Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Aug 26, 2025; 17(8): 107991
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i8.107991
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i8.107991
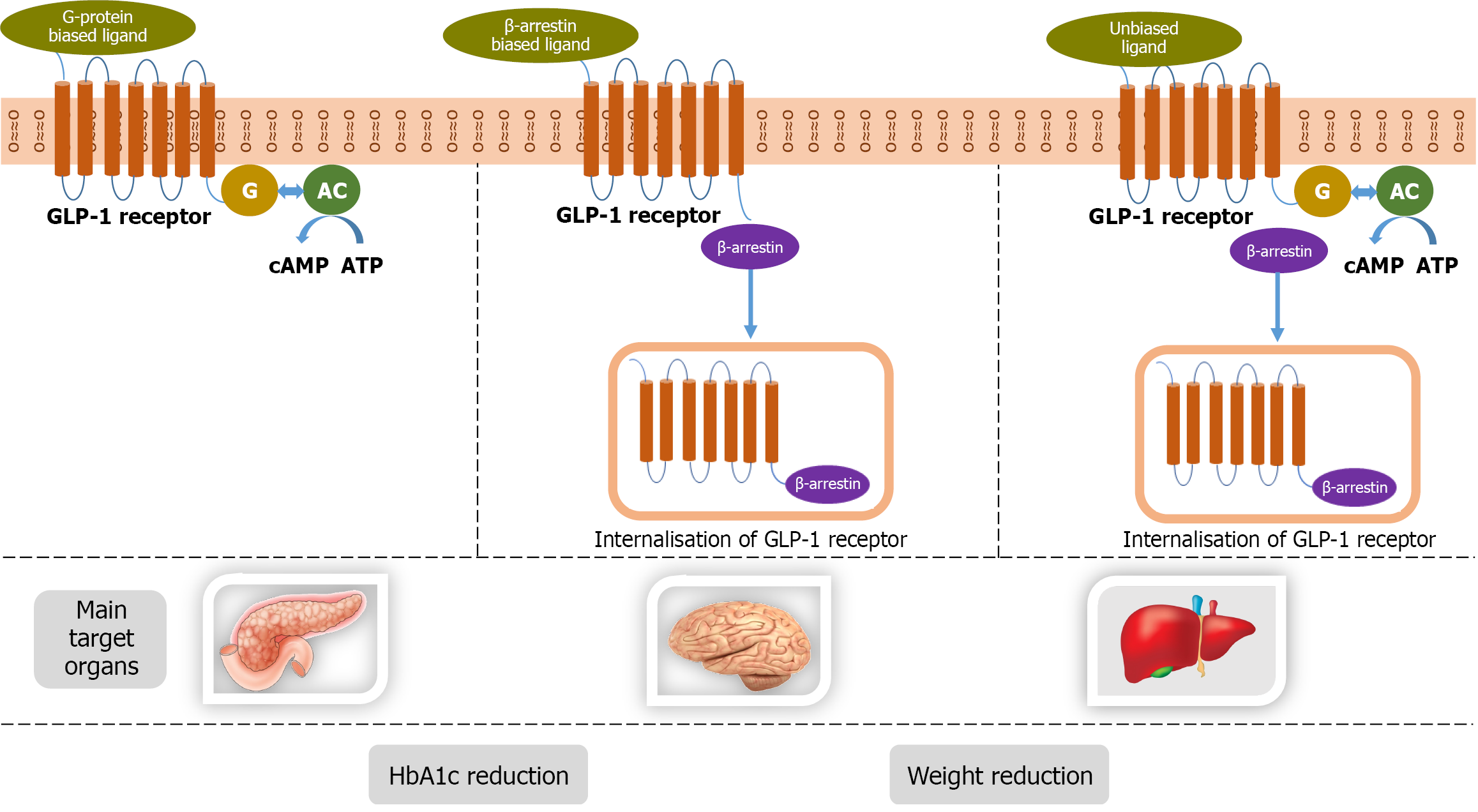
Figure 1 Elaborates the molecular aspects of the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists at cellular level.
cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; HbA1c: Glycated hemoglobin; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1.
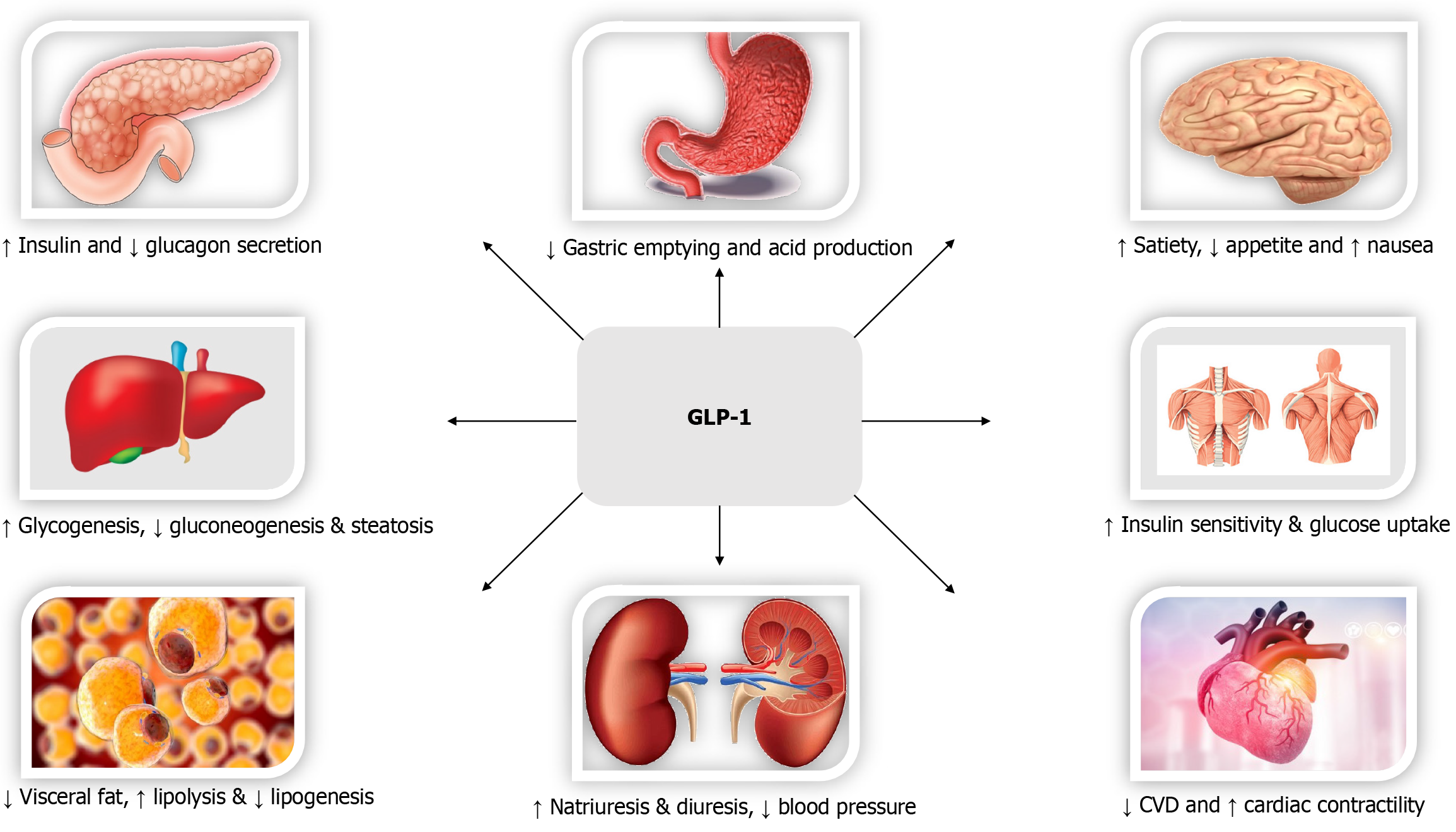
Figure 2 The biological effects and cardiometabolic benefits of glucagon-like peptide 1.
GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; CVD: Cardiovascular disease.
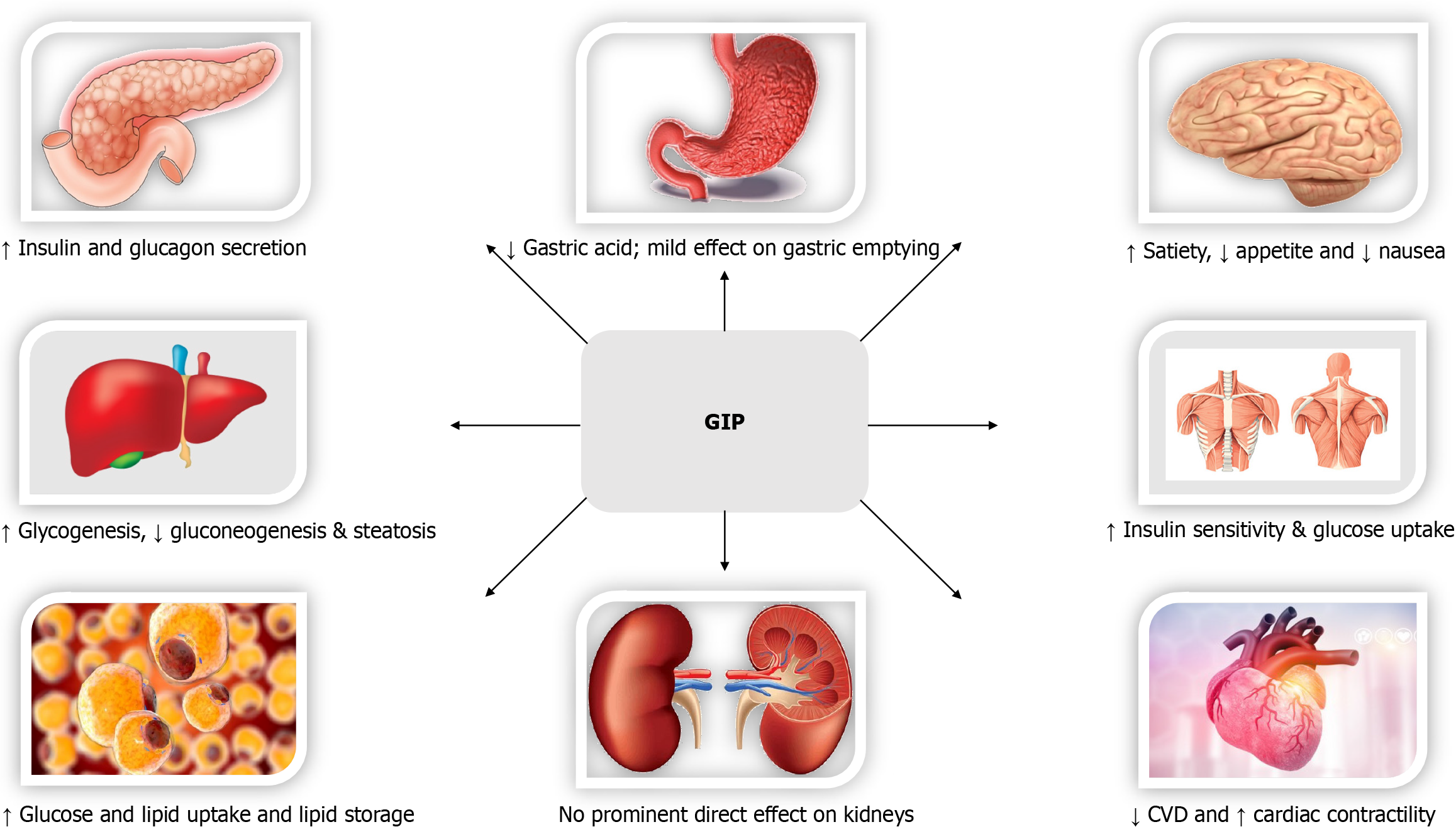
Figure 3 The biological effects and cardiometabolic benefits of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.
CVD: Cardiovascular disease; GIP: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.
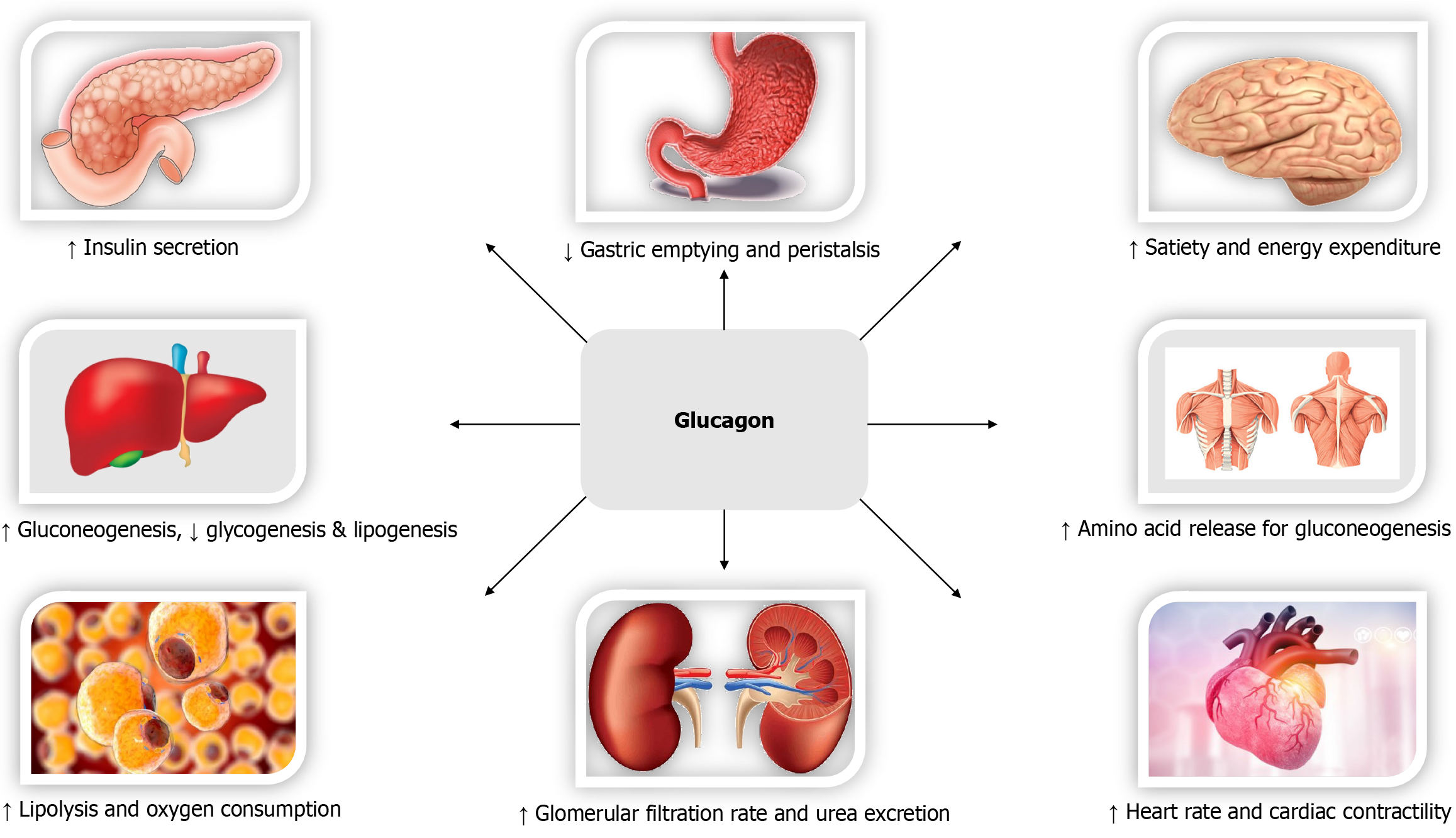
Figure 4
The biological effects and cardiometabolic benefits of glucagon.
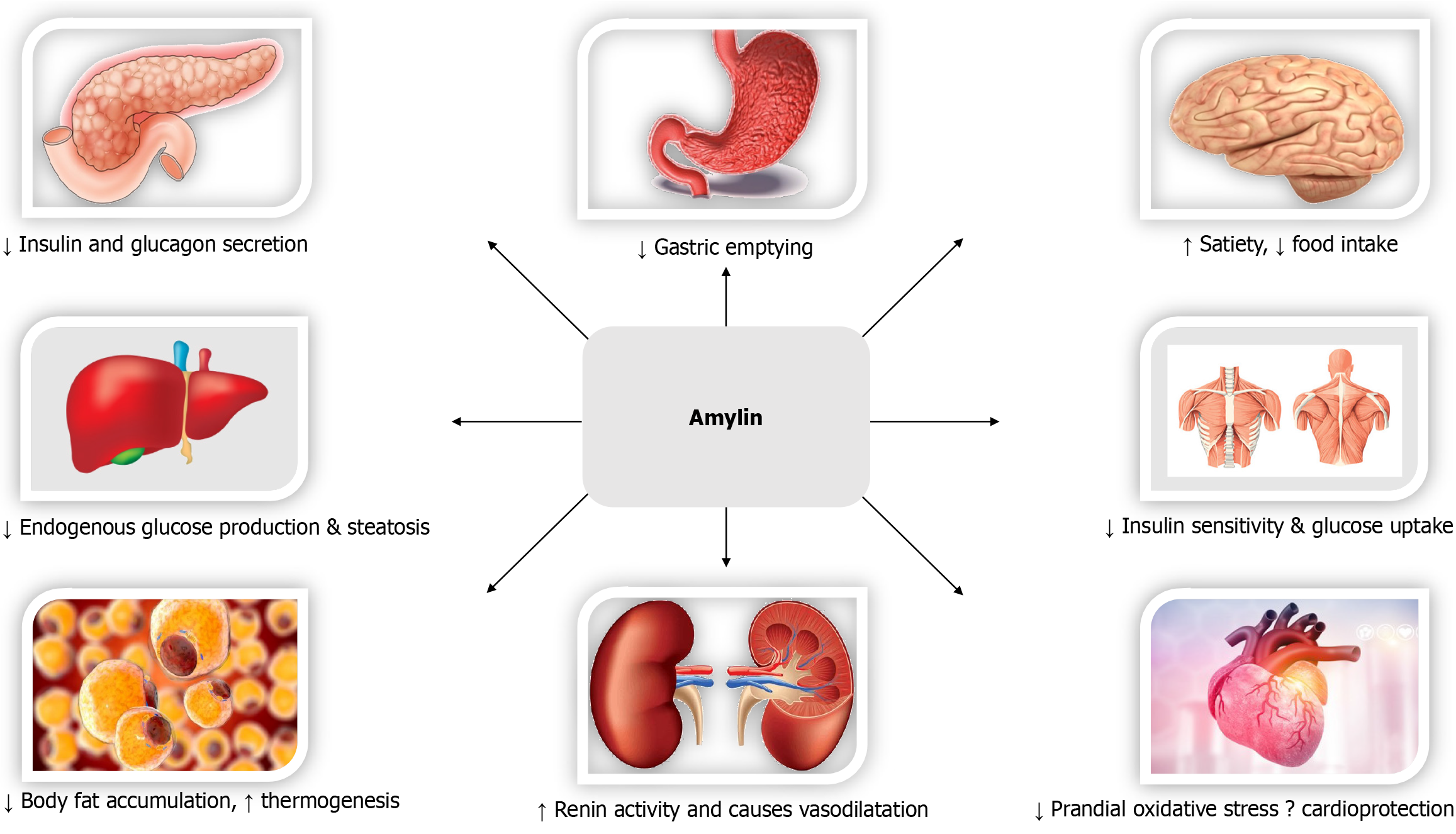
Figure 5
The biological effects and cardiometabolic benefits of amylin.
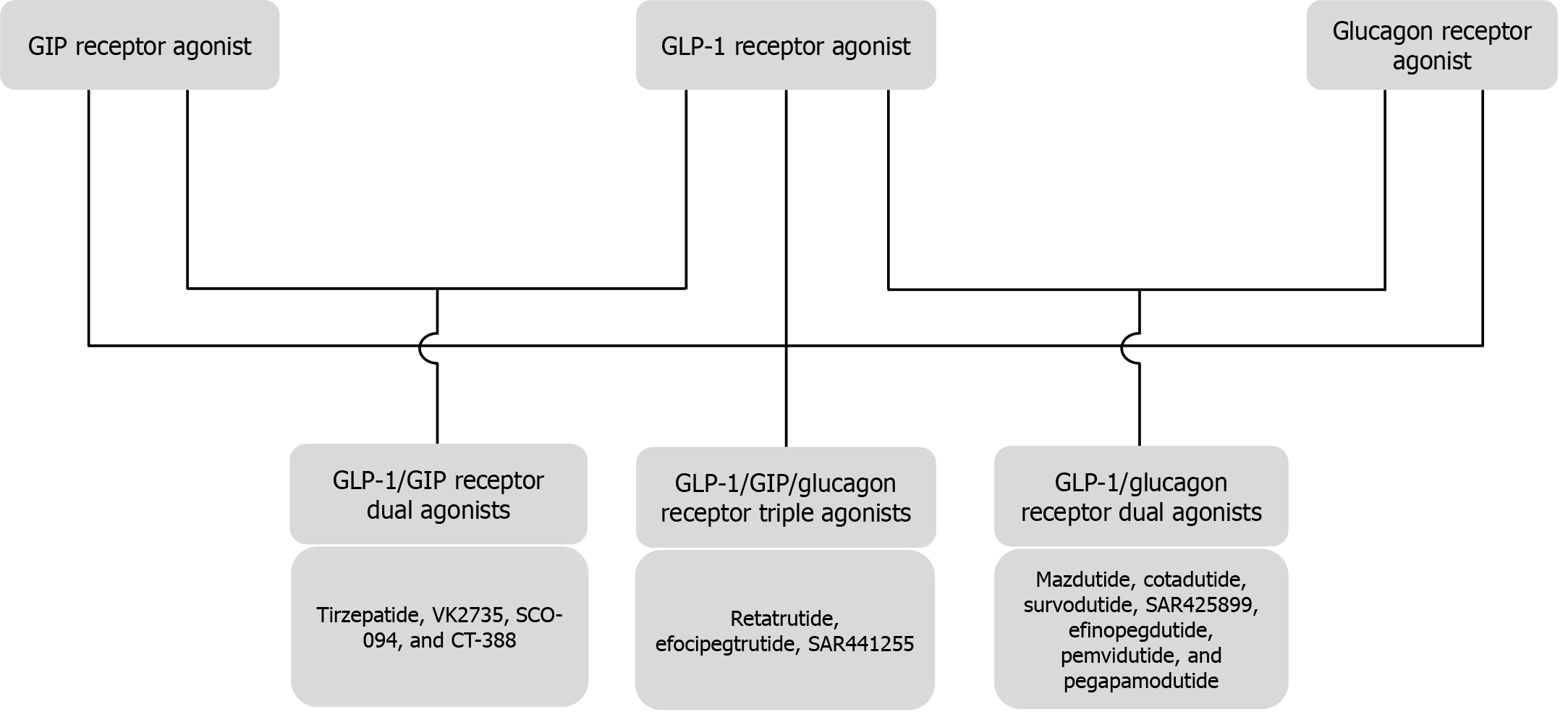
Figure 6 Flow chart showing different incretin agonists in combinations and the drug molecules in use/under development.
GIP: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1.
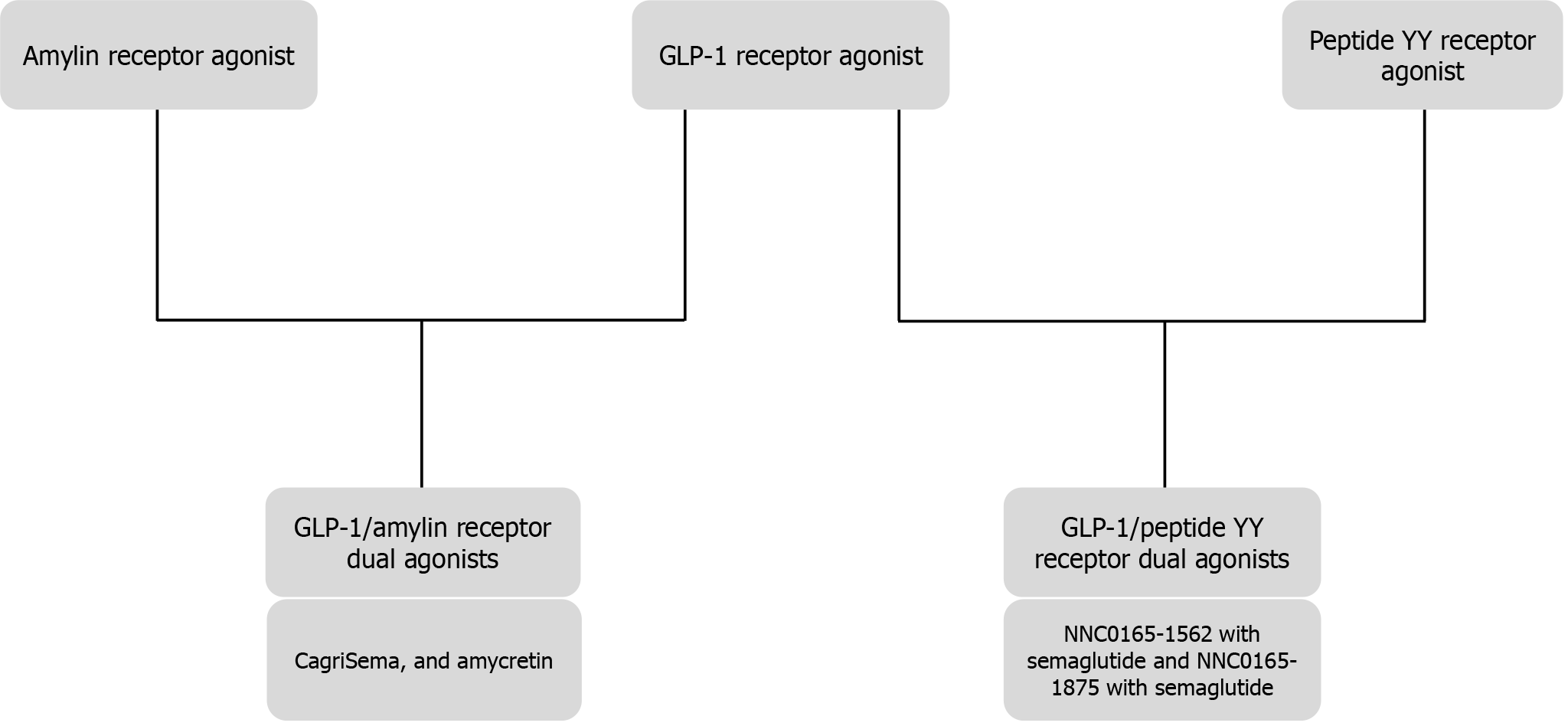
Figure 7 Flow chart showing the drug combinations of glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists with amylin receptor agonists and peptide YY agonists, the available drug molecules in use/under development.
GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1.
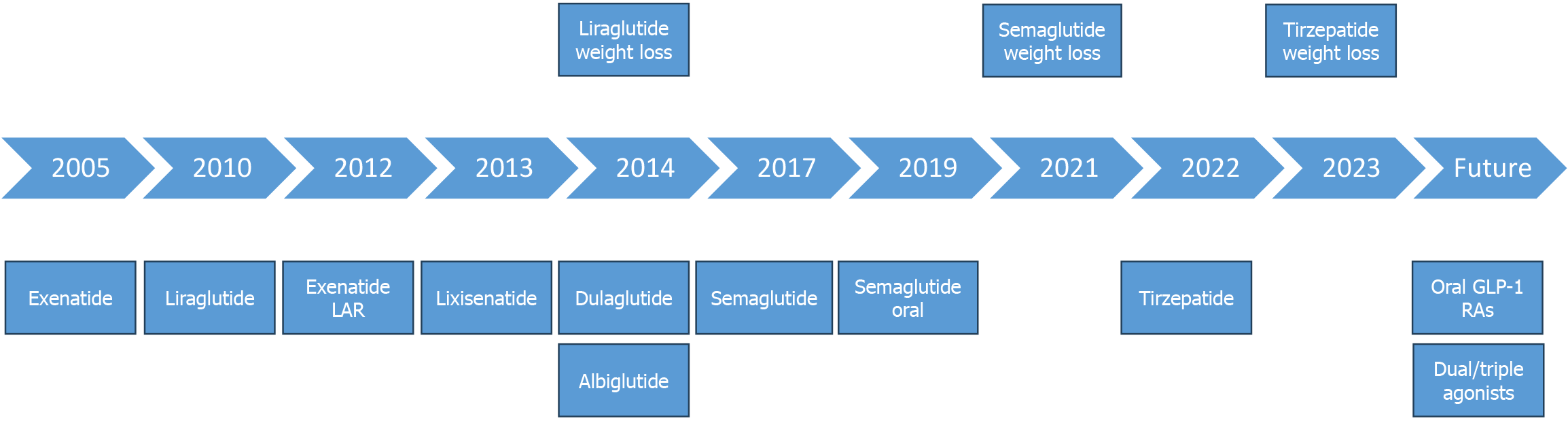
Figure 8 Stages of development of various incretin agonists.
GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; LAR: Long-acting release.
- Citation: Bhat S, Fernandez CJ, Lakshmi V, Pappachan JM. Efficacy and safety of incretin co-agonists: Transformative advances in cardiometabolic healthcare. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(8): 107991
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i8/107991.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i8.107991