Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2012; 4(8): 372-378
Published online Aug 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i8.372
Published online Aug 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i8.372
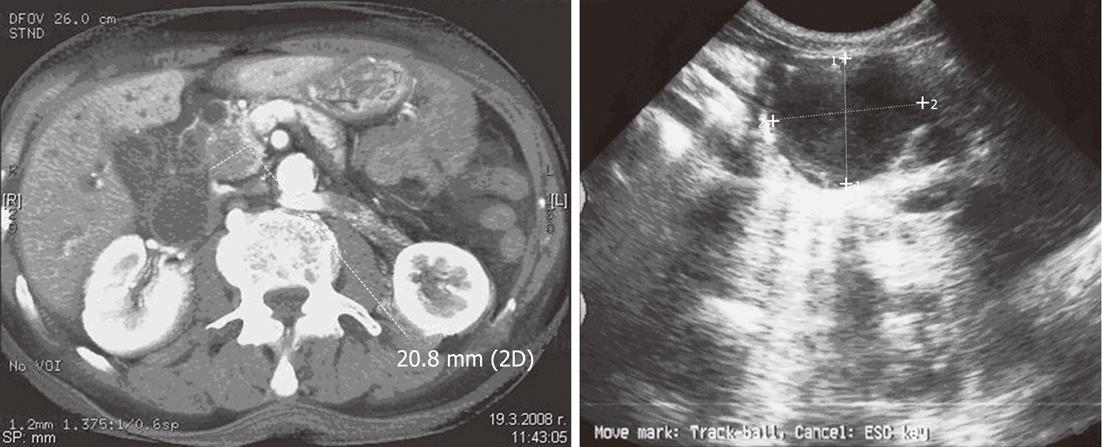
Figure 1 Computed tomography and ultrasound images of microcystic pancreatic lesions/serous cystic neoplasm.
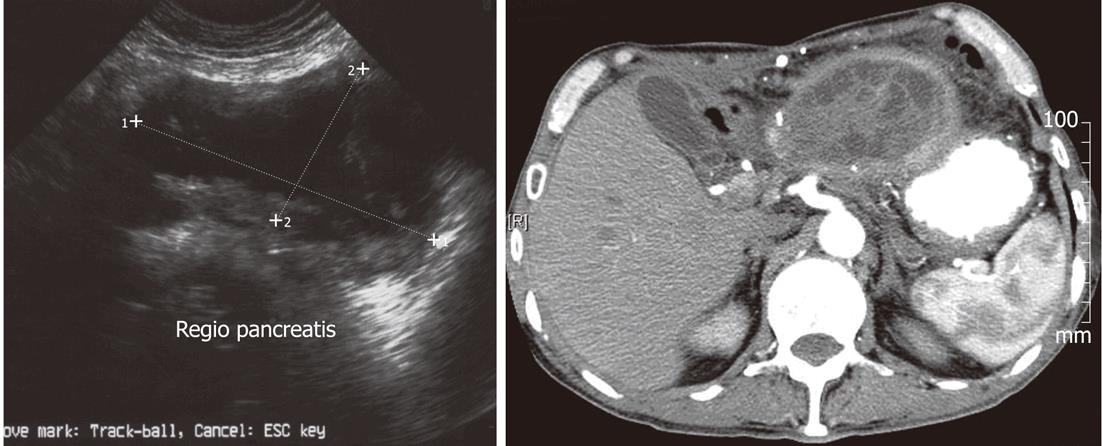
Figure 2 Ultrasound and computed tomography image of septated macrocyst-mucinous cystic neoplasm/mucinous cystic neoplasm.
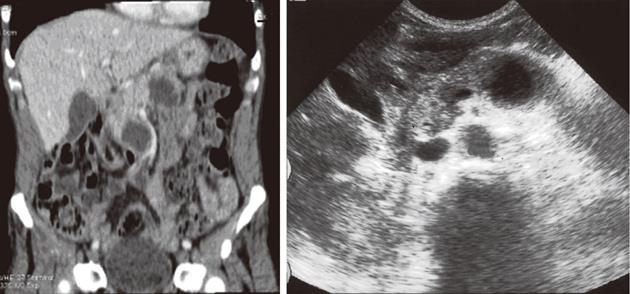
Figure 3 Multidetector computed tomography coronal reconstruction and ultrasound images of multiple branch duct type of intraductal papillary mucinous tumors.
Note the dilated pancreatic duct on ultrasound image.
Figure 4 Cytological preparation with immuno-reactivity to P-53 in 80%-95% of the cells.
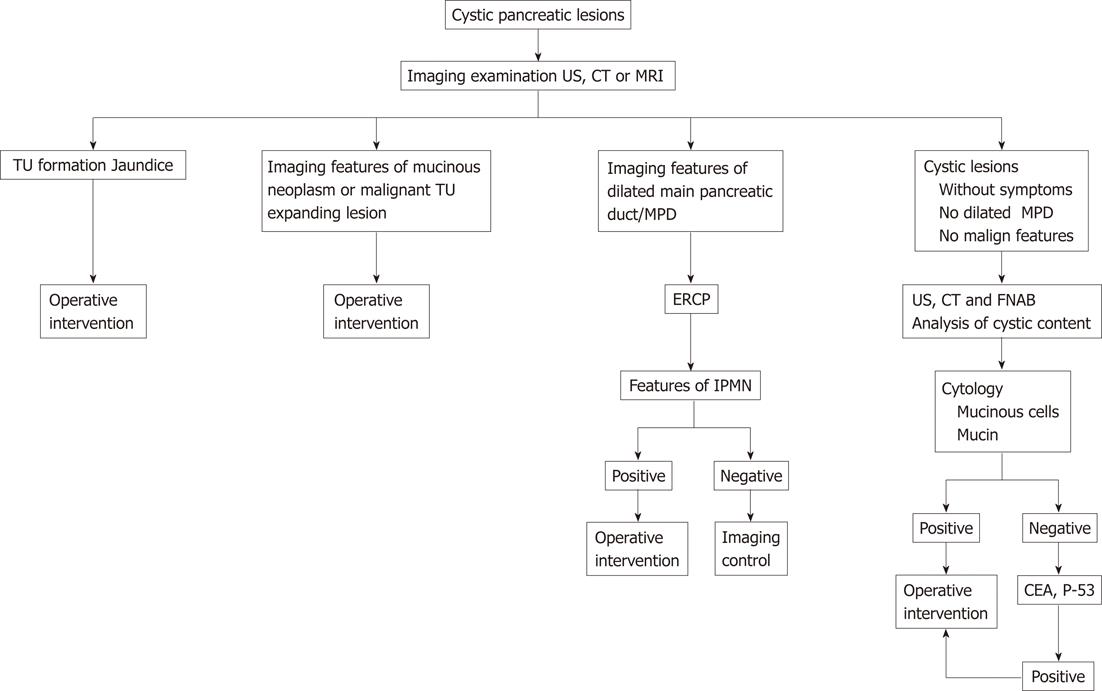
Figure 5 Proposed diagnostic algorithm and therapeutic behavior of suspected pancreatic cystic neoplasms.
US: Ultrasound; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; FNAB: fine needle aspiration biopsy.
- Citation: Hilendarov AD, Deenichin GP, Velkova KG. Imaging investigation of pancreatic cystic lesions and proposal for therapeutic guidelines. World J Radiol 2012; 4(8): 372-378
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v4/i8/372.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v4.i8.372