Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2022; 14(7): 194-208
Published online Jul 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i7.194
Published online Jul 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i7.194
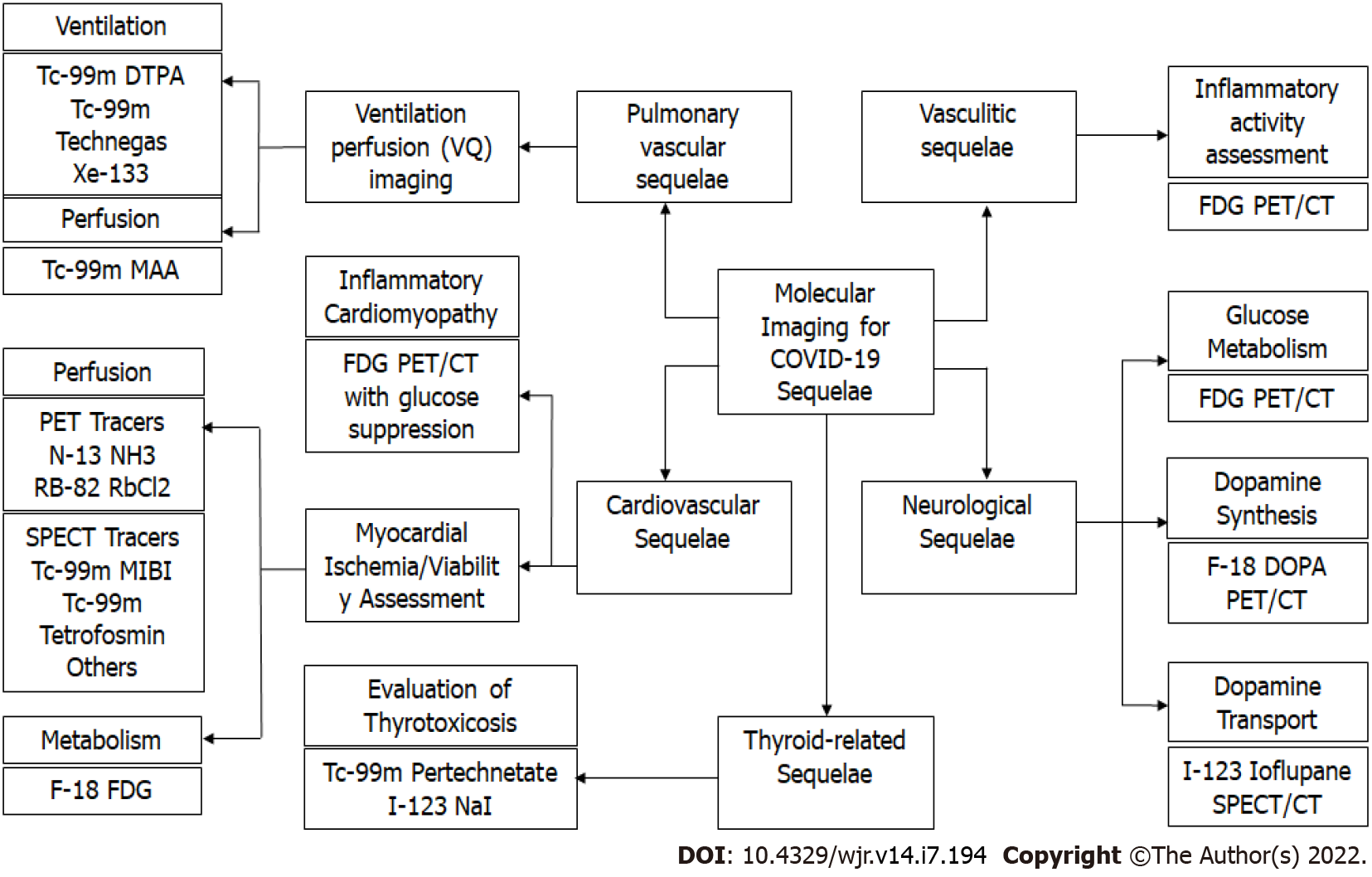
Figure 1 Molecular Imaging modalities for evaluating coronavirus disease 2019 sequelae.
CT: Computed tomography; DOPA: L-6-fluoro-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalnine; DTPA: Diethylenetriamine pentaacetate; FDG: Fluorodeoxyglucose; MAA: Macroaggregated albumin; MIBI: Methoxy isobutyl isonitrile; PET: Positron emission tomography; SPECT: Single-photon emission computerized tomography.
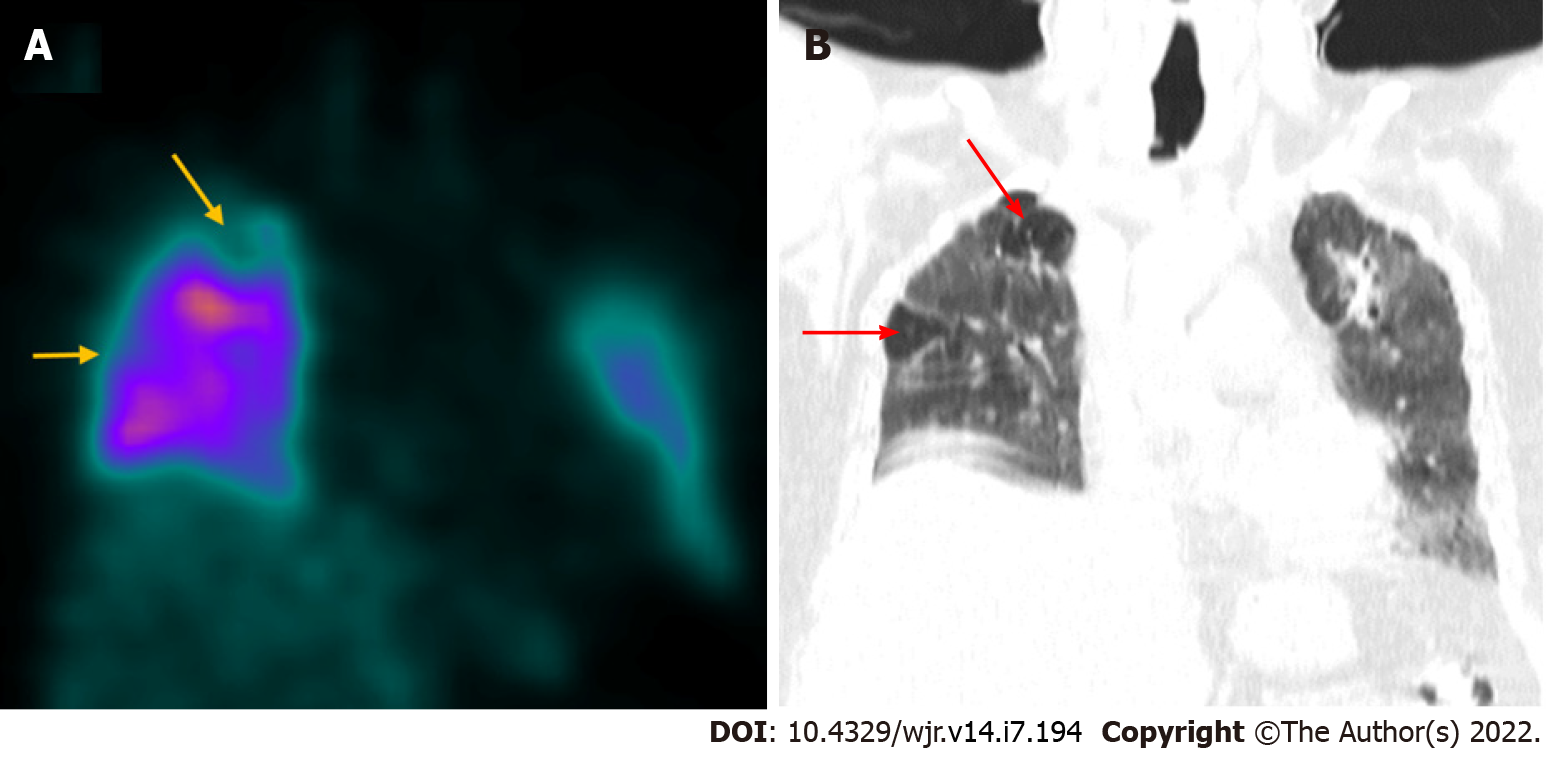
Figure 2 Coronavirus disease 2019 related pulmonary thromboembolism.
A 60-year-old male with history of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection 2 mo ago underwent Tc-99m macro-aggregated albumin lung perfusion imaging to rule out pulmonary thromboembolism. A: Coronal SPECT images show reduced tracer uptake (yellow arrows) in sub-segmental defects involving the right lung apex and the lateral segment of the RML; B: Corresponding coronal CT image shows relatively normal lung parenchyma (red arrows) in the above-mentioned sites (mismatched defects) suggestive of pulmonary thromboembolism. The rest of the lung parenchyma shows ground glass changes, fibrotic bands, and bronchiectatic changes consistent with post-COVID recovery phase.
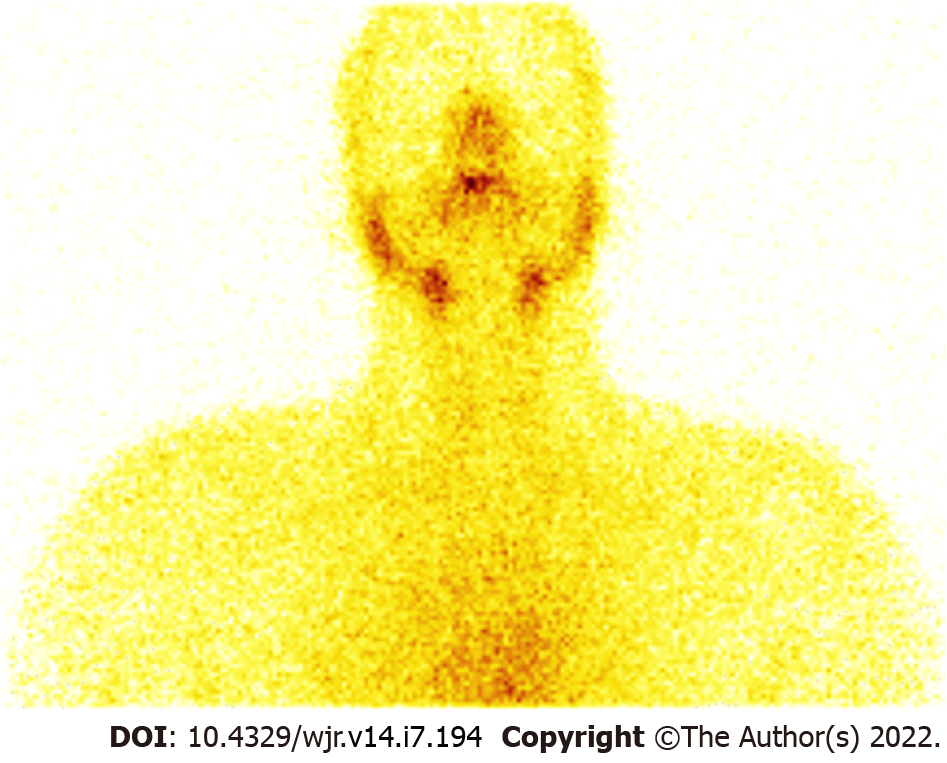
Figure 3 Coronavirus disease 2019 related thyroiditis.
A 36-year-old male had complaints of painful neck swelling and fever for 1 wk and a past history of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) (2 mo ago). His serum TSH levels were found to be suppressed (0.013 microIU/mL). With a clinical suspicion of thyroiditis, he was referred for thyroid scintigraphy, which revealed very faint heterogeneous tracer uptake in the region of the thyroid and increased background tracer activity. In the given clinical and biochemical context, scan findings were suggestive of COVID-19 related thyroiditis.
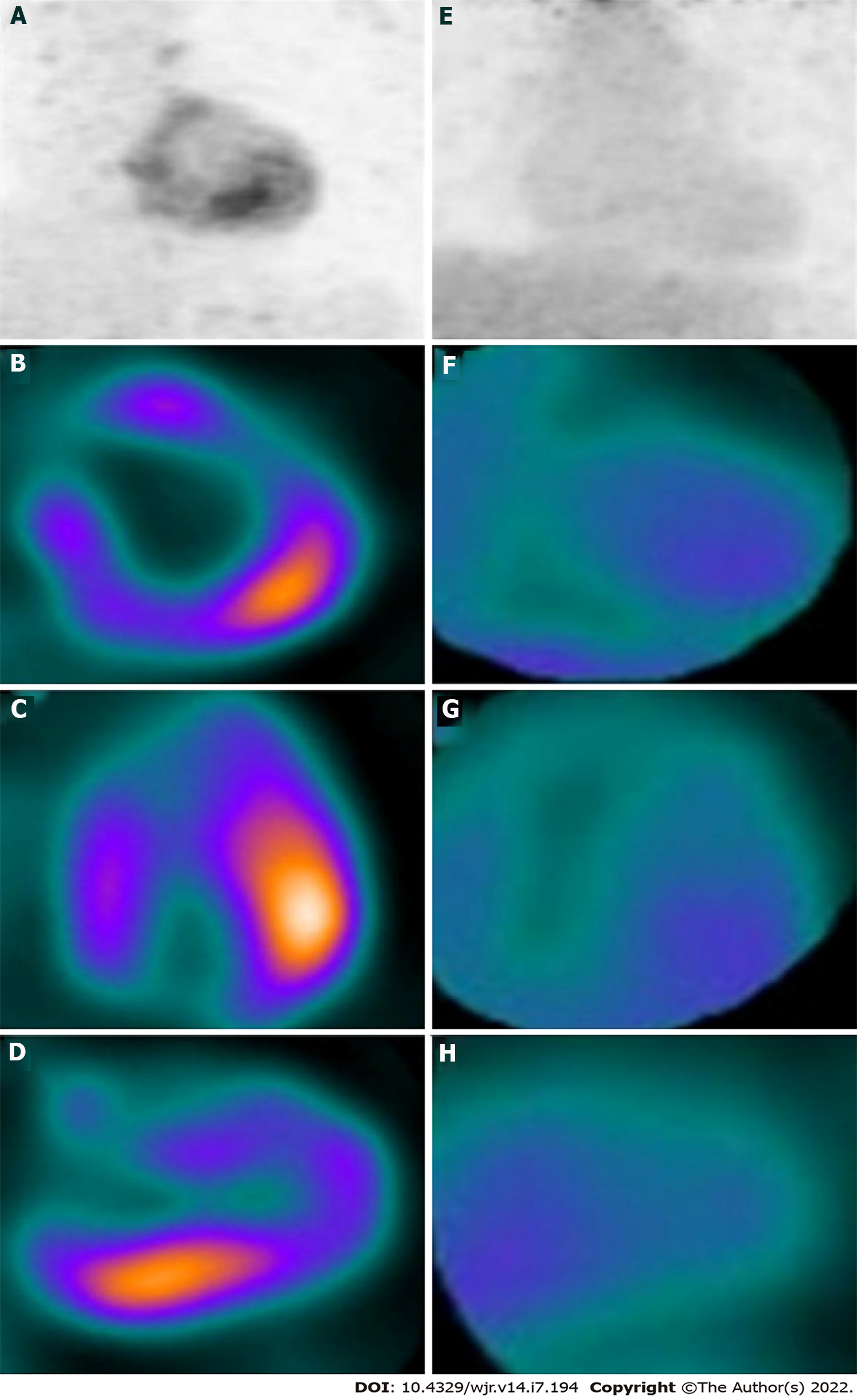
Figure 4 Coronavirus disease 2019 related myocarditis.
A 14-year-old male child underwent regional 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) to assess myocardial inflammation. Baseline maximum intensity projection (A), short axis (B), horizontal long axis (C), and vertical long axis (D) images showing increased 18F-FDG uptake in the inferolateral wall of the left ventricular myocardium. Corresponding follow-up images (E to H) after 6 wk showing resolution of hypermetabolism in the inferolateral wall with no other FDG avid focus. Citation: Satapathy S, Kumar R, Kavanal AJ, Krishnaraju VS, Ramachandran A, Deo P, Dhir V, Mittal BR. COVID-19 related multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C): Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT to assess myocardial involvement. J Nucl Cardiol 2021. Copyright © The Authors 2021. Published by American Society of Nuclear Cardiology.
- Citation: Chandekar KR, Satapathy S, Singh H, Bhattacharya A. Molecular imaging as a tool for evaluation of COVID-19 sequelae – A review of literature. World J Radiol 2022; 14(7): 194-208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v14/i7/194.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v14.i7.194