Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
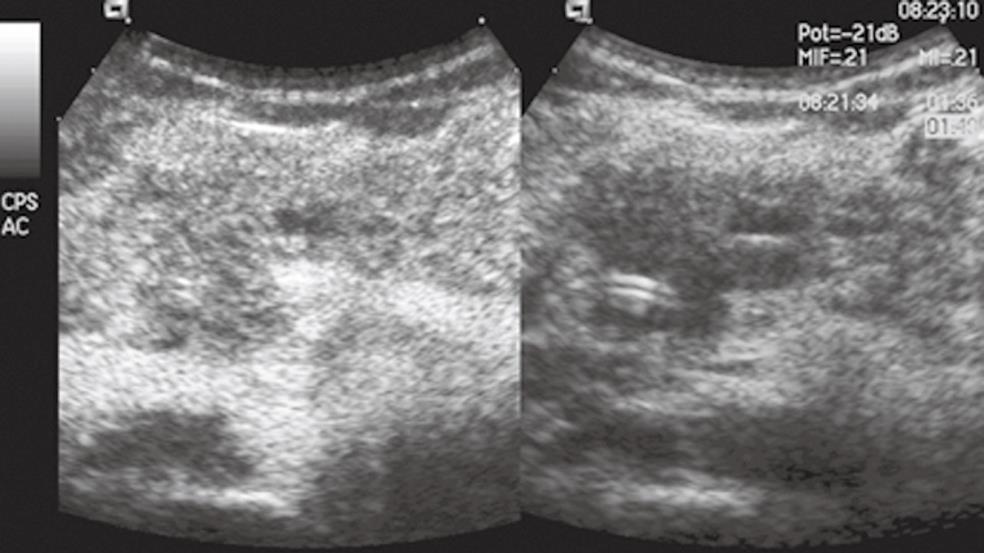
Figure 1 Focal autoimmune pancreatitis.
The pancreatic head mass is hypoechoic in conventional ultrasound (US) (right side of the split-screen) and inhomogeneously isovascular in contrast-enhanced US (CEUS) (left side of the split-screen).
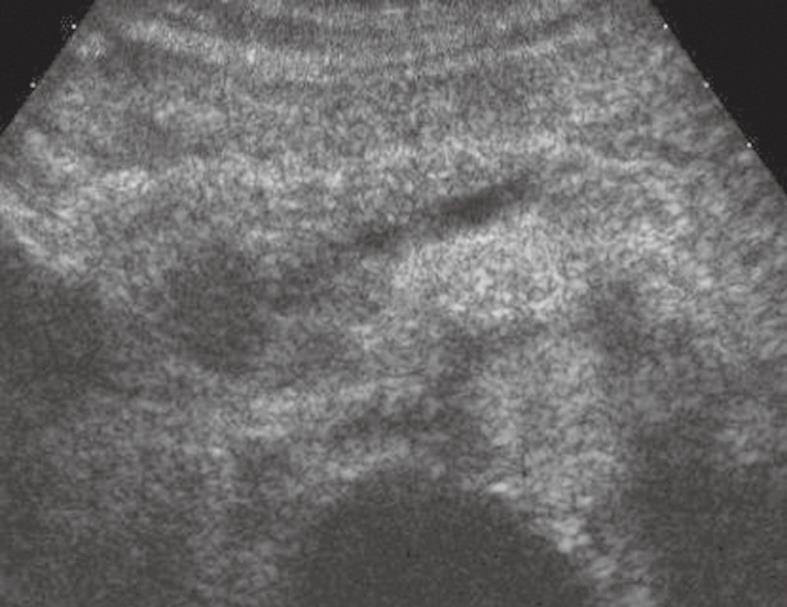
Figure 2 Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
The pancreatic head solid lesion is hypoechoic in CEUS with upstream dilation of the main pancreatic duct.
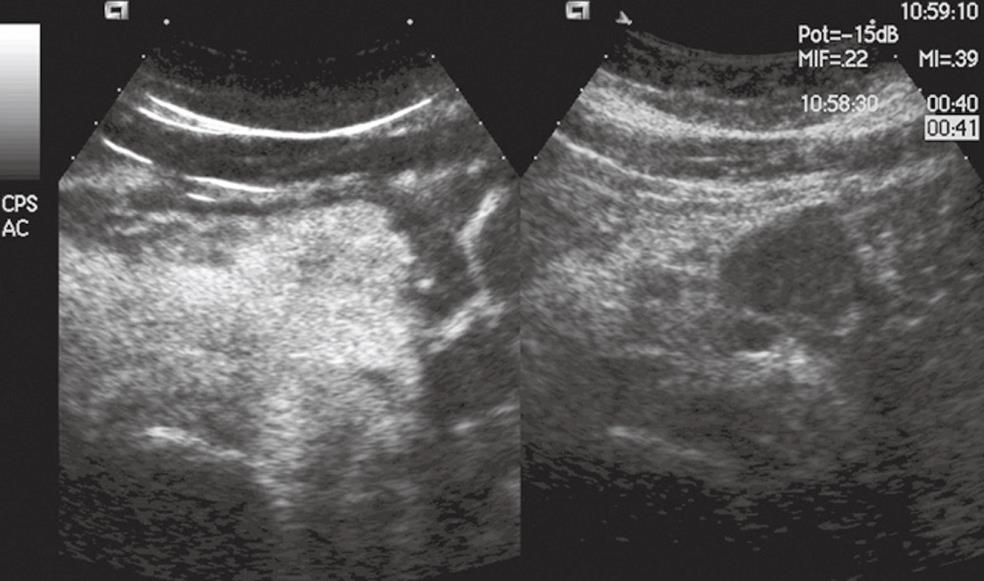
Figure 3 Pancreatic endocrine tumor.
The pancreatic body mass is solid and hypoechoic in conventional US (right side of the split-screen) and hypervascular in CEUS (left side of the split-screen).
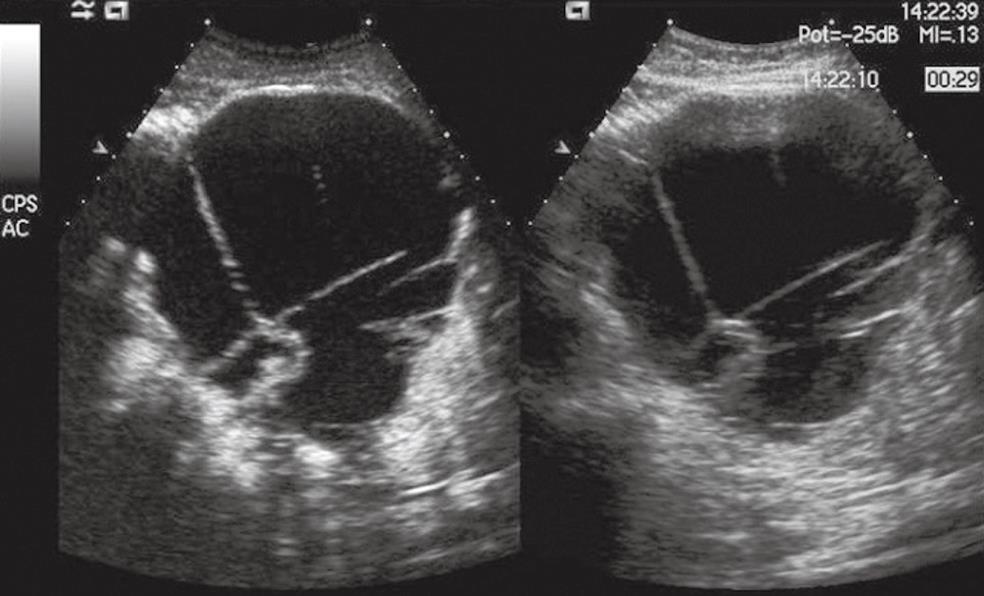
Figure 4 Pancreatic mucinous cystoadenocarcinoma.
A voluminous cystic mass is seen in the pancreatic body with septa and nodules in conventional US (right side of the split-screen) and is enhanced in CEUS (left side of the split-screen).
- Citation: D’Onofrio M, Gallotti A, Principe F, Mucelli RP. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the pancreas. World J Radiol 2010; 2(3): 97-102
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v2/i3/97.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v2.i3.97