Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Jul 15, 2023; 14(7): 1013-1026
Published online Jul 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i7.1013
Published online Jul 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i7.1013
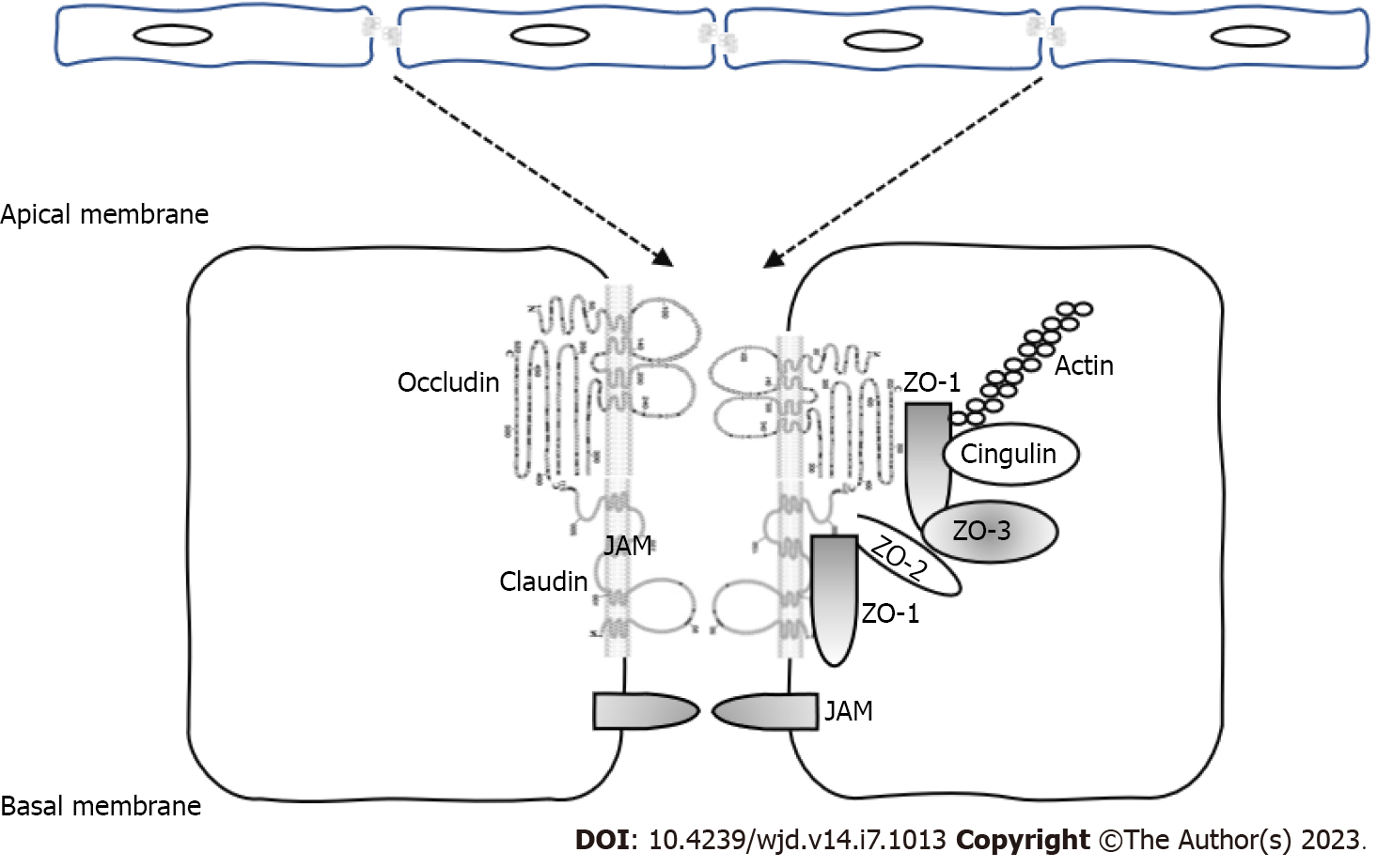
Figure 1 Molecular organization of the tight junctions.
Claudins, occludin and junctional adhesion molecules are the major integral membrane proteins of tight junctions (TJs). Claudins form TJ strands, corresponding to membrane kissing points. TJ-associated membrane proteins are localized at apical cell-cell junctions by interacting with the zonula occludens family of scaffolding proteins, serving as links between TJs and the actin cytoskeleton. JAM: Junctional adhesion molecules; ZO: Zonula occludens.
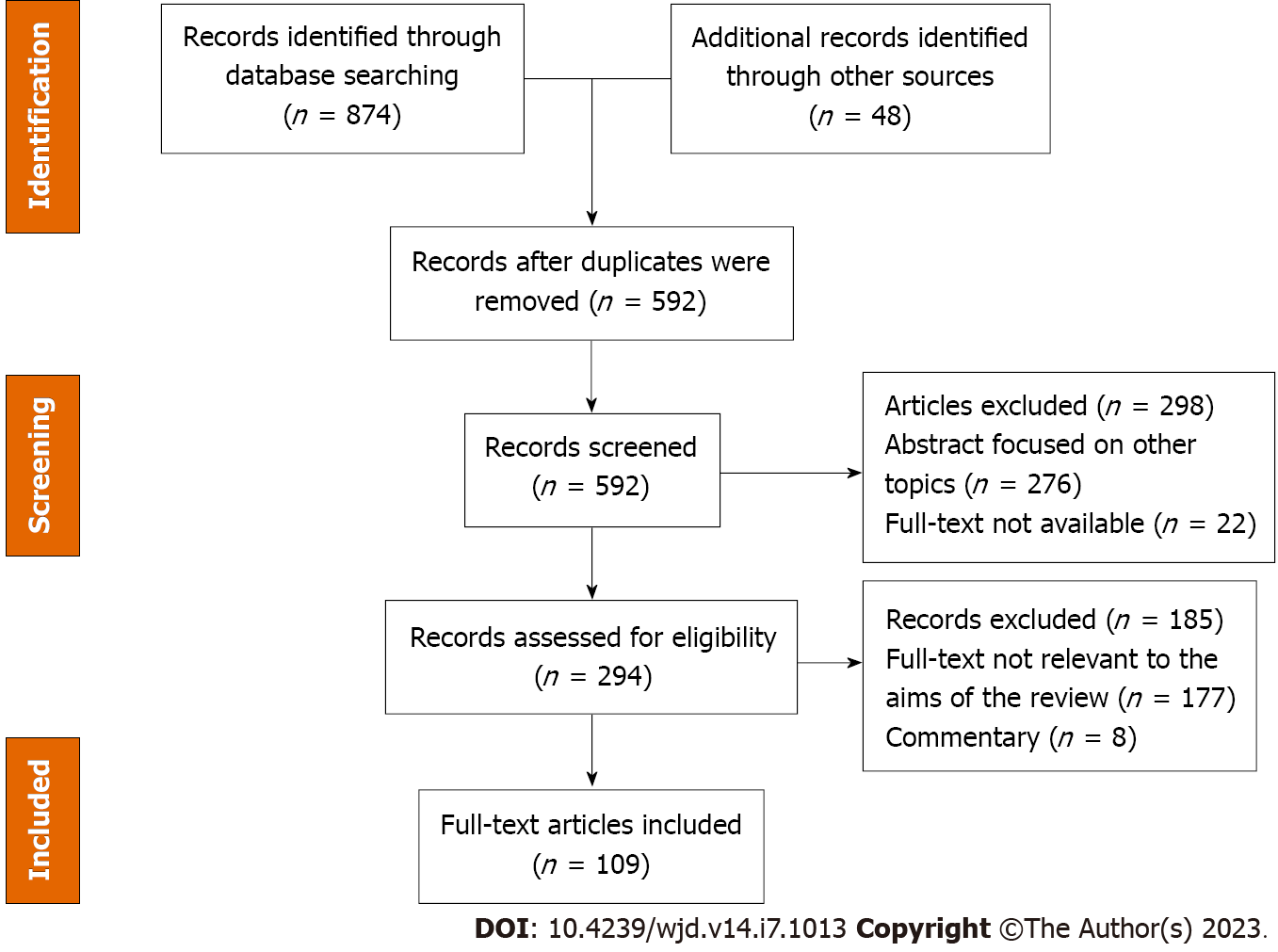
Figure 2 Study flowchart according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines.
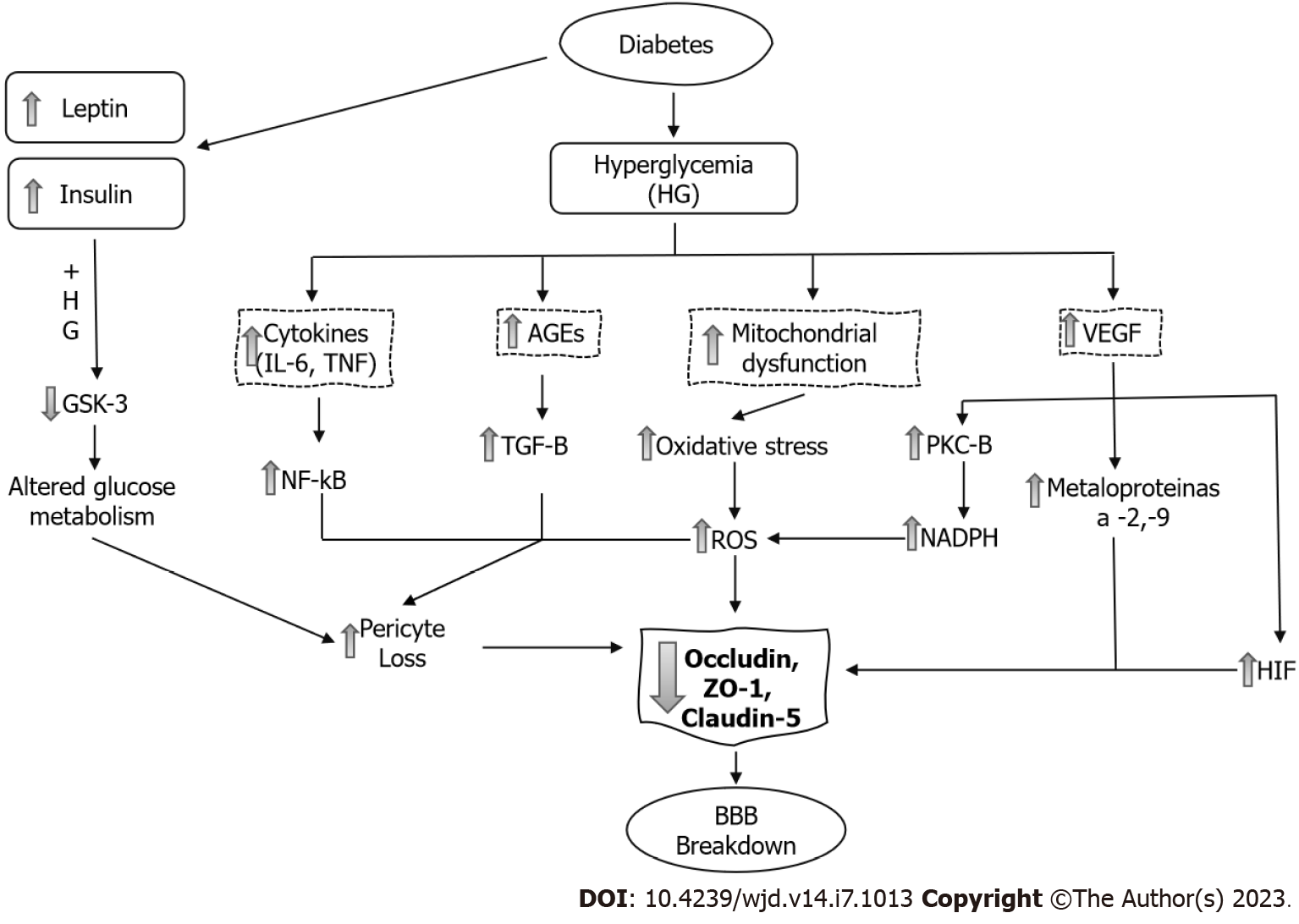
Figure 3 Mechanisms of blood-brain-barrier dysfunction in diabetes mellitus.
AGE: Advanced glycation end-product; BBB: Blood-brain-barrier; GSK-3: Glycogen synthase kinase 3; HG: Hyperglycemia; HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor; IL-6: Interleukin 6; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; PKC-B: Protein kinase C; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; ZO-1: Zonula occludens.
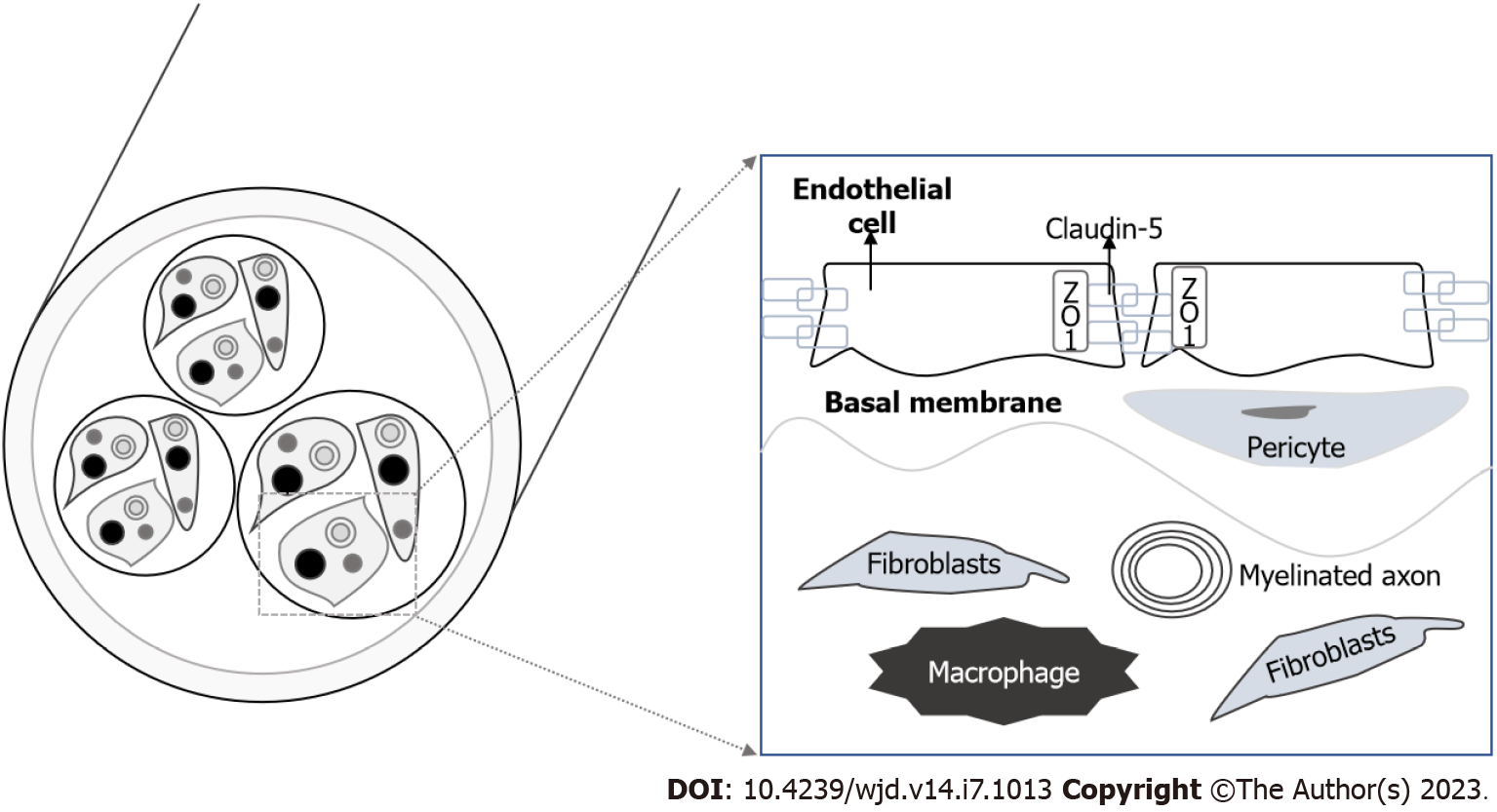
Figure 4 Blood-nerve-barrier and cellular structure of the endothelial cells and tight junctions.
ZO: Zonula occludens.
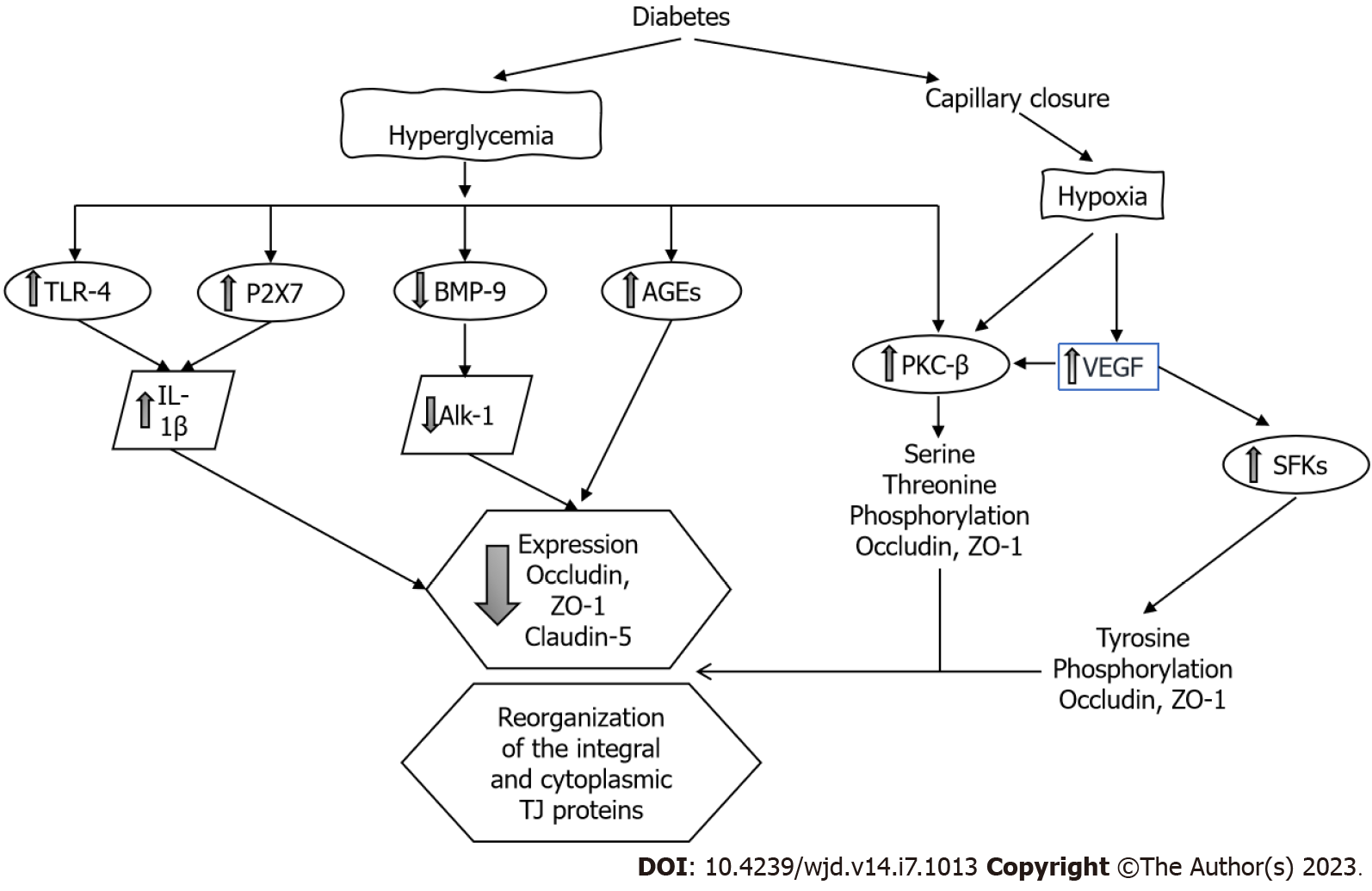
Figure 5 Mechanisms of blood-retina-barrier dysfunction in diabetes mellitus.
AGEs: Advanced glycation end-products; Alk-1: Activin-like kinase receptor type I; BMP-9: Bone morphogenetic protein 9; IL-1: Interleukin 1 beta; P2X7: Purinergic receptor; PKC-: Protein kinase C beta; SFK: Src family of cytoplasmic proteins; TJ: Tight junction; TLR-4: Toll-like receptor 4; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; ZO-1: Zonula occludens 1.
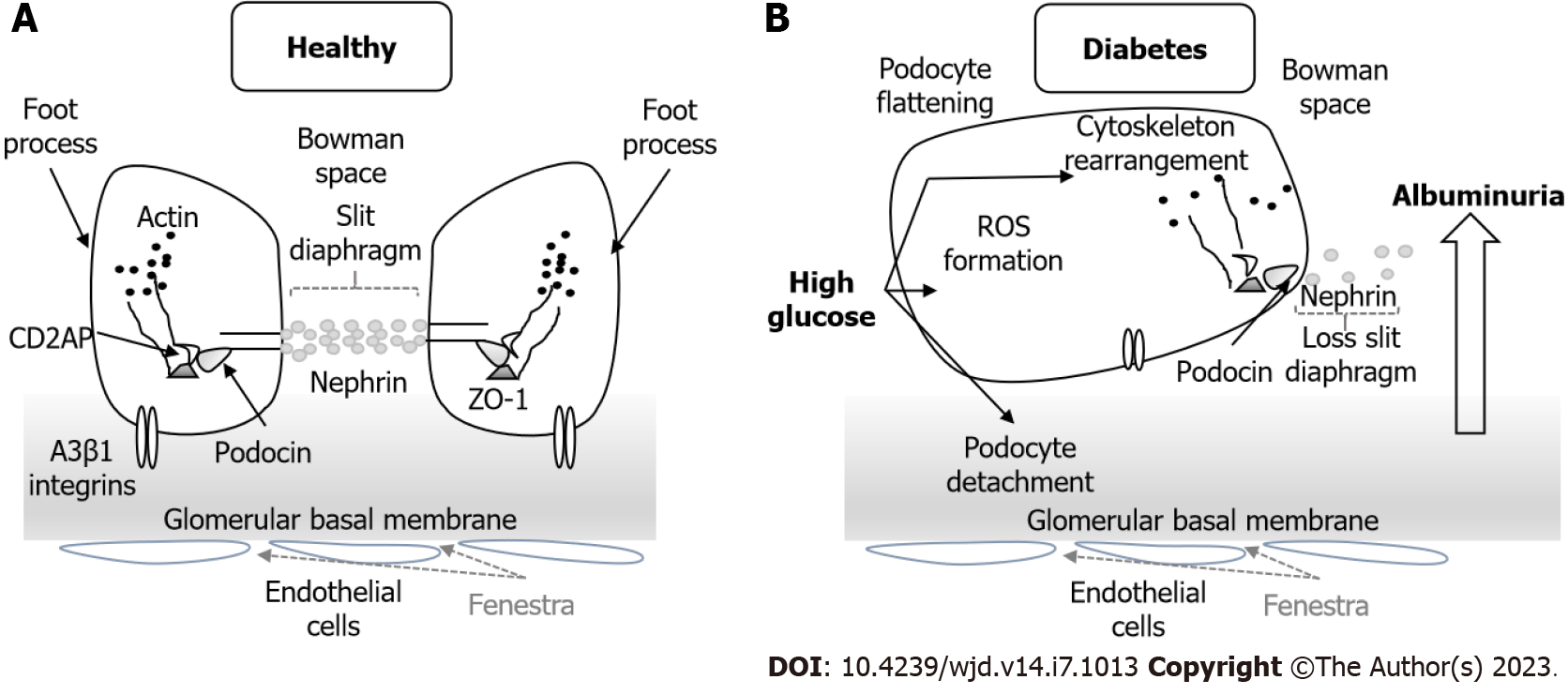
Figure 6 Podocyte structure.
A: Normal structure of the podocyte with the morphology of the foot process and the slit diaphragm; B: In diabetic nephropathy the podocyte structure and slit diaphragm are injured with slit diaphragm disruption, podocyte detachment and cytoskeleton rearrangement. These changes lead to albuminuria and progressive kidney disease. ROS: Reactive oxygen species; ZO: Zonula occludens.
- Citation: Robles-Osorio ML, Sabath E. Tight junction disruption and the pathogenesis of the chronic complications of diabetes mellitus: A narrative review. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(7): 1013-1026
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i7/1013.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i7.1013