-fro” murmur.
CFA: Common femoral artery.
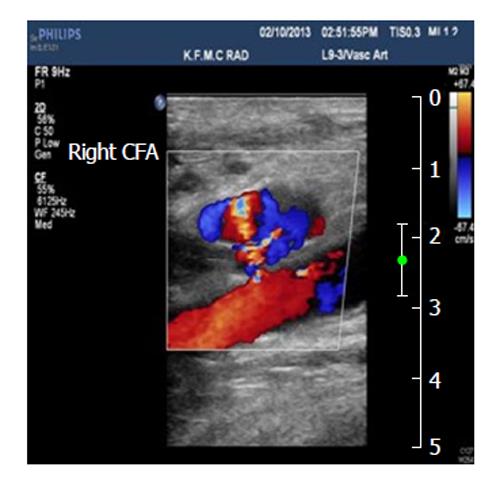
Figure 3 Pseudoaneurysm communicated with the right common femoral artery, and the blood flow patterns and velocities in the affected area.
CFA: Common femoral artery.
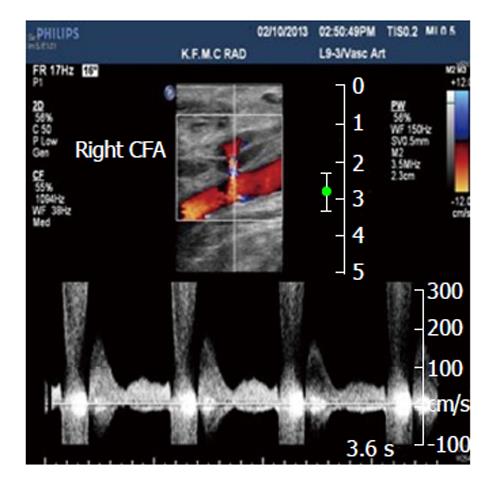
Figure 4 Spectral analysis of the right common femoral artery showing prominent flow with a component of reversed flow, in the region of the neck of the pseudoaneurysm.
CFA: Common femoral artery.
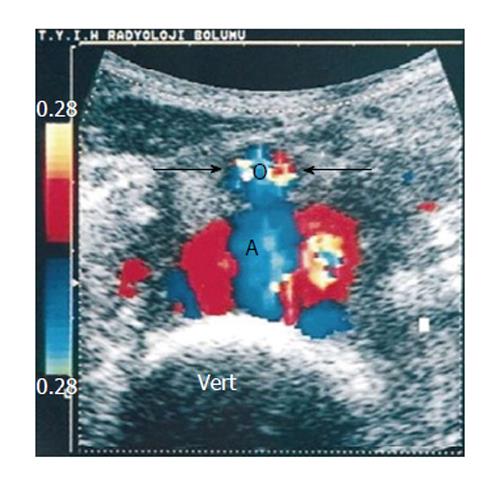
Figure 5 Transverse color Doppler sonogram shows turbulent flow in the pseudoaneurysm.
Note the anterior displacement of the normal-sized aorta (arrows and AO) and the drape of the posterior wall of the pseudoaneurysm over the anterior aspect of the spine (vert)[84].
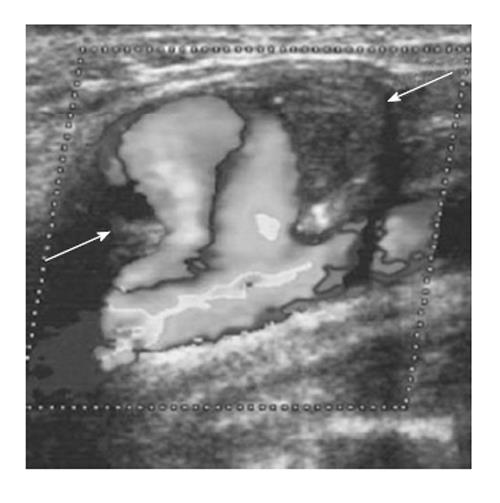
Figure 6 Color Doppler sonogram showing the blood flow of the right common carotid artery, and the haematoma with the rotatory flow within its cavity (arrows).
Note the large neck connecting the carotid to the pseudoaneurysm[90].
- Citation: Mahmoud MZ, Al-Saadi M, Abuderman A, Alzimami KS, Alkhorayef M, Almagli B, Sulieman A. "To-and-fro" waveform in the diagnosis of arterial pseudoaneurysms. World J Radiol 2015; 7(5): 89-99
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v7/i5/89.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i5.89