Published online Mar 27, 2013. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v5.i3.47
Revised: December 12, 2012
Accepted: January 23, 2013
Published online: March 27, 2013
Processing time: 259 Days and 13.9 Hours
Duodenal diverticula (DD) are frequently encountered and are usually asymptomatic, with an incidence at autopsy of 22%. Perforation of DD is a rare complication (around 160 cases reported) with potentially dramatic consequences. However, little evidence regarding its treatment is available in the literature. The aim of this study was to review our experience of perforated DD, with a focus on surgical management. Between January 2001 and June 2011, all perforated DD were retrospectively reviewed at a single centre. Seven cases (5 women and 2 men; median age: 72.4 years old, rang: 48-91 years) were found. The median American Society of Anesthesiologists’ score in this population was 3 (range: 3-4). The perforation was located in the second portion of duodenum (D2) in six patients and in the third portion (D3) in one patient. Six of these patients were treated surgically: five patients underwent DD resection with direct closure and one was treated by surgical drainage and laparostomy. One patient was treated conservatively. One patient died and one patient presented a leak that was successfully treated conservatively. The median hospital stay was 21.1 d (range: 15-30 d). Perforated DD is an uncommon presentation of a common pathology. Diverticular excision with direct closure seems to offer the best chance of survival and was associated with a low morbidity, even in fragile patients.
- Citation: Rossetti A, Buchs NC, Bucher P, Dominguez S, Morel P. Perforated duodenal diverticulum, a rare complication of a common pathology: A seven-patient case series. World J Gastrointest Surg 2013; 5(3): 47-50
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v5/i3/47.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v5.i3.47
Duodenal diverticulum (DD) is common, with a reported prevalence of 22% at autopsy[1]. A similar incidence has been reported during endoscopicretrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)[2,3]. The most frequent location is the second and third portions of the duodenum (D2-D3)[4].
Although, DD is rarely symptomatic and only 5% of patients present with symptoms due to the compression of neighbouring organs, cholestasis (in cases of periampullary diverticulum), haemorrhage, inflammation or perforation[4]. One hundred and sixty-two cases of perforated DD have been reported in the literature[5-8]. The supposed cause of perforation in 57% of cases is ischaemic processes due to distension related to food retention in the diverticula[9]. Other reported causes are ulcerations, enterocolitihs, blunt abdominal trauma and perforation due to the ERCP procedure[5,9-12].
However, diagnosis remains a challenge, with many potential differential diagnoses, including perforated duodenal ulcer. Helical computed tomography (CT) has emerged as a useful diagnostic tool and most centers now use CT routinely to confirm the diagnosis. Yet surgical exploration in unstable and septic patients is still considered mandatory, especially if the diagnosis is not clear[13,14].
The appropriate surgical management remains under debate. A surgical approach is usually advocated. However, some groups[5,14,15] have reported using a more conservative approach, and demonstrated that non-operative management is a safe and practical alternative to surgery in selected patients. The aim of this study was to review our 11-year experience with perforated DD at a single centre with a special focus on surgical management.
Between January 2001 and June 2011, all perforated DD were retrospectively reviewed at a single center. Only non-traumatic cases were included. Iatrogenic perforations (e.g. during endoscopy) were excluded from the study. For all the analyzed patients a CT-scan was performed at the admission. Seven cases (five women and two men; median age: 72.4 years old, range: 48-91 years) were found. The median American Society of Anesthesiologists’ (ASA) score in this population was 3 (range: 3-4). Six cases were treated surgically and one with a naso-gastric tube and antibiotics (Taylor’s approach for upper digestive perforation).
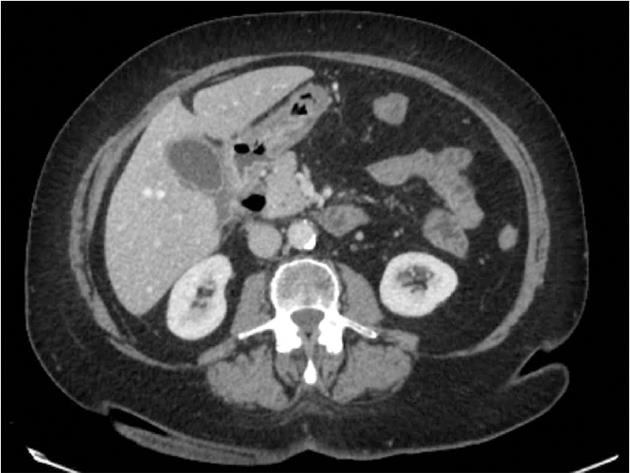
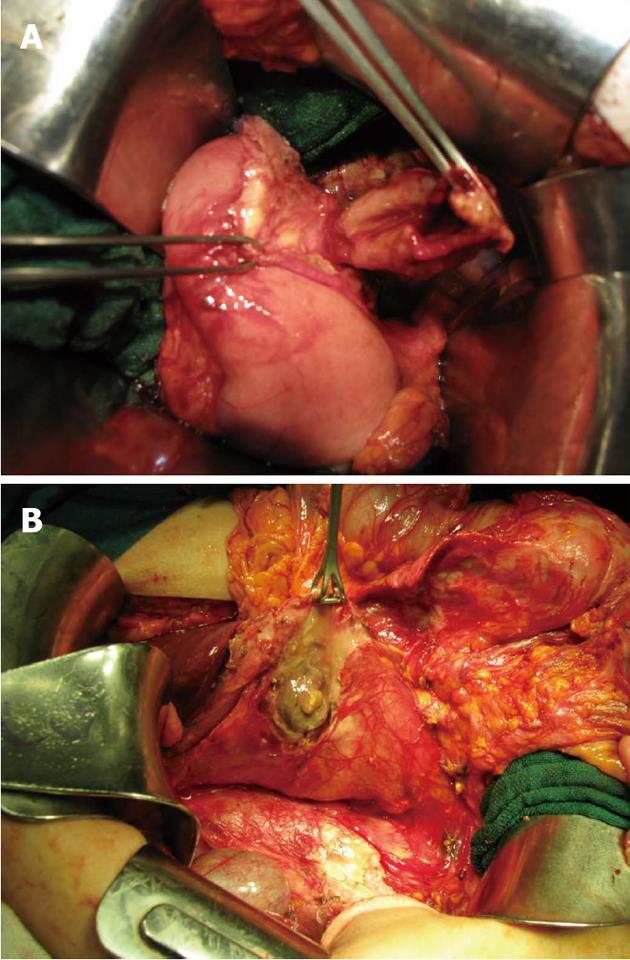
We report herein a series of seven cases of spontaneous DD perforation (Table 1). The clinical presentation was abdominal pain in six cases and bilateral basithoracic pain in one case. Of note, only one patient was admitted with severe septic shock. All the patients presented elevated leucocyte count and C-reactive protein. Diagnosis was performed by CT scans in 42.8% (3 out of 7) of the cases (Figure 1). Diagnosis of the other cases was made intra-operatively. Six patients underwent surgery (85.7%). Of these, five cases had an ASA score of 3 and one an ASA score of 4. The perforated DD was located at the D2 level in six cases (85.7%) (Figure 2A and B) and at the D3 level in one case. All the patients received endovenous antibiotics therapy for 10 d (ceftriaxone and metronidazole). In five cases surgical treatment (Table 2) involved resection of the DD and direct duodenal suture. A nutritional jejunostomy was also performed in three cases.
| Case | Age (yr) | ASA | Symptoms | Shock | Diagnosis | Perforation localization | Follow-up |
| 1 | 91 | 3 | RUQ acute pain, nausea and vomiting | No | Surgery | D2 | Alive at present after 12 yr |
| 2 | 68 | 4 | Epigastria acute pain, septic shock | Yes | Surgery | D2 | Died |
| 3 | 83 | 3 | RUQ acute pain, nausea and vomiting | No | CT scan | D2 | Lost after 5 yr of follow-up |
| 4 | 78 | 3 | Epigastria acute pain, nausea and vomiting | No | Surgery | D2 | Lost after 5 yr of follow-up |
| 5 | 76 | 3 | Bilateral basithoracic pain | No | CT scan | D2 | Lost after 9 yr of follow-up |
| 6 | 65 | 3 | Epigastria and RUQ acute pain, nausea and vomiting | No | Surgery | D2 | Alive after 1 yr of follow-up |
| 7 | 48 | 3 | RUQ pain irradiating to the back | No | CT scan | D3 | Alive after 2 yr of follow-up |
| Case | Localization | Treatment | Morbidity-mortality | Hospital stay (d) |
| 1 | D2 | Excision, direct duodenal suture and nutritional jejunostomy | 26 | |
| 2 | D2 | Drain and laparostomy | Died (cardiac comorbidity) | 1 |
| 3 | D2 | Excision, direct duodenal suture and nutritional jejunostomy | 18 | |
| 4 | D2 | Excision and direct duodenal suture | Conservatively treated suture leak on POD day 5 | 30 |
| 5 | D2 | Gastric tube and antibiotics therapy | 16 | |
| 6 | D2 | Excision and direct duodenal suture | 15 | |
| 7 | D3 | Excision, direct duodenal suture, nutritional jejunostomy and bilio-duodenal drain | 22 |
A transpapillary bilio-duodenal drain was used in the patient with a D3 perforation due to the proximity of Vater’s papilla. Only one patient presented with septic shock, and at laparotomy, a damage control approach was chosen (drainage and laparostomy) given the instability of the patient, and the important bowel edema that did not allowed to close the abdominal wall.
The non-surgically treated case was treated with antibiotics and a naso-gastric tube because presented with only bilateral basithoracic pain, and a diagnosis of a cover DD perforation was performed on CT scan. An image control (Upper passage opacification Rx with gastrographine®) was performed after 7 d after the oral intake. In terms of outcome, a suture leak occurred in one patient at post-operative day-5; this leak did not require surgery and was conservatively treated with success (nasogastric tube and endovenous antibiotics). One patient died (mortality: 14.3%) after a cardiac complication-cardiac failure. This patient was admitted in a critical condition with severe septic shock and the preferred surgical treatment was damage control surgery. Oral intake was restored for all the patients on average seven days after the operation. The median hospital stay was 21.1 d (range: 15-30 d). No long-term complications were detected (median follow-up of 63 mo).
Perforation is an uncommon complication of DD and also one of the most serious[16]. In this paper, we present one of the largest series (seven patients) published to date. The overall outcomes are encouraging, with a low mortality rate and acceptable morbidity. In fact, the most recent review reported rates of morbidity and mortality of 33% and 8%-34% respectively[5]. Our results compare favorably with these data.
Although well known as a possible complication of DD, few reports of perforation can be found in the literature. In fact, Thorson et al[5] recently reviewed the available literature and found only 162 cases. The leitmotif remains a difficult preoperative diagnosis. Indeed, the symptoms are often non specific and vague. Yet, one of the most frequent patterns of presentation seems to be right upper abdominal pain associated with nausea and vomiting, as found in our series. Moreover, the differential diagnosis is wide and can be confusing. The most difficult differential diagnosis is a perforated duodenal ulcer, which can show the same pattern in the clinic and on CT scan. Since the wide diffusion of CT, the preoperative diagnosis of perforated DD has increased, and this is currently the best imaging modality available. Although the final diagnosis is often made in the operating room, CT is undeniably helpful and can sometimes differentiate perforated DD from a perforated duodenal ulcer. In addition, perforation may cause retroperitoneal abscesses[16,17]. However, we did not find extended abscesses of the retroperitoneal area in our case series, probably thanks to the early performance of CT scans (maximum delay of 6 h). Therefore, CT is usually the first diagnostic procedure to be performed even though its specificity is below 100%.
In terms of the location of the perforation, the second and third duodenal portions are involved in most cases[5,14], as observed in our series. As a corollary to its rarity, the management of perforated DD remains subject to debate. No surgical guidelines have been published for perforated DD, as only case reports and small series (up to 8 patients) have been reported in the literature[5,16,17]. In general, the surgical approach was considered the treatment of choice. However, several recent cases were treated with bowel rest, a naso-gastric tube and antibiotics, with encouraging results in selected patients[5,15]. If a surgical intervention is highly indicated for unstable patients, the conservative approach deserves consideration since its use appears to be attractive in more stable patients. This option may be particularly useful in a patient of advanced age or in a patient with multiple medical comorbidities who is a prohibitive operative risk[14]. On the other hand, in a patient with mild abdominal symptoms and no evidence of impending sepsis, non-operative management may suffice[14]. Taylor’s approach is widely and successfully used for upper digestive perforation and perforated DD could be treated using the same technique. In the present series, the only patient who underwent conservative treatment was selected for such treatment because he presented with mild symptoms and a clear diagnosis was possible preoperatively. Therefore, in selected patients with a precise CT-scan diagnosis and good clinical condition, conservative treatment can be considered.
In terms of surgical approach, several technical options are available, ranging from local excision to the Whipple procedure, depending on the location of the DD and the inflammatory status[18]. Moreover, laparoscopic diverticulectomy has also been reported to give good results[19]. In their recent review, Thorson et al[5] found diverticulectomy to be the most common treatment (49%). In our series, five patients were surgically treated with an almost identical procedure: excision of the DD and direct suture, with a drain placed in the resection area.
Nutritional jejunostomy was performed in three of the five cases and a naso-gastric tube was left in place for at least 7 d. Of note, in one case, a transcystic biliary drain was necessary due to the location of the perforated periampullary DD. This was introduced in order to prevent biliary stenosis in relation to the duodenal suture. Perforation of a DD is a very serious complication and may be fatal. Early CT scan is recommended for diagnosis in suspected cases. Our therapeutic strategy for a perforated DD is resection of the diverticula and direct suture when possible, associated with drainage and placement of a nutritional jejunostomy. A conservative approach is attractive in selected patients.
P- Reviewers Martinez-Cecilia D, Yen HH S- Editor Zhai HH L- Editor A E- Editor Xiong L
| 1. | Ackermann W. Diverticula and variations of the duodenum. Ann Surg. 1943;117:403-413. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Leivonen MK, Halttunen JA, Kivilaakso EO. Duodenal diverticulum at endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, analysis of 123 patients. Hepatogastroenterology. 1996;43:961-966. [PubMed] |
| 3. | Suda K, Mizuguchi K, Matsumoto M. A histopathological study on the etiology of duodenal diverticulum related to the fusion of the pancreatic anlage. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983;78:335-338. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Thorson CM, Paz Ruiz PS, Roeder RA, Sleeman D, Casillas VJ. The perforated duodenal diverticulum. Arch Surg. 2012;147:81-88. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Umbricht-Sprüngli RE, Hollinger A, Meier L, Largiadèr F. [Complications of diverticuli of the proximal small intestine. 3 case reports and review of the literature]. Chirurg. 1992;63:568-571. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Papalambros E, Felekouras E, Sigala F, Kiriakopoulos A, Giannopoulos A, Aessopos A, Bastounis E, Mirilas P, Hepp W. Retroperitoneal perforation of a duodenal diverticulum with colonic necrosis -- report of a case. Zentralbl Chir. 2005;130:270-273. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | JONES TW, MERENDINO KA. The perplexing duodenal diverticulum. Surgery. 1960;48:1068-1084. [PubMed] |
| 9. | Duarte B, Nagy KK, Cintron J. Perforated duodenal diverticulum. Br J Surg. 1992;79:877-881. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Franzen D, Gürtler T, Metzger U. [Solitary duodenal diverticulum with enterolith as a rare cause of acute abdomen]. Swiss Surg. 2002;8:277-279. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Poostizadeh A, Gow KW, Al-Mahmeed T, Allardyce DB. Traumatic perforation of duodenal diverticulum. J Trauma. 1997;43:370-371. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Elder J, Stevenson G. Delayed perforation of a duodenal diverticulum by a biliary endoprosthesis. Can Assoc Radiol J. 1993;44:45-48. [PubMed] |
| 13. | Oddo F, Chevallier P, Souci J, Baque J, Buckley MJ, Fabiani P, Diaine B, Coussement A. [Radiologic aspects of the complications of duodenal diverticula]. J Radiol. 1999;80:134-140. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Miller G, Mueller C, Yim D, Macari M, Liang H, Marcus S, Shamamian P. Perforated duodenal diverticulitis: a report of three cases. Dig Surg. 2005;22:198-202. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Ames JT, Federle MP, Pealer KM. Perforated duodenal diverticulum: clinical and imaging findings in eight patients. Abdom Imaging. 2009;34:135-139. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Lobo DN, Balfour TW, Iftikhar SY, Rowlands BJ. Periampullary diverticula and pancreaticobiliary disease. Br J Surg. 1999;86:588-597. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 97] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Andromanakos N, Filippou D, Skandalakis P, Kouraklis G, Kostakis A. An extended retroperitoneal abscess caused by duodenal diverticulum perforation: report of a case and short review of the literature. Am Surg. 2007;73:85-88. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Schnueriger B, Vorburger SA, Banz VM, Schoepfer AM, Candinas D. Diagnosis and management of the symptomatic duodenal diverticulum: a case series and a short review of the literature. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12:1571-1576. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Kijima T, Masuda H, Yoshida S, Tatokoro M, Yokoyama M, Numao N, Saito K, Koga F, Fujii Y, Kihara K. Antimicrobial prophylaxis is not necessary in clean category minimally invasive surgery for renal and adrenal tumors: a prospective study of 373 consecutive patients. Urology. 2012;80:570-575. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |