Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
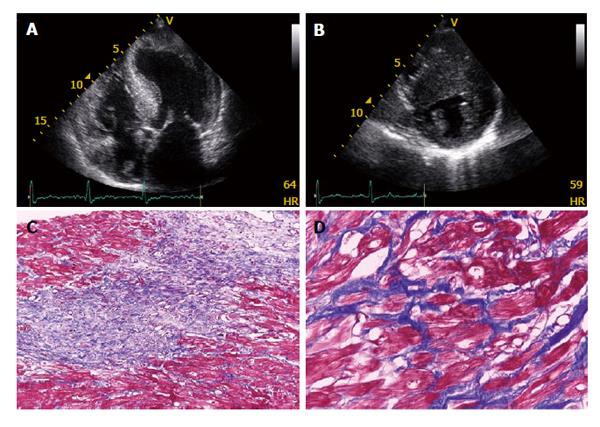
Figure 1 Echocardiographical and pathological features of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
A: An apical 4-chamber view of a patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy showing a hypertrophied, non-dilated left ventricle; B: Excessive thickness of interventricular septum (eccentric hypertrophy) is also optimally visualized from parasternal short axis views; C: Myocardial disarray and extensive fibrosis (× 10 Trichrome Masson); D: Myocardial disarray and interstitial fibrosis (× 40 Trichrome Masson).
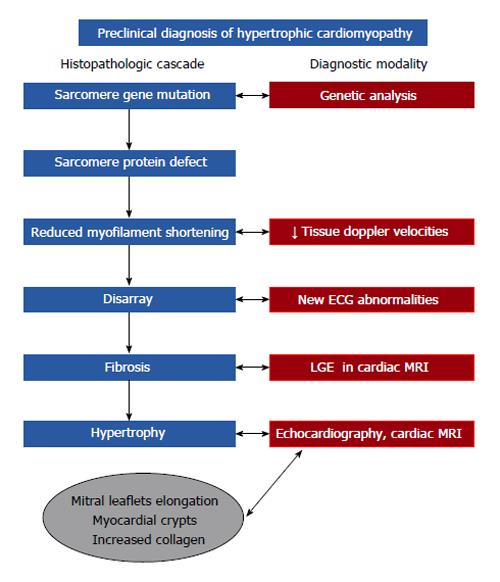
Figure 2 Preclinical diagnosis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
The figure shows histopathological cascade of the disease and diagnostic modalities used to detect abnormalities in each stage. LGE: Late gadolinium enhancement; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
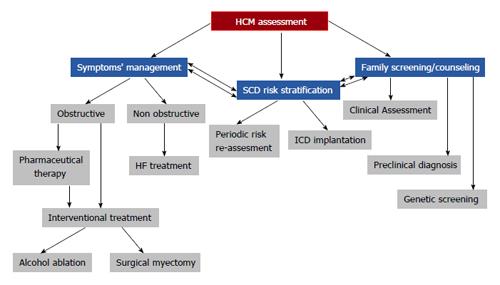
Figure 3 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy assessment algorithm.
A clinician dealing with a HCM patient should face 3 major issues: symptom management based on the existence or not of left ventricular outflow obstruction; sudden cardiac death risk stratification and prevention; and finally, family counseling and advice. HF: Heart failure; SCD: Sudden cardiac death; ICD: Implantable cardioverter defibrillator; HCM: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Citation: Efthimiadis GK, Pagourelias ED, Gossios T, Zegkos T. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in 2013: Current speculations and future perspectives. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(2): 26-37
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i2/26.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i2.26