Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2015; 6(4): 409-418
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.409
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.409
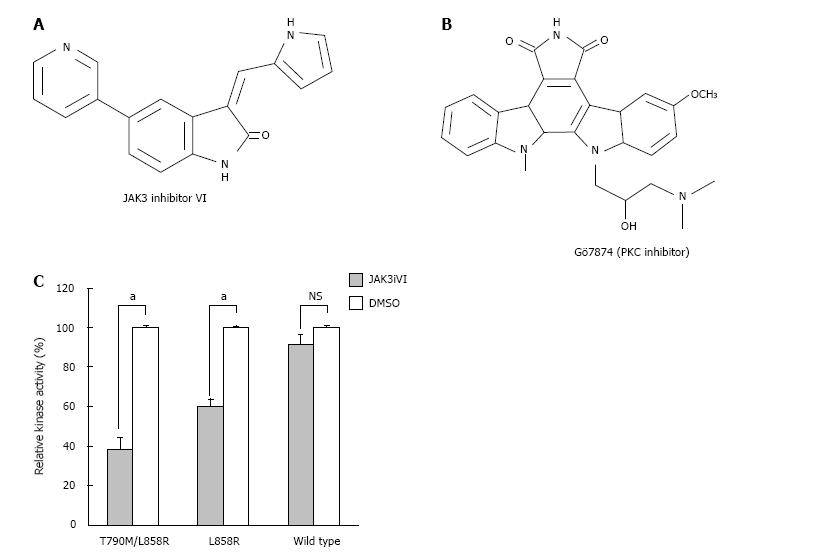
Figure 1 Janus kinase 3 inhibitor VI selectively inhibits kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor gatekeeper mutant T790M/L858R in vitro.
A, B: Chemical structures of JAK3 inhibitor VI (A) and Gö7874 (B) are shown; C: Effects of JAK3 inhibitor VI on kinase activities of WT, L858R, and T790M/L858R EGFRs were compared. Recombinant EGFR kinase domains were treated using JAK3 inhibitor VI at 10 μmol/L, and phosphorylation was initiated by adding ATP in the presence of an artificial substrate peptide. Phosphorylation levels were measured by ELISA using an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 4); aP < 0.05. NS: Not significant; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; JAK3: Janus kinase 3.
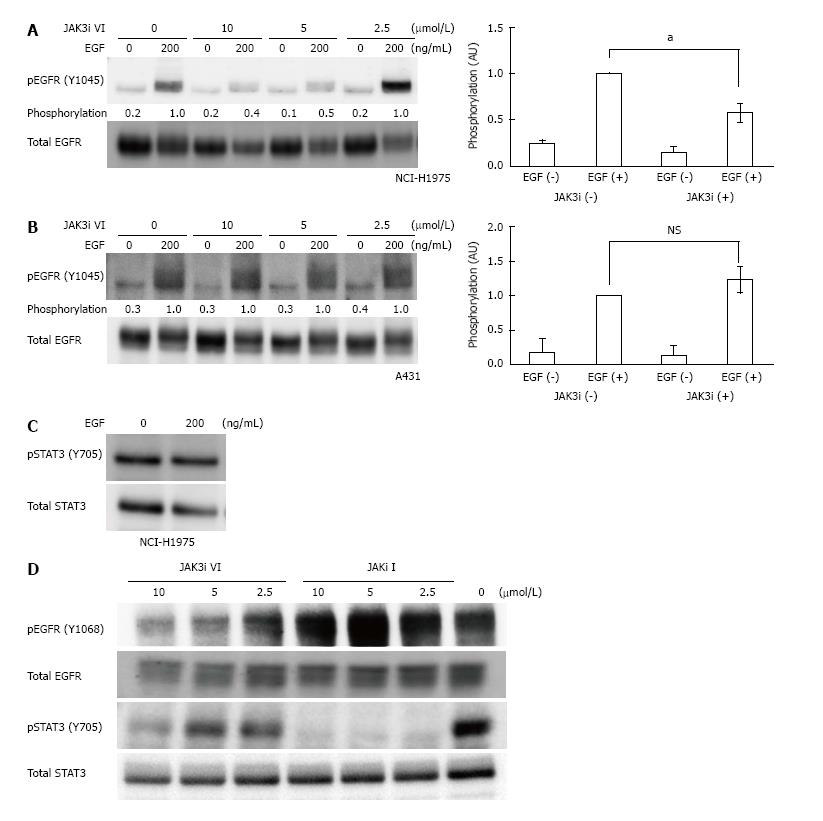
Figure 2 Janus kinase 3 inhibitor VI reduces epidermal growth factor receptor autophosphorylation in NCI-H1975 cells harboring epidermal growth factor receptor T790M/L858R.
A-B: NCI-H1975 (A) or A431 (B) cells were treated with the indicated concentration of JAK3 inhibitor VI and were stimulated using 200 ng/mL EGF. Phosphorylation levels of EGFR Y1045 were analyzed using Western blotting. Phosphorylation levels of EGFR were normalized against total EGFR levels. Relative phosphorylation levels to the sample treated with DMSO and 200 ng/mL EGF are indicated. Right panels show the averages of relative phosphorylation levels from three independent experiments; C: NCI-H1975 cells were stimulated using 200 ng/mL EGF. Phosphorylation levels of STAT3 Y705 were analyzed using Western blotting; D: NCI-H1975 cells were treated using JAK3 inhibitor VI or JAK inhibitor I, as indicated. Phosphorylation levels of EGFR Y1068 and STAT3 Y705 were analyzed using Western blotting with phospho-specific antibodies. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 3); aP < 0.05. NS: Not significant; EGF (-): 0 ng/mL EGF; EGF (+): 200 ng/mL EGF; JAK3i (-): 0 μmol/L JAK3 inhibitor VI; JAK3i (+): 10 μmol/L JAK3 inhibitor VI; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; JAK3: Janus kinase 3.
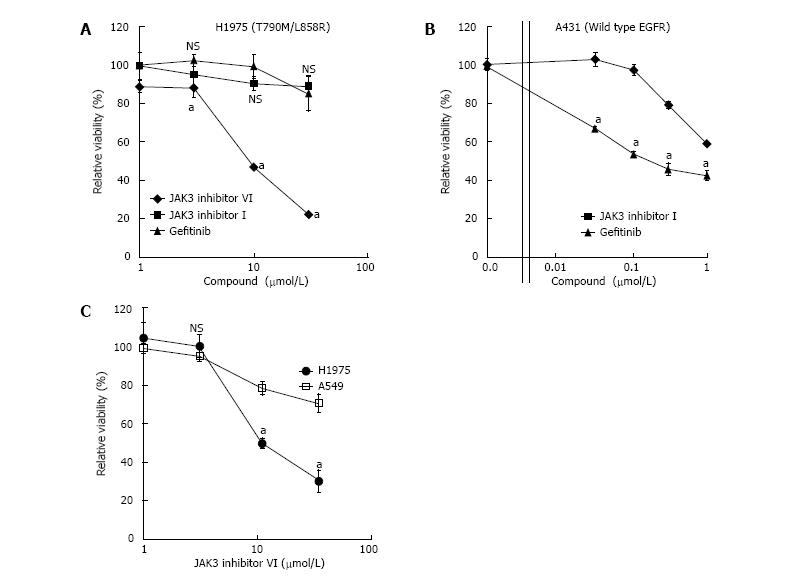
Figure 3 Janus kinase 3 inhibitor VI suppresses proliferation of NCI-H1975 cells.
A, B: NCI-H1975 (A) or A431 (B) cells were treated with JAK3 inhibitor VI, JAK inhibitor I, or gefitinib. Effects of indicated concentration of kinase inhibitors on cell proliferation were analyzed using the MTT assay; C: Effects of JAK3 inhibitor VI on proliferation were compared between NCI-H1975 and A549 cells using the MTT assay. Error bars indicate S.E.M. (n = at least 3); aP < 0.05. NS: Not significant; JAK3: Janus kinase 3; MTT: 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide.
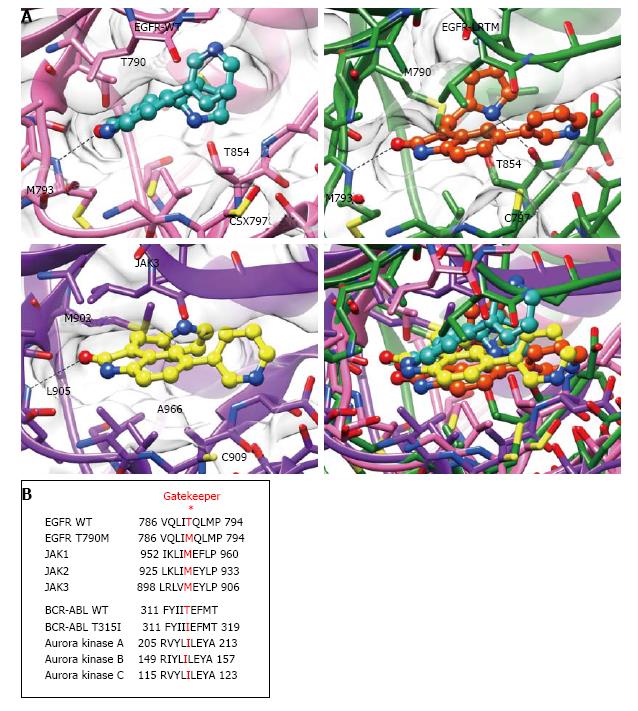
Figure 4 Structural analysis of janus kinase 3 inhibitor VI binding to the epidermal growth factor receptor T790M.
A: JAK3 inhibitor VI (cyan in EGFR WT: top left, red in EGFR T790M/L858R: top right, or yellow in JAK3: bottom left) was modeled into EGFR WT, EGFR T790M/L858R (LRTM), or JAK3. A superimposed image is also shown (bottom right). The dotted lines indicate putative hydrogen bonds; B: Amino acid sequence alignments of EGFRs and JAKs, and BCR-ABL and Aurora kinases. Asterisk indicates the gatekeeper residues. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; JAK: Janus kinase; WT: Wild type.
- Citation: Nishiya N, Sakamoto Y, Oku Y, Nonaka T, Uehara Y. JAK3 inhibitor VI is a mutant specific inhibitor for epidermal growth factor receptor with the gatekeeper mutation T790M. World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(4): 409-418
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i4/409.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.409