Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2014; 6(8): 613-618
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.613
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.613
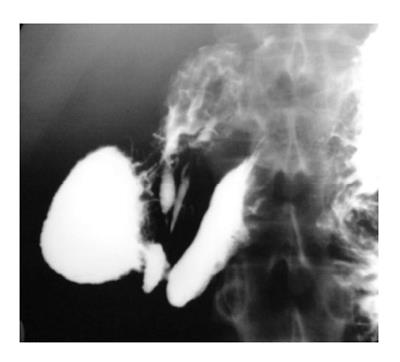
Figure 1 Upper gastrointestinal barium study reveals that the duodenojejunal flexure does not cross the left of the midline suggestive of malrotation.
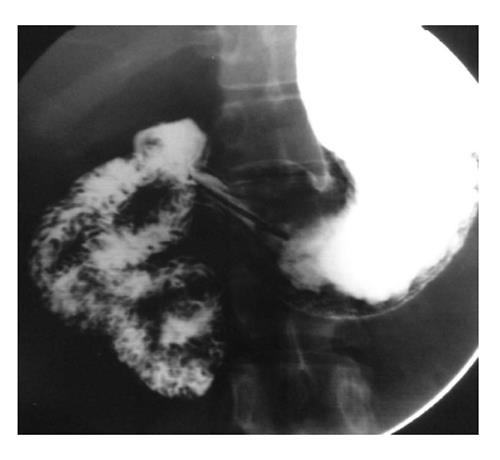
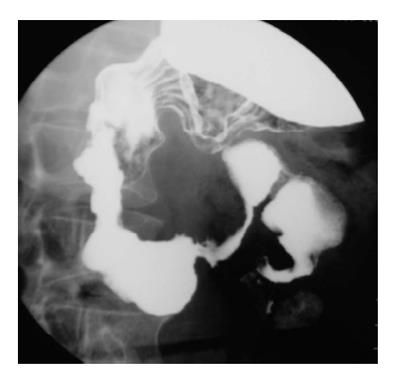
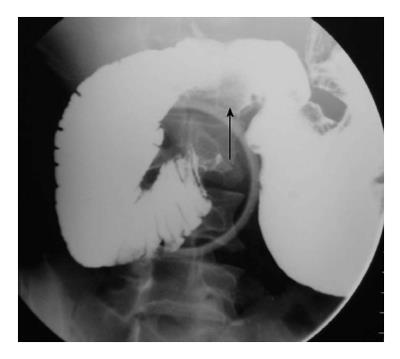
Figure 2 Widening of the duodenal C-loop is noted.
Ultrasonography (not shown) showed a well-defined cystic lesion suggestive of duplication. This is a non-specific barium finding.
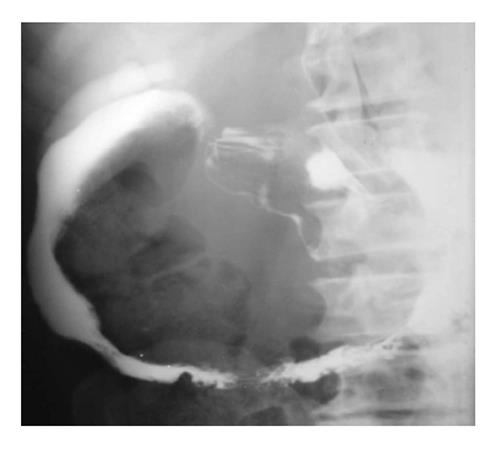
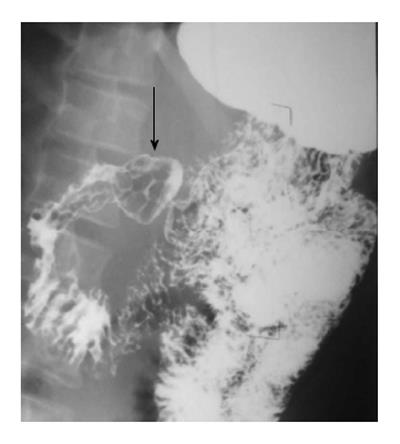
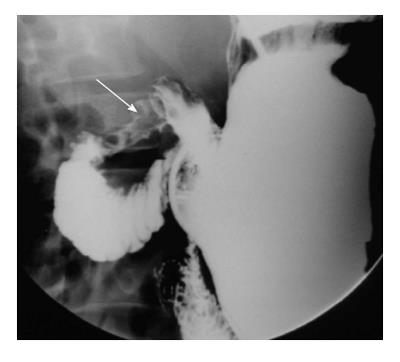
Figure 3 Barium filled out pouching is noted along the medial aspect of the second part of the duodenum (arrow) suggestive of a duodenal diverticulum.
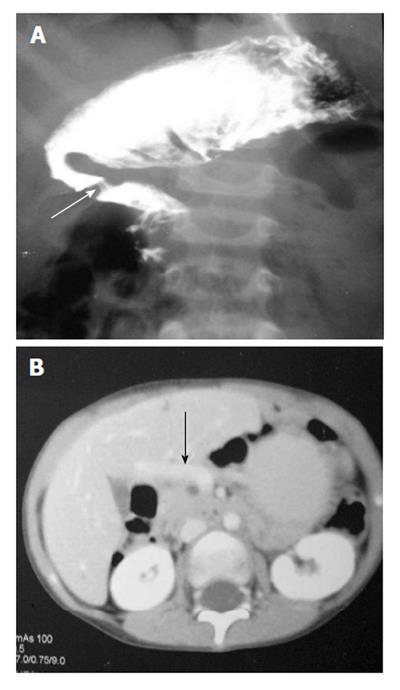
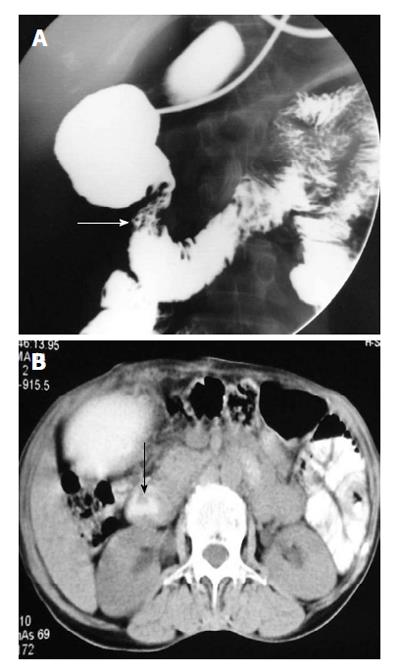
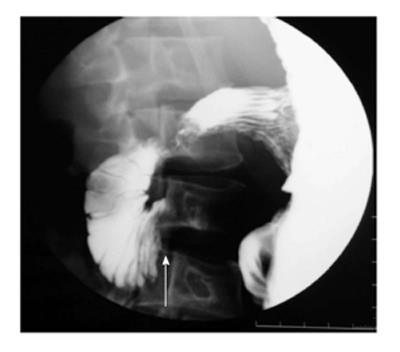
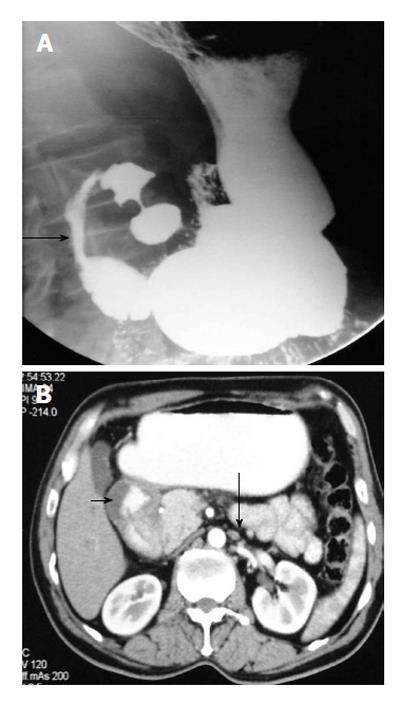
Figure 4 Upper gastrointestinal barium study (A) shows a band like extrinsic narrowing of the first part of the duodenum (arrow), axial computed tomography image (B) reveals the anomalous position of the portal vein anterior to the duodenum (arrow) suggestive of preduodenal portal vein.
Figure 5 Upper gastrointestinal barium study (A) demonstrates smooth circumferential extrinsic narrowing of the second part of the duodenum (arrow), axial computed tomography image (B) shows pancreatic parenchyma incompletely surrounding the duodenum (arrow), features suggestive of partial annular pancreas.
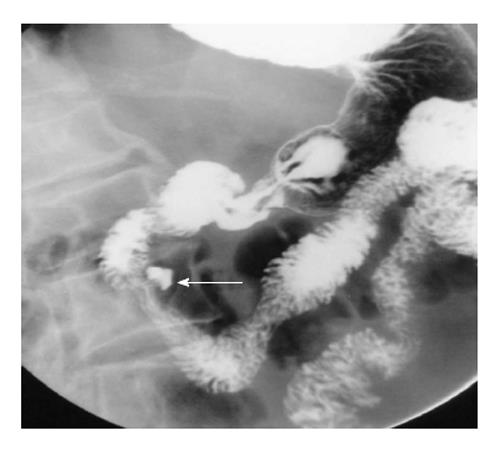
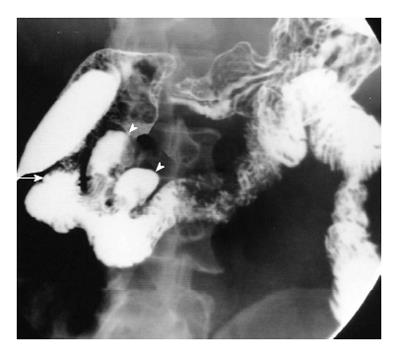
Figure 6 A short segment narrowing (arrow) suggestive of a web is noted at the junction of first and second part of duodenum.
In addition, multiple diverticula are seen at the medial aspect of the second part of the duodenum (arrowheads).
Figure 7 Multiple nodular filling defects are noted in the duodenal cap (arrow) along with fold thickening in the second part of the duodenum.
These findings suggest a diagnosis of Brunner gland hyperplasia.
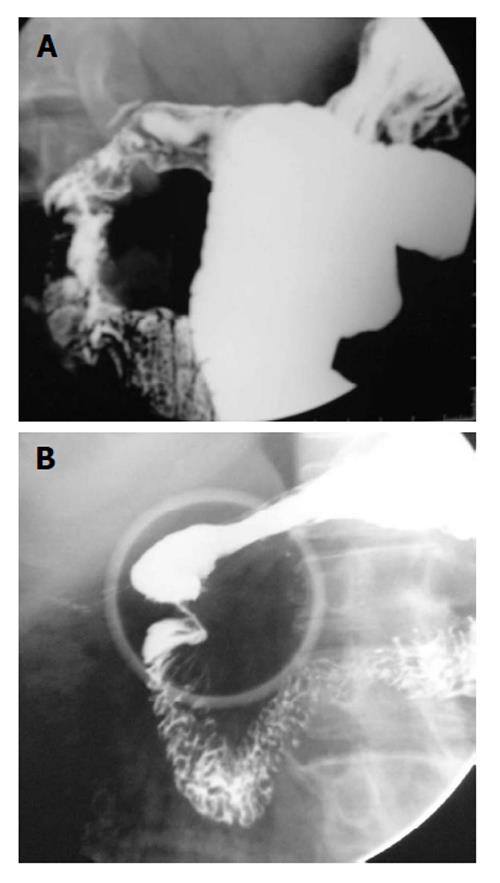
Figure 8 Upper gastrointestinal barium study shows deformity of the duodenal cap (A), stricture is noted at the junction of first and second part of the duodenum (B).
These findings are secondary to healed bulbar (A) and post bulbar duodenal ulcers (B).
Figure 9 There is narrowing of the distal second part of the duodenum with reflux of barium into the common bile ducts.
This patient had concomitant involvement of the ileocecal junction (not shown). Histopathology revealed a diagnosis of gastrointestinal tuberculosis.
Figure 10 A long segment narrowing with irregular outline and proximal dilatation is noted in the fourth part of duodenum.
In addition few strictures are also noted in proximal jejunum. Detailed evaluation in this patient revealed a diagnosis of Crohn's disease.
Figure 11 Mild luminal narrowing with ulceration is noted in the proximal duodenum.
Computed tomography of this patient (not shown) revealed mural thickening of the duodenum with cystic changes suggestive of cystic dystrophy.
Figure 12 Upper gastrointestinal barium study shows cut off of the duodenum at the junction of second and third part with collapsed distal duodenum suggestive of superior mesenteric artery syndrome.
Figure 13 A mass is noted in relation to the medial aspect of the first and second part of the duodenum with ulceration (arrow).
In addition stricture with mucosal irregularity is seen in distal third part of duodenum. Endoscopic biopsy revealed adenocarcinoma.
Figure 14 A long segment narrowing of the second part (arrow) of the duodenum is noted (A), axial computed tomography image (B) shows circumferential mural thickening of the duodenum (short arrow) with few para-aortic lymph nodes (long arrow).
Endoscopic biopsy revealed a diagnosis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Citation: Gupta P, Debi U, Sinha SK, Prasad KK. Upper gastrointestinal barium evaluation of duodenal pathology: A pictorial review. World J Radiol 2014; 6(8): 613-618
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i8/613.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.613