Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
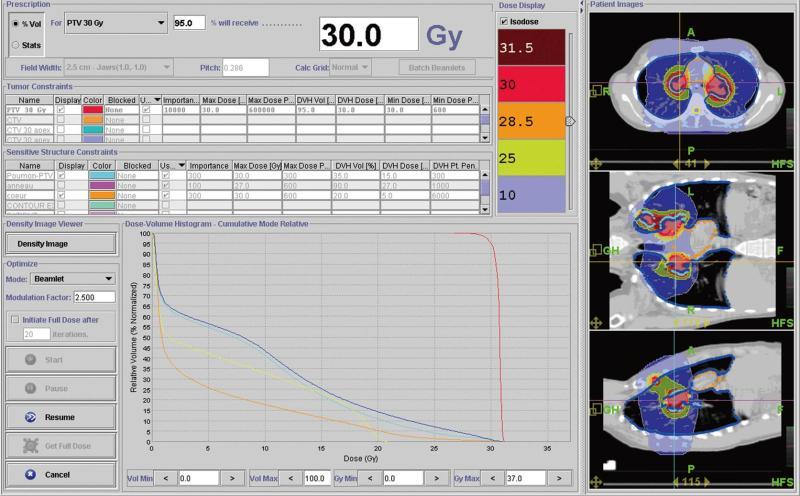
Figure 1 This figure shows the dose distribution during radiotherapy for the first patient who was diagnosed with multiple pleural and mediastinal tumors and also the dose-volumes histograms showing the sparing of some organs at risk (for example heart in orange with 5 Gy received by 20% of heart volume, in red planning target volume (planning treatment volume with homogeneous dose distribution and adequate coverage).
Since irradiation to the bilateral hilum increases the risk of radiation pneumonitis, every effort was made to decrease the doses to the lung. Helical tomotherapy could be particularly useful in this setting. In this example, no more than 10% of the volume defined as the [lung - PTV] received 20 Gy.
- Citation: Kirova YM, Chargari C. Applications of new irradiation modalities in patients with lymphoma: Promises and uncertainties. World J Radiol 2011; 3(3): 66-69
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v3/i3/66.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v3.i3.66