Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Radiol. May 28, 2023; 15(5): 136-145
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v15.i5.136
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v15.i5.136
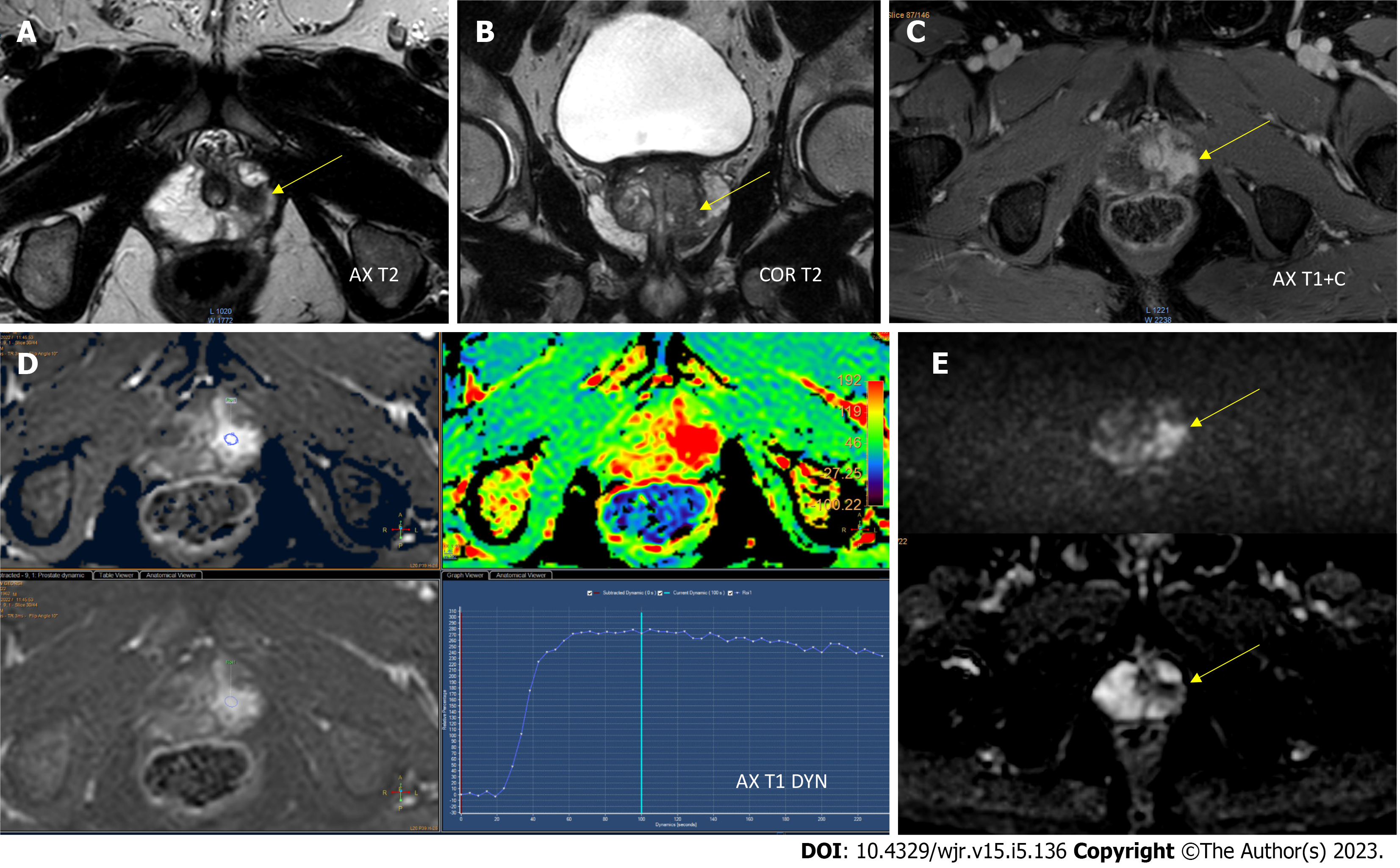
Figure 1 Apical peripheral zone with a Prostate Imaging-Reporting & Data System 5 lesion.
A and B: Axial (A) and coronal (B) T2-weighted imaging (WI) revealed a homogeneous hypointense lesion in the anterior peripheral zone of the apex; C: Postcontrast axial T1WI showed pronounced enhancement of the lesion; D: Early dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging showed positive enhancement within the lesion and provided a wash-out signal intensity curve; E: Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) diffusion restriction [DWI (b = 1000 s/mm2)] provided a marked hyperintense signal above the background, while the ADC map image showed a lesion with hypointense signal below the background.
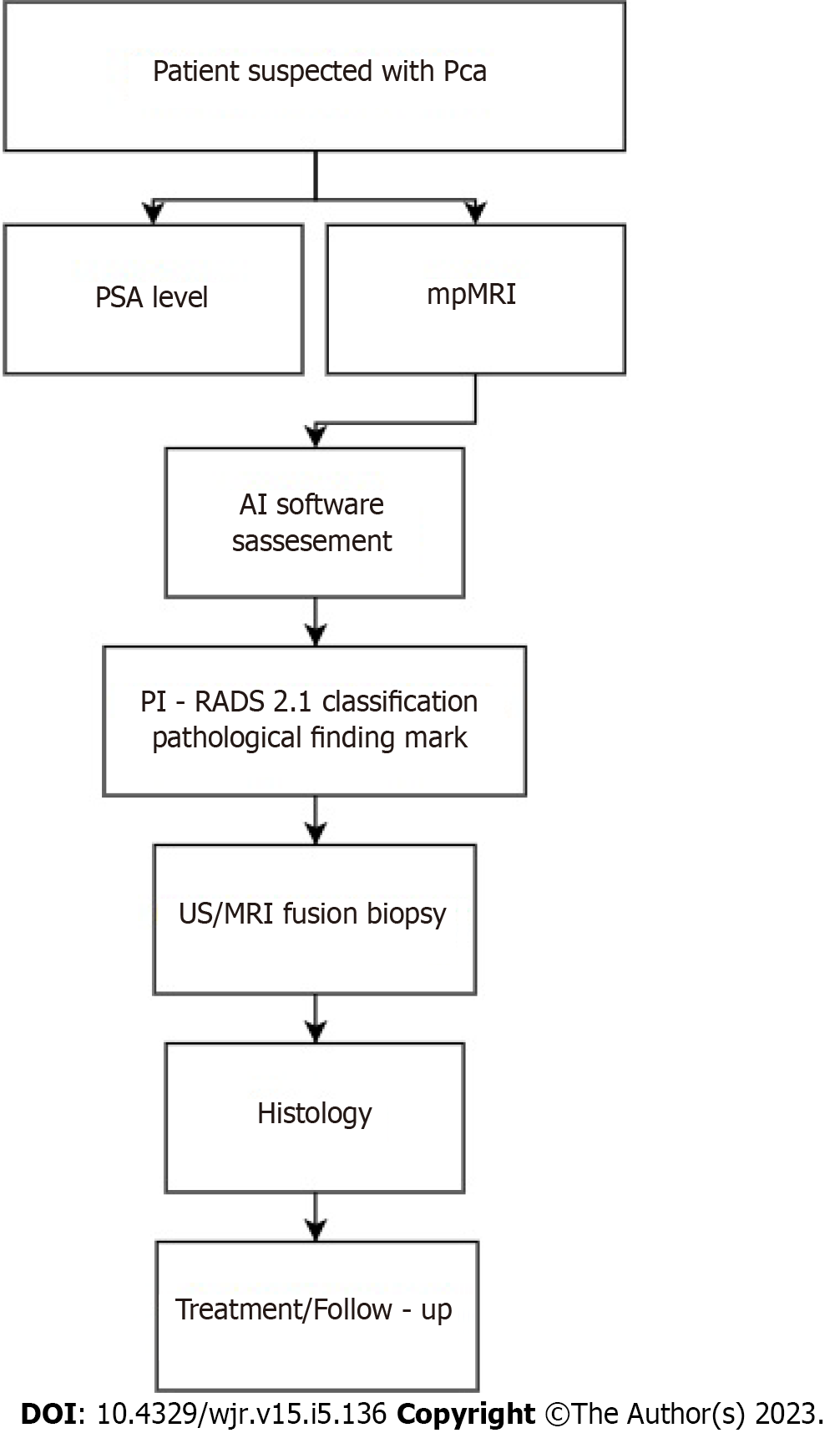
Figure 2 Prostate cancer diagnosis algorithm.
AI: Artificial intelligence; mpMRI: Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; Pca: Prostate cancer; PI-RADS: Prostate Imaging-Reporting & Data System; PSA: Prostate-specific antigen; US: Ultrasound.
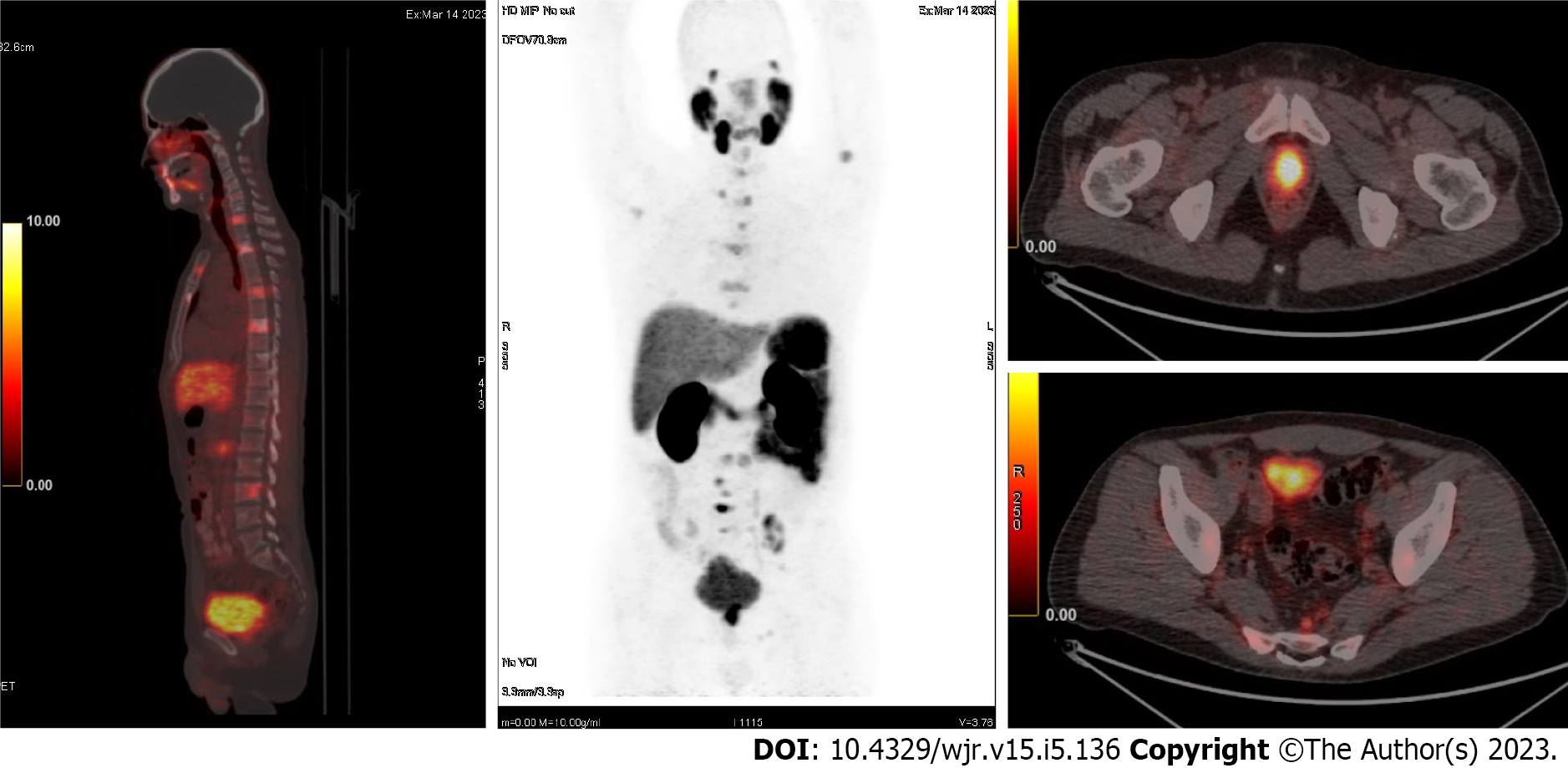
Figure 3 68GA prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography-computed tomographic images for a patient with prostate cancer (adenocarcinoma).
The imaging revealed a primary tumor and diffuse lymph node metastatic spread as well as multiple spinal metastases.
- Citation: Chervenkov L, Sirakov N, Kostov G, Velikova T, Hadjidekov G. Future of prostate imaging: Artificial intelligence in assessing prostatic magnetic resonance imaging. World J Radiol 2023; 15(5): 136-145
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v15/i5/136.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v15.i5.136