Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. May 28, 2012; 4(5): 236-240
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i5.236
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i5.236
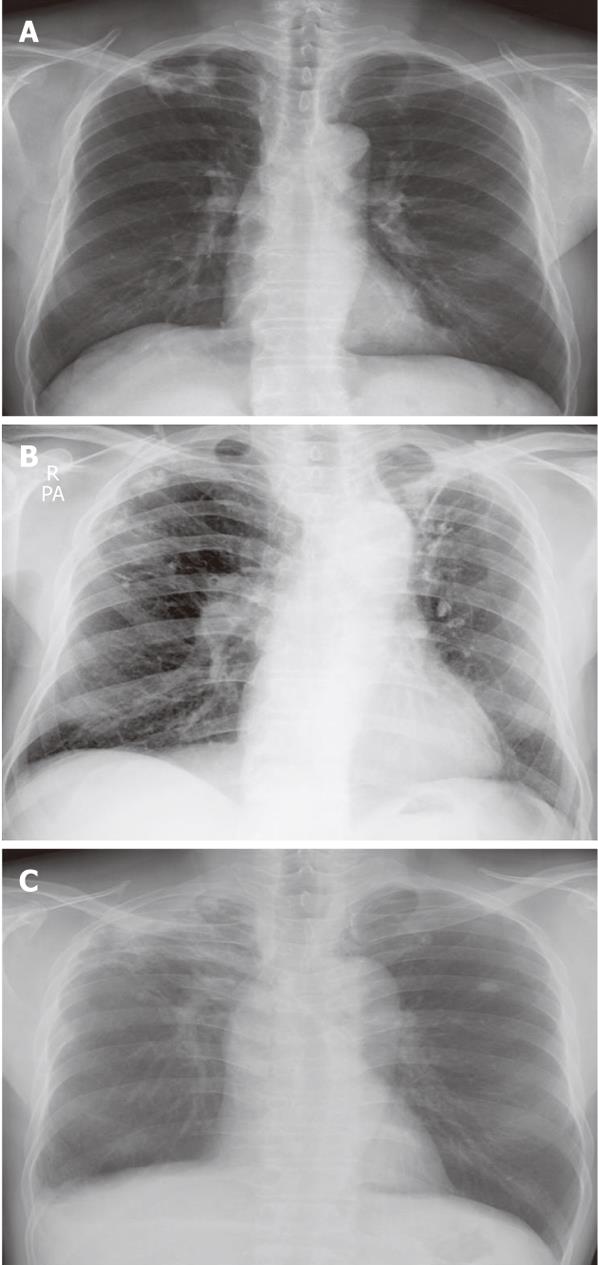
Figure 1 Initial chest radiography.
A calcified granuloma suggestive of a former tuberculosis infection was detected in the right upper lung field on the chest radiograph.
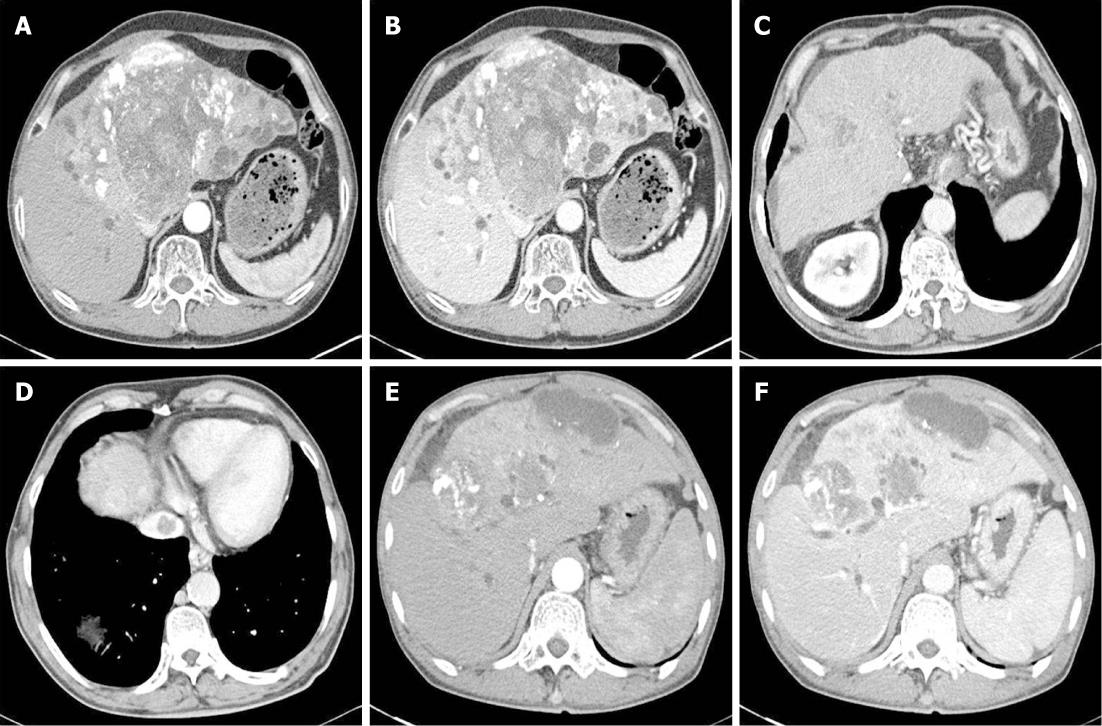
Figure 2 Abdominal computed tomography on diagnosis of reactivated tuberculosis.
A, B: Arterial phase and portal phase. Computed tomography (CT) performed after the last transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) session revealed lipiodol uptake in large hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) in S2, S3, S4 and S5 segments and increased dilatation of both intrahepatic duct (IHD) as compared to the initial CT; C, D: CT performed after the last TACE session revealed a slight increase in the interval of lipiodol uptake, with no additional uptake in the small HCCs in S4 and S8; a newly developed thrombosis was noted in the inferior vena cava; E, F: Arterial phase and portal phase. A large HCC in S4, S5 and S8 with partial lipiodol uptake was seen, accompanied dilatation of the IHD.
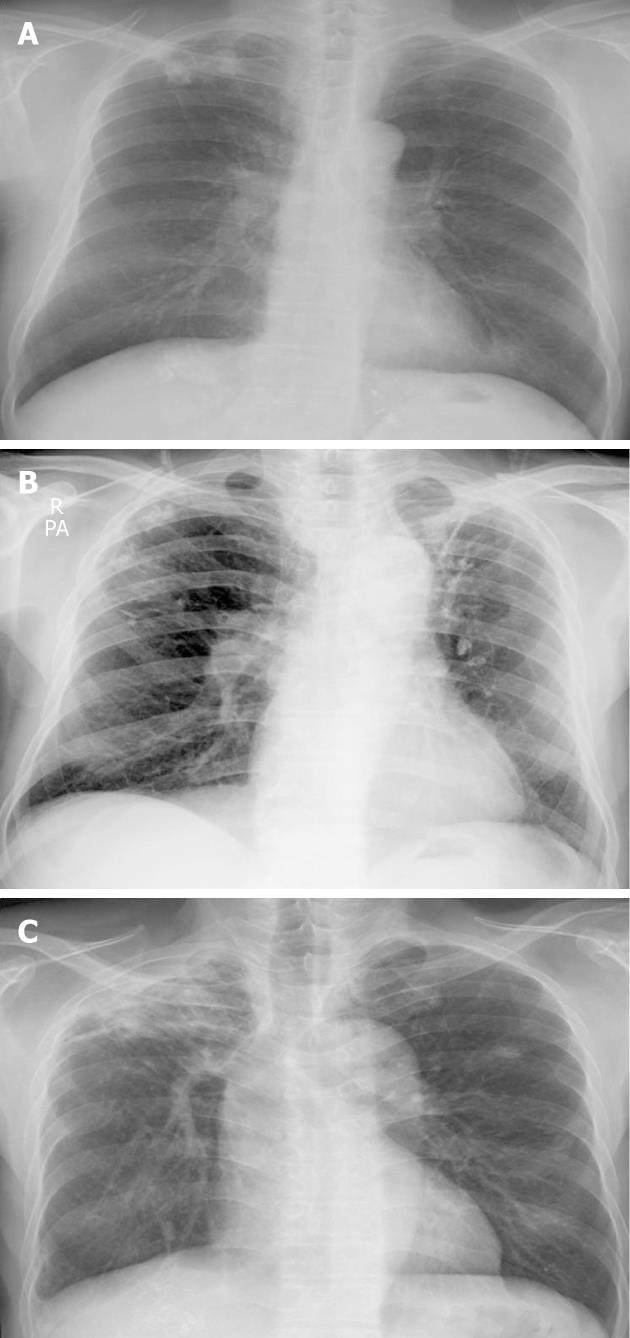
Figure 3 Chest radiography in the reactivated tuberculosis state.
No interval changes were seen on the subsequent chest radiograph.
- Citation: Kim YJ, Goh PG, Moon HS, Lee ES, Kim SH, Lee BS, Lee HY. Reactivation of tuberculosis in hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: A report of 3 cases. World J Radiol 2012; 4(5): 236-240
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v4/i5/236.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v4.i5.236