Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2017; 8(2): 56-65
Published online Feb 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i2.56
Published online Feb 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i2.56
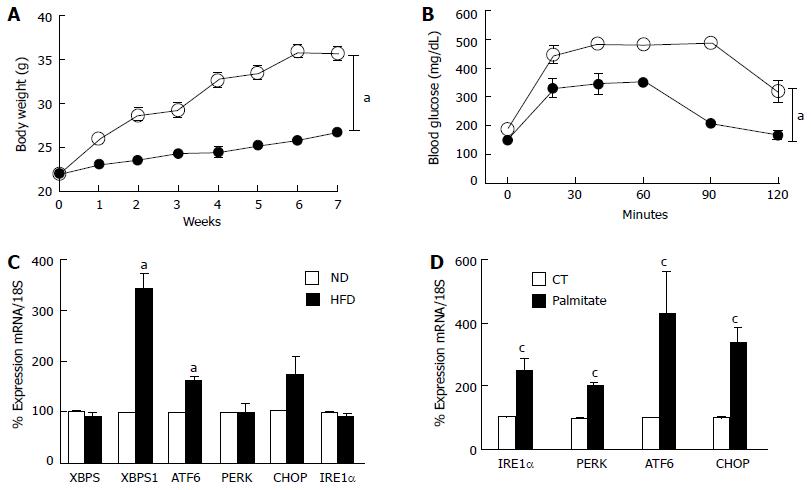
Figure 1 High fat diet/palmitate triggered endoplasmic-reticulum-stress markers in retina and Müller cells.
A: Total body weight (grams) recorded weekly was significantly higher in mice fed with HFD for 8 wk compared to ND; B: Glucose tolerance was impaired after 8 wk of HFD compared to ND; C: Realtime PCR showing increases in mRNA levels of XBP1S and ATF6, while no change in XBP1, PERK, CHOP and IRE1α mRNA in retina after 8 wk of HFD compared to ND; D: Realtime PCR showing significant increases in IRE1α, PERK, ATF6 and CHOP mRNA levels in rMC1 treated with palmitate compared to control (CT) (aP < 0.05 vs ND, n = 3-4 and cP < 0.05 vs CT, area under the curve across all the time points was calculated, n = 3-4). HFD: High fat diet; PERK: Protein Kinase RNA-like endoplasmic-reticulum kinase; XBP: Xbox binding protein; ATF6: Activating transcription factor 6; CHOP: CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein; IRE1: Inositol requiring enzyme 1.
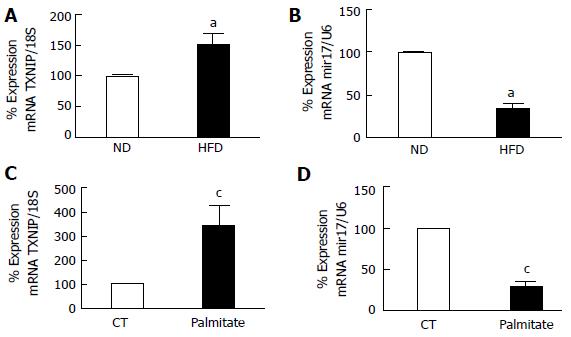
Figure 2 Realtime polymerase chain reaction.
It shows significant (A) increase in TXNIP mRNA and (B) miR-17-5p dysregulation in retina after 8 wk of HFD compared to ND. Realtime PCR showing significant (C) increase in TXNIP mRNA levels (D) reduction in miR-17-5p in rMC1 treated with palmitate compared to control (CT) (aP < 0.05 vs ND, n = 3-4 and cP < 0.05 vs CT, n = 3). ND: Normal diet; HFD: High fat diet.
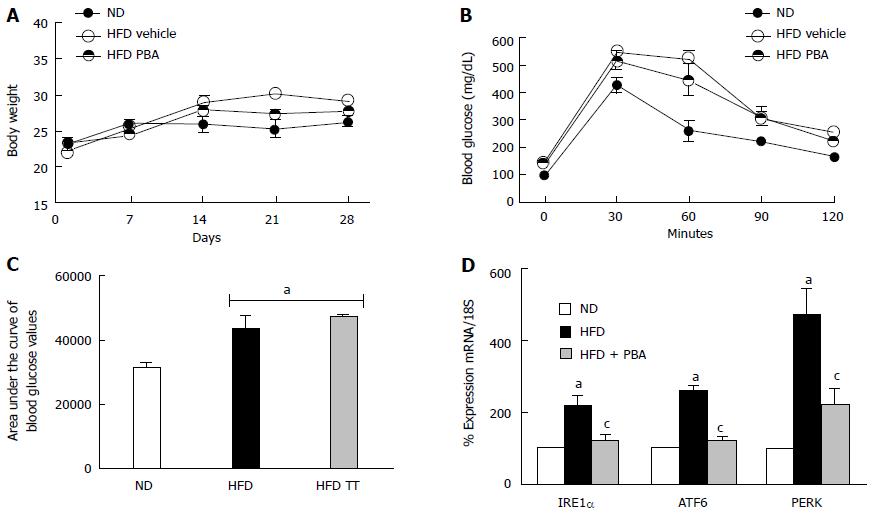
Figure 3 PBA mitigated high fat diet-mediated endoplasmic-reticulum-stress.
A: Total body weight (g) recorded weekly for 4 wk was not changed among the different groups; B: Glucose tolerance was impaired after 4 wk of HFD compared to ND, and was not restored with PBA treatment; C: Statistical analysis of area under the curve showing an increase in blood glucose levels in HFD compared to ND, which was not reversed by the treatment; D: Realtime PCR showing significant increases in IRE1α, ATF6, and PERK mRNA levels in mice kept on HFD for 4 wk compared to ND, which were nullified with PBA treatment (aP < 0.05 vs ND, cP < 0.05 vs HFD, n = 3-4). ND: Normal diet; HFD: High fat diet; PBA: Phenyl-butyric acid; PERK: Protein Kinase RNA-like endoplasmic-reticulum kinase; IRE: Inositol requiring enzyme.
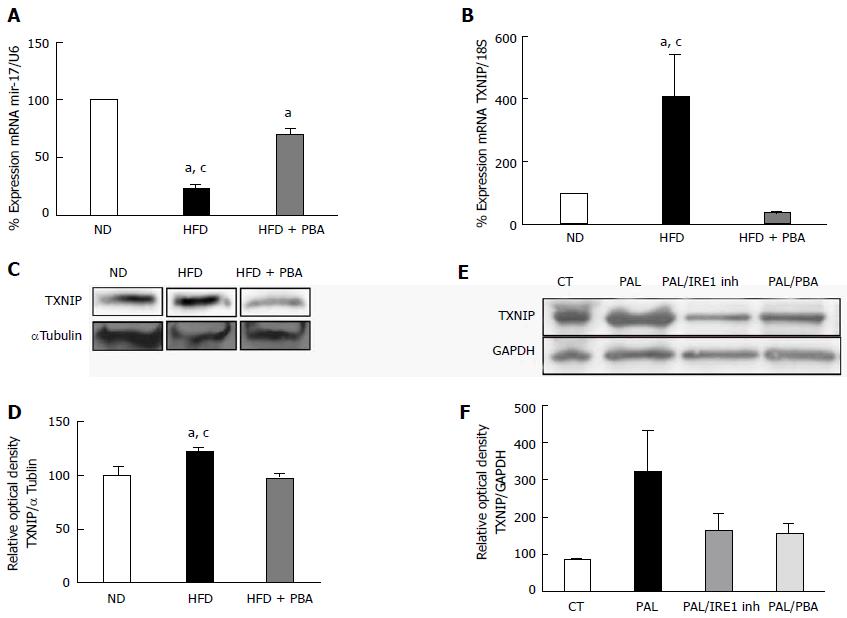
Figure 4 Dysregulation of realtime polymerase chain reaction.
It shows significant (A) reduction in miR-17-5p and (B) increase in TXNIP mRNA levels in mice kept on HFD for 4 wk compared to ND, which were reversed with PBA treatment (n = 3-4); C: Representative western blot were cut from the same membrane for TXNIP and αtubulin from retina (D) Statistical analysis showed an upregulation in TXNIP expression in HFD mice compared to ND, PBA treatment nullified this effect (n = 4-5) (aP < 0.05 vs ND, cP < 0.05 vs HFD + PBA) (E) Representative western blot of TXNIP and GAPDH from rMC1 treated with palmitate (pal), after the addition of IRE inhibitor or PBA; D: Statistical analysis showed a trend increase in TXNIP expression, which is reversed by IRE inhibitor or PBA (P = 0.076, n = 3). HFD: High fat diet; ND: Normal diet; PBA: Phenyl-butyric acid; TXNIP: Thioredoxin-interacting protein; CT: Control; PAL: Palmitate; PAL/IRE1: Palmitate + inositol requiring enzyme 1; PAL/PBA: Palmitate + phenyl-butyric acid.
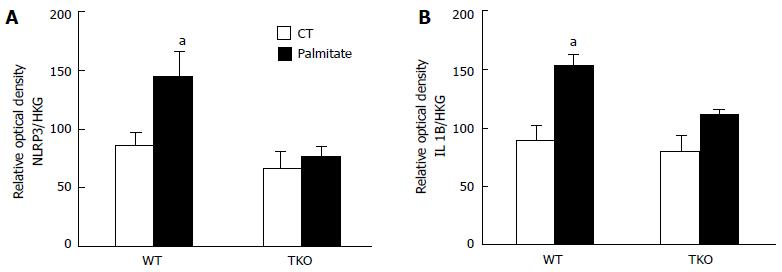
Figure 5 Statistical analysis showed an increase in.
(A) NLRP3 and (B) IL1β expression following palmitate treatment in primary Müller cells isolated from WT but no effect on TKO. Actin and α-tubulin were used as housekeeping genes (HKG), to which NLRP3 and IL1β expression was normalized (aP < 0.05 vs ND, n = 3).
- Citation: Coucha M, Mohamed IN, Elshaer SL, Mbata O, Bartasis ML, El-Remessy AB. High fat diet dysregulates microRNA-17-5p and triggers retinal inflammation: Role of endoplasmic-reticulum-stress. World J Diabetes 2017; 8(2): 56-65
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v8/i2/56.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v8.i2.56