Copyright
©2009 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
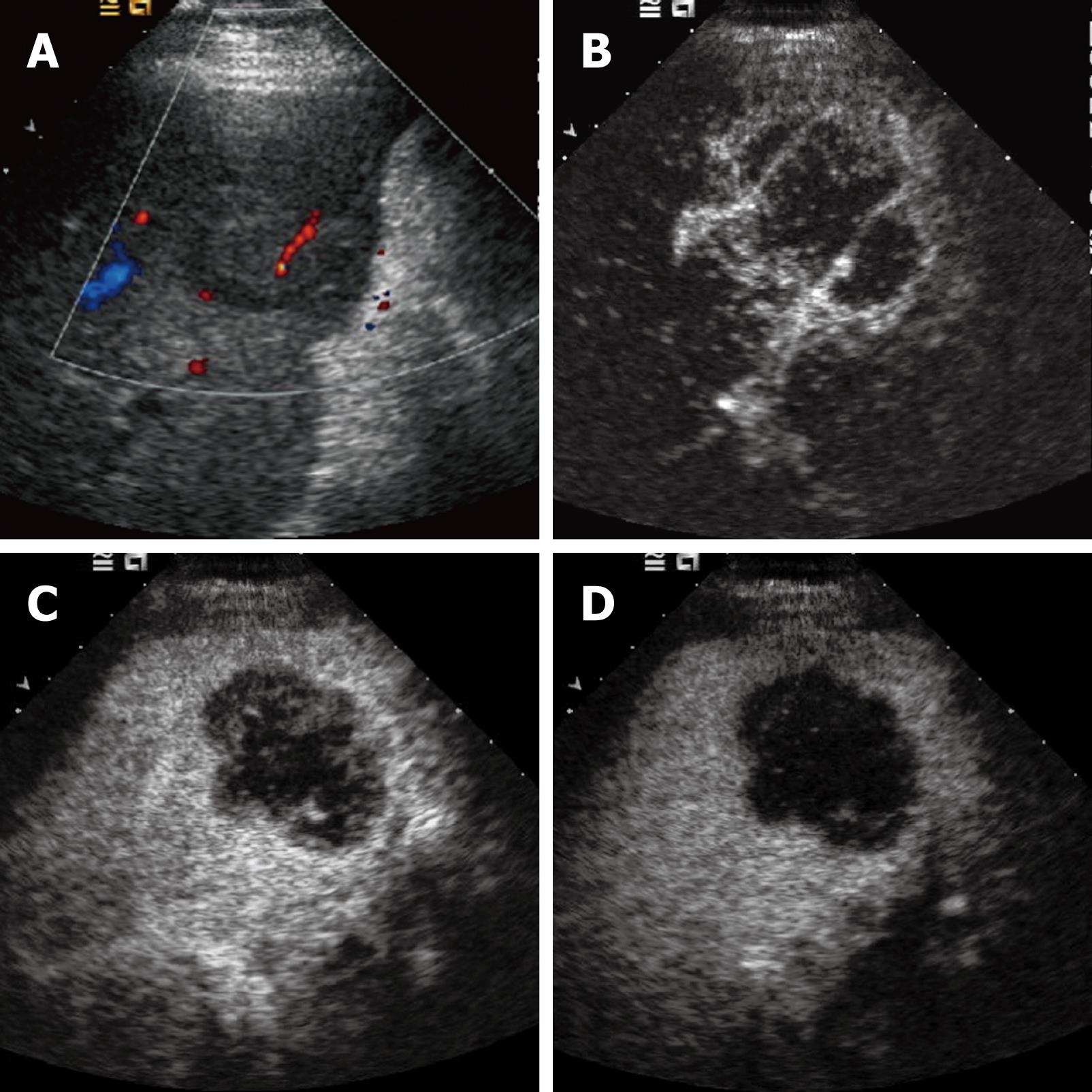
Figure 1 Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Baseline ultrasound shows an isoechoic mass in segment 5 of the liver; B: The lesion shows peripheral rim-like hyper-enhancement 26 s after contrast agent injection on CEUS; C: The lesion becomes hypo-enhanced 52 s after contrast agent injection; D: The lesion continues to be hypo-enhanced 121 s after contrast agent injection.
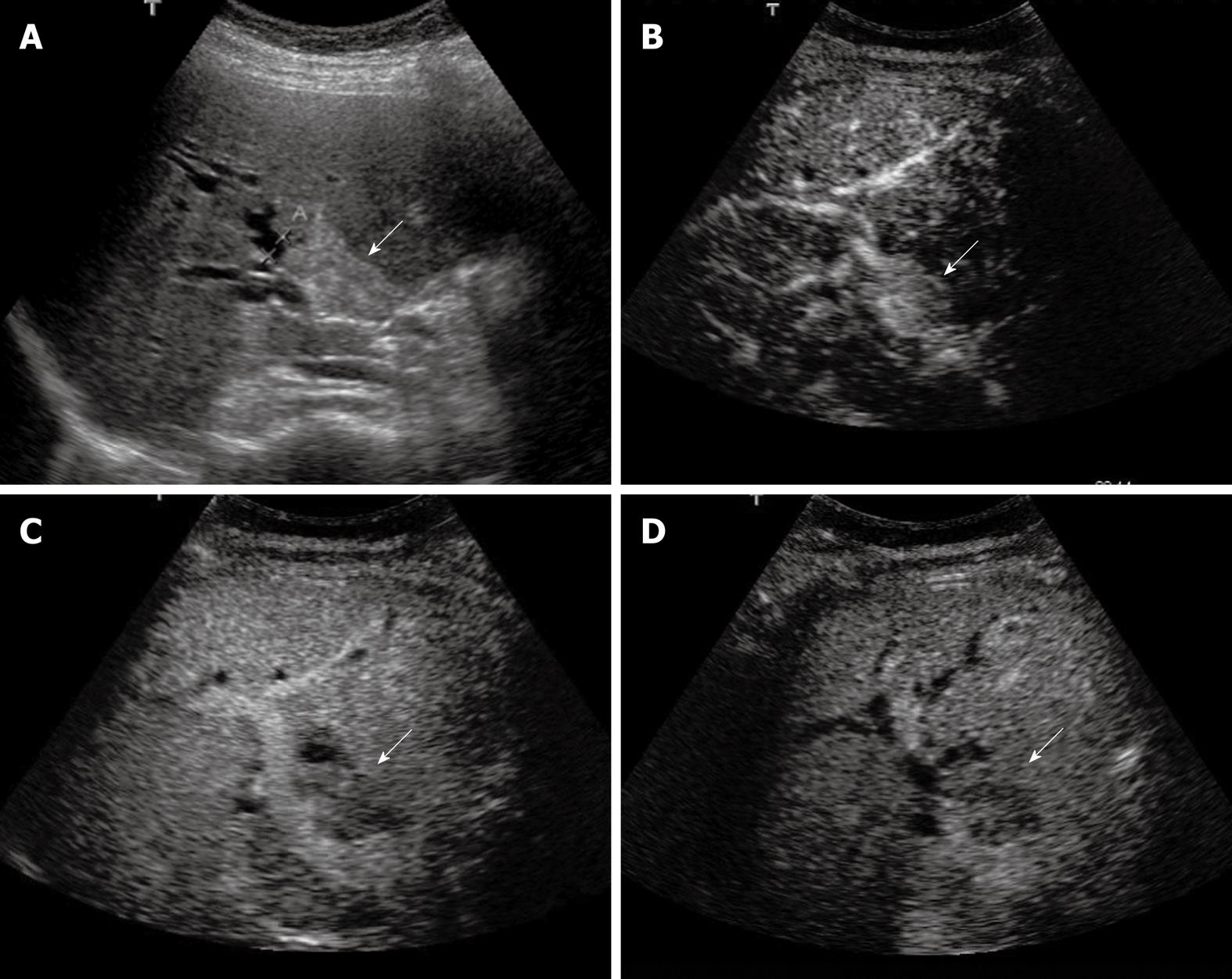
Figure 2 Klatskin tumor.
A: Baseline ultrasound shows a hyperechoic mass (arrow) in the hilar bile duct; B: The lesion (arrow) shows homogeneous hyper-enhancement 14 s after contrast agent injection on CEUS; C: The lesion (arrow) becomes hypo-enhanced 45 s after contrast agent injection; D: The lesion (arrow) continues to be hypo-enhanced 126 s after contrast agent injection.
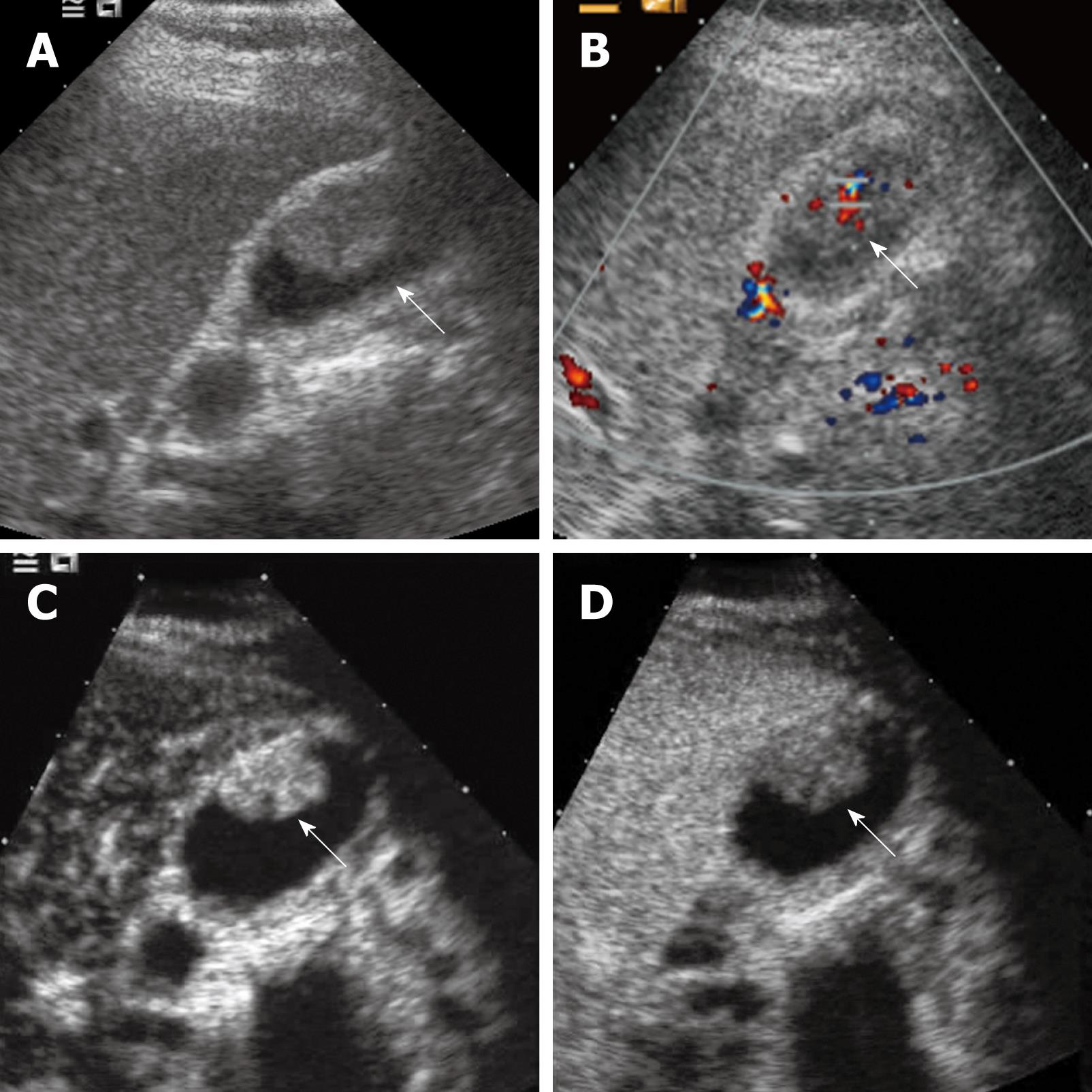
Figure 3 Gallbladder carcinoma.
A: Baseline ultrasound shows an isoechoic mass (arrow) in the gallbladder cavity; B: The lesion (arrow) shows hypervascularity on color Doppler flow imaging; C: The lesion (arrow) shows homogeneous hyper-enhancement 19 s after contrast agent injection on CEUS; D: The lesion (arrow) becomes hypo-enhanced 34 s after contrast agent injection.
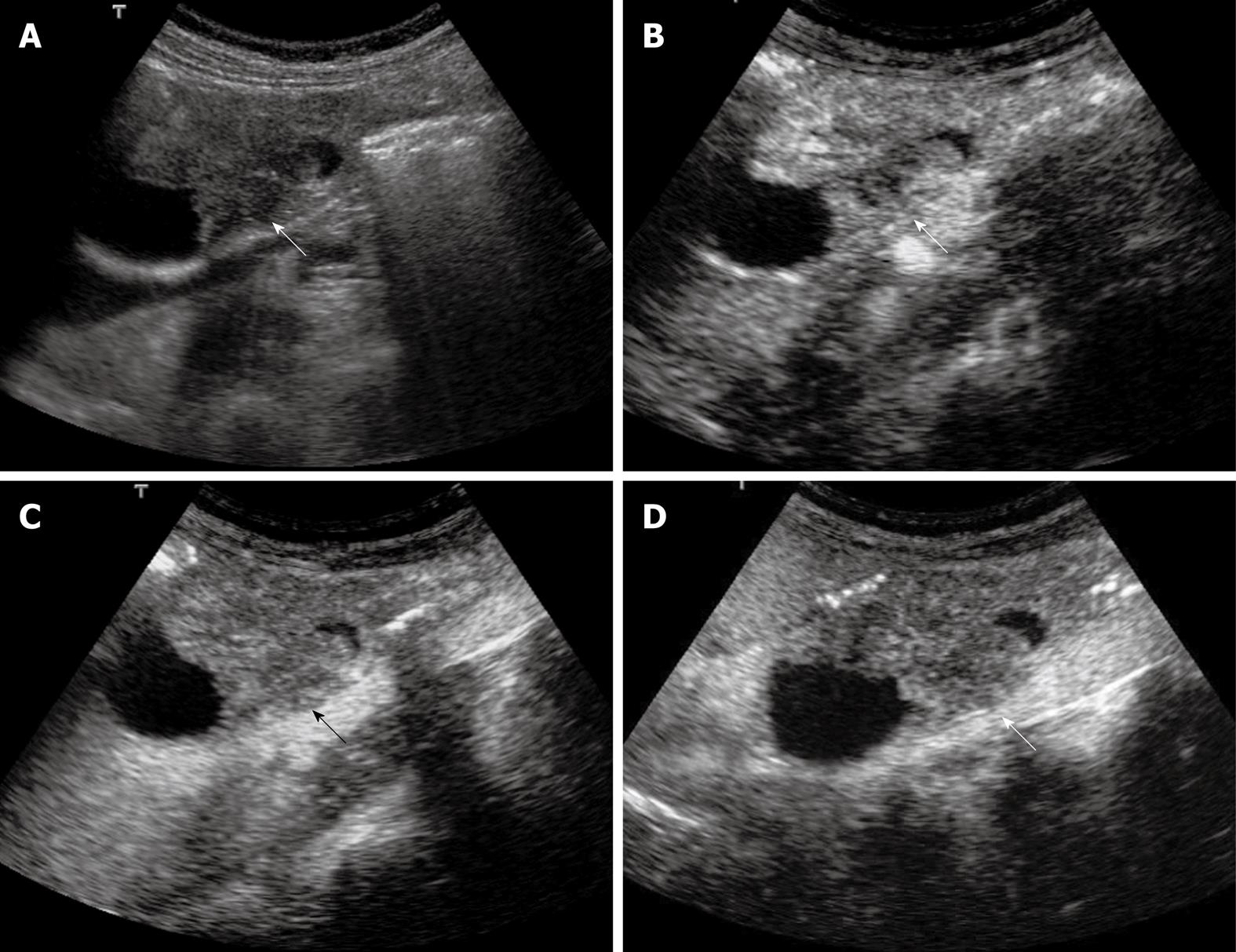
Figure 4 Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Baseline ultrasound shows an isoechoic mass (arrow) in the lower portion of the common bile duct; B: The lesion (arrow) shows heterogeneous iso-enhancement 13 s after contrast agent injection on CEUS; C: The lesion (arrow) continues to be iso-enhanced 56 s after contrast agent injection; D: The lesion (arrow) becomes hypo-enhanced 107 s after contrast agent injection.
- Citation: Xu HX. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the biliary system: Potential uses and indications. World J Radiol 2009; 1(1): 37-44
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v1/i1/37.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v1.i1.37