Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2025; 17(6): 102722
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.102722
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.102722
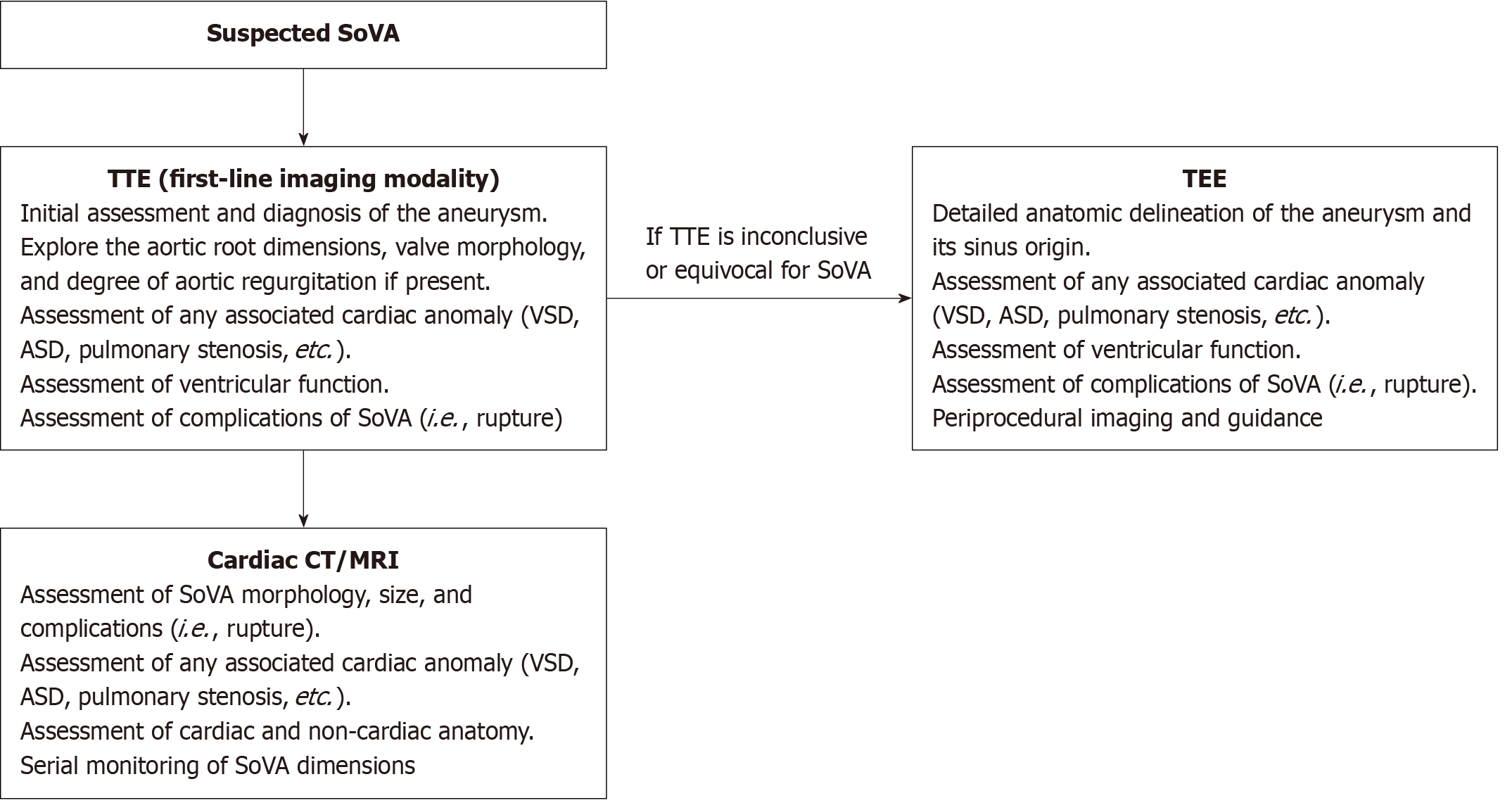
Figure 1 Proposed diagnostic algorithm for the assessment of suspected sinus of Valsalva aneurysm.
Transthoracic echocardiogram is first line, followed by transesophageal echocardiogram if findings are not diagnostic or equivocal for the aneurysm. Cardiac computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used for further assessment after confirmation of diagnosis on echocardiography. MRI has a higher temporal resolution than CT and offers excellent soft tissue contrast and anatomical delineation. As such, MRI is preferred over CT for concurrent valvular assessment and flow information. TTE: Transthoracic echocardiogram; VSD: Ventricular septal defect; ASD: Atrial septal defect; SoVA: Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm; TEE: Transesophageal echocardiogram; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: English K. Diagnosis and treatment options for sinus of Valsalva aneurysms: A narrative review. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(6): 102722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i6/102722.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.102722