Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2022; 13(12): 1106-1121
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1106
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1106
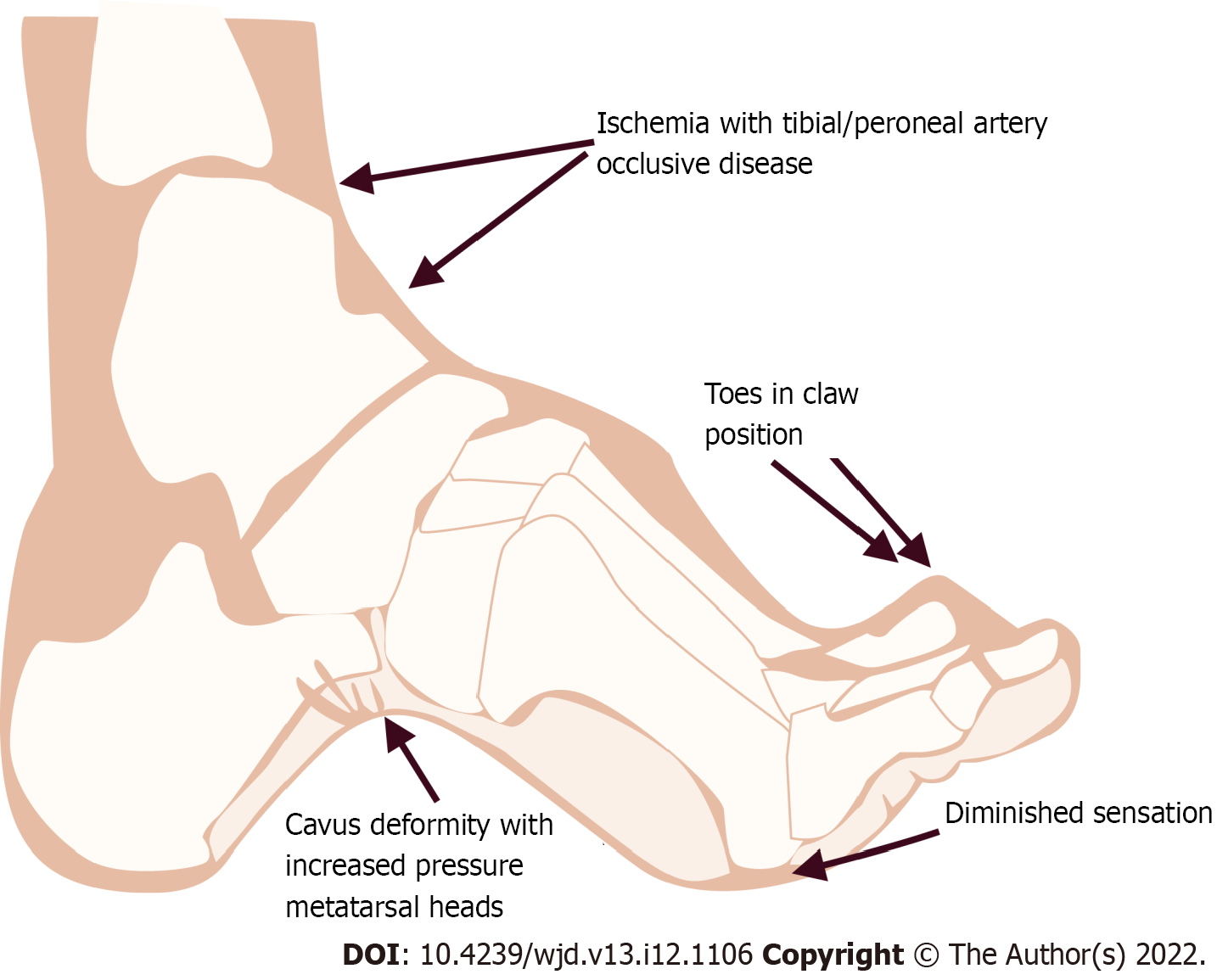
Figure 1 Ethiopathogenesis of diabetic foot leading to vascular complications.
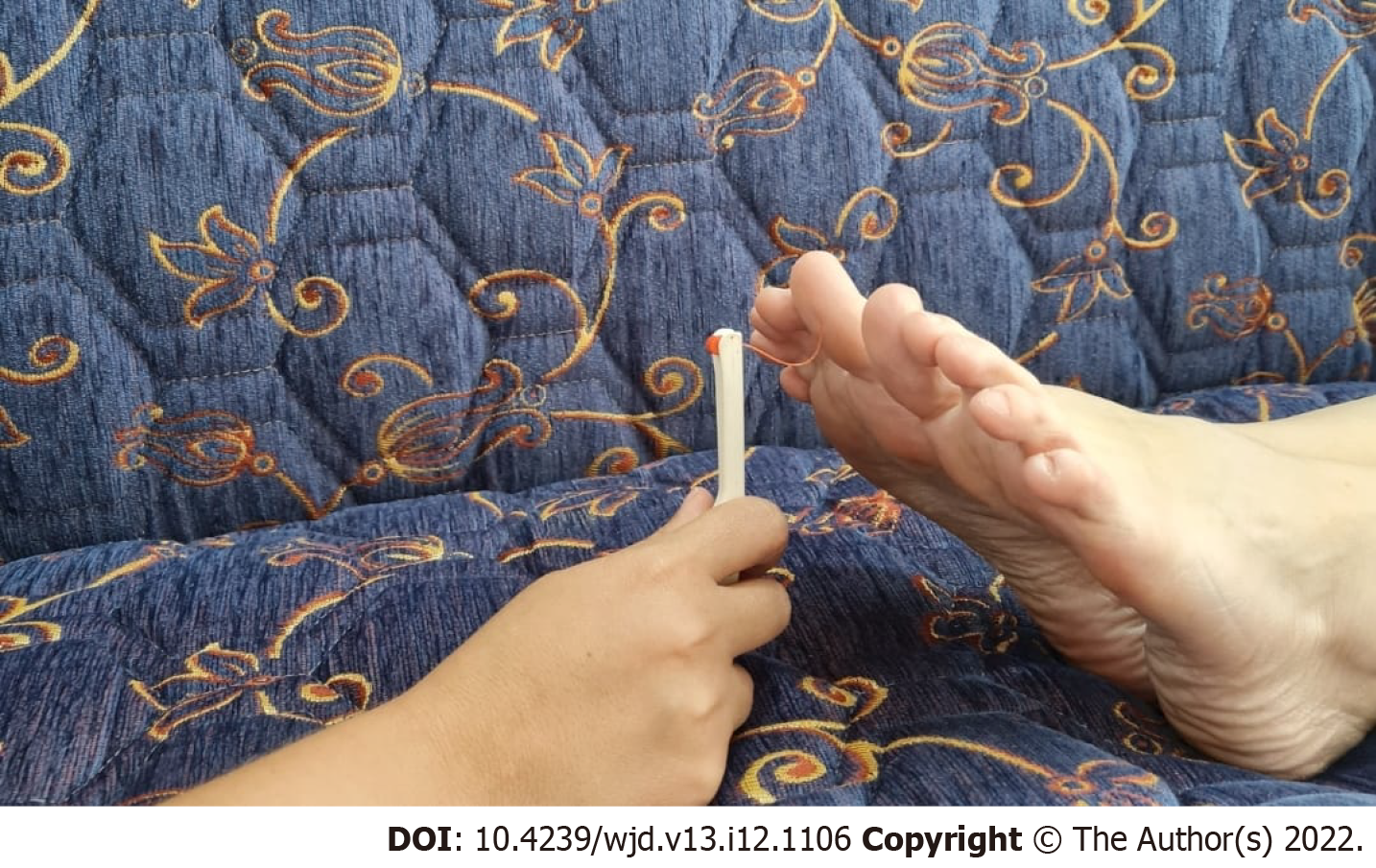
Figure 2 Monofilament test is a diagnostic tool to detect diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
When the nylon line bends, the force is 10 grams. It is used for diabetic foot contact and stress testing.
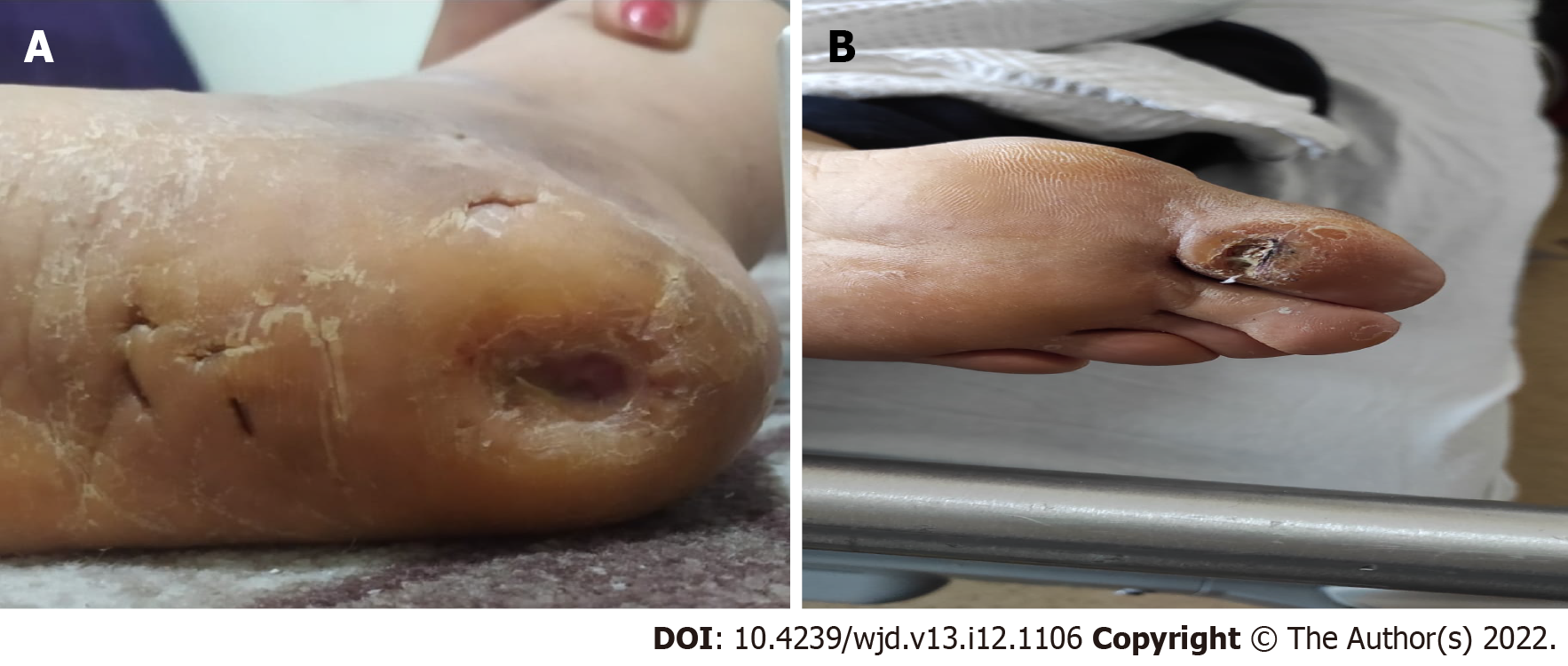
Figure 3 Callus formation as a presentation of diabetic neuropathy.
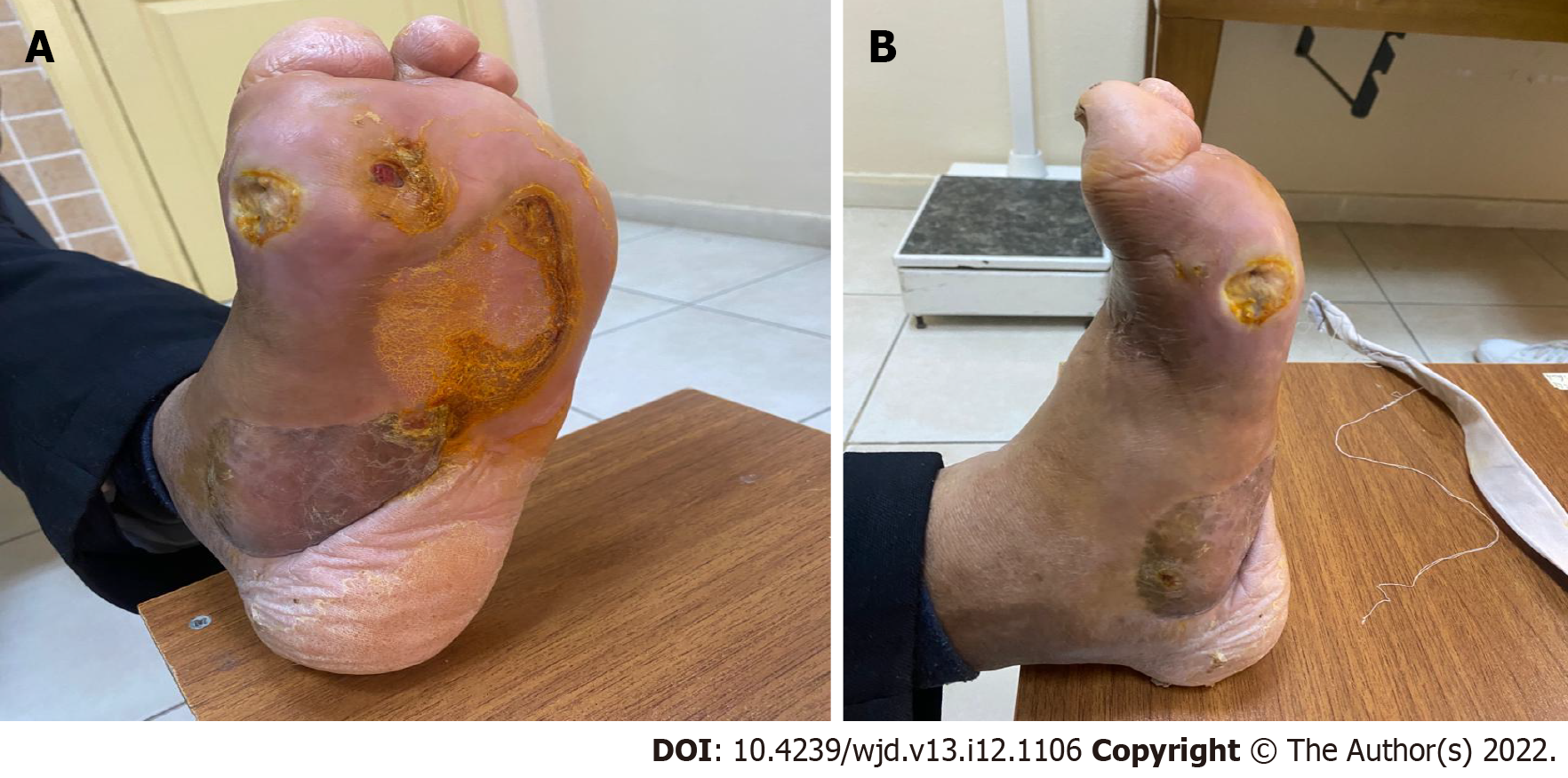
Figure 4 Charcot neuroarthropathy is a chronic devastating and destructive disease of bone structure and joint in patients with neuropathy.
A and B: Rocker-bottom foot deformity to charcot process.
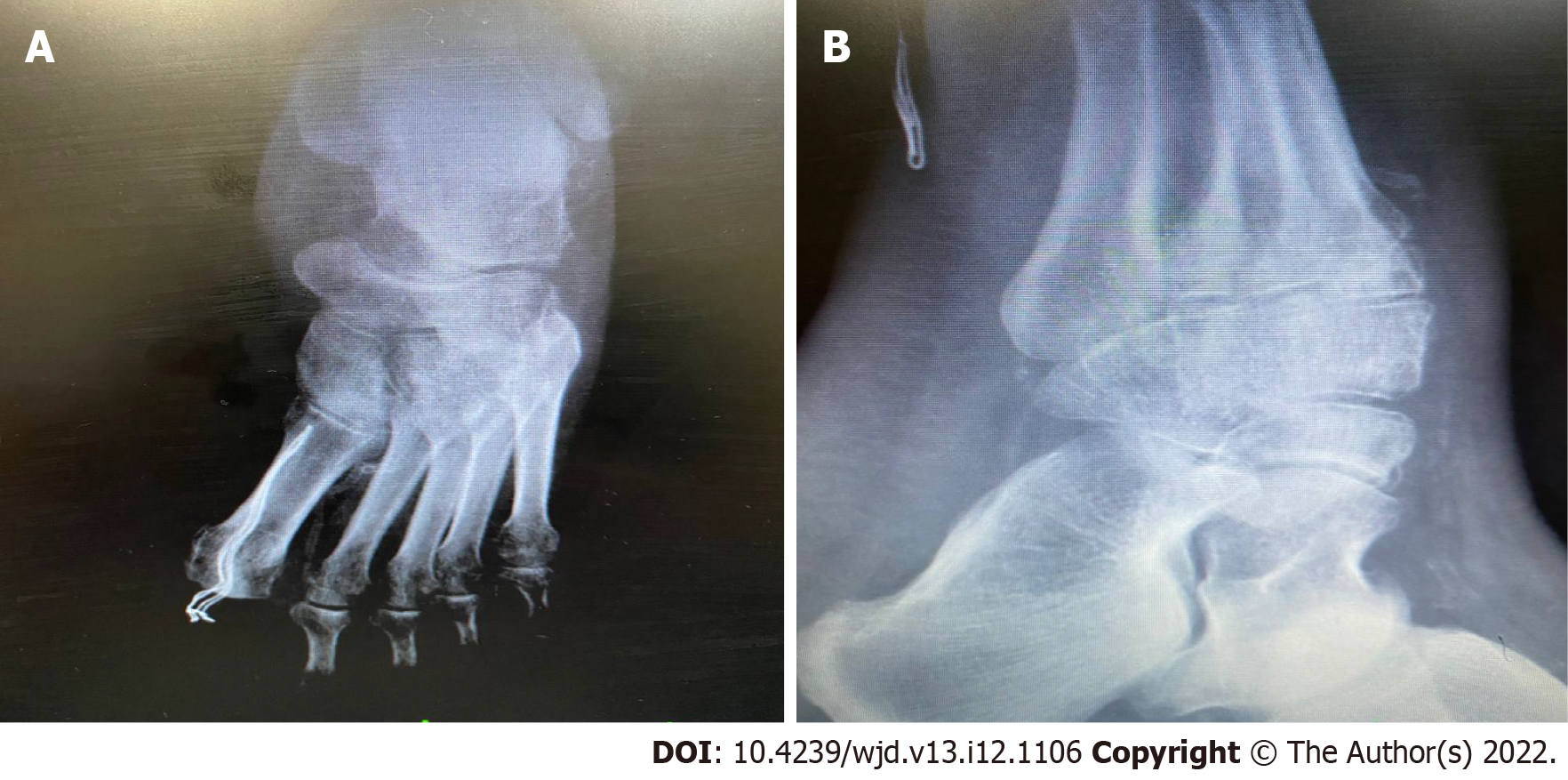
Figure 5 Radiographic findings.
A and B: Radiographic findings of charcot neuroarthropathy.
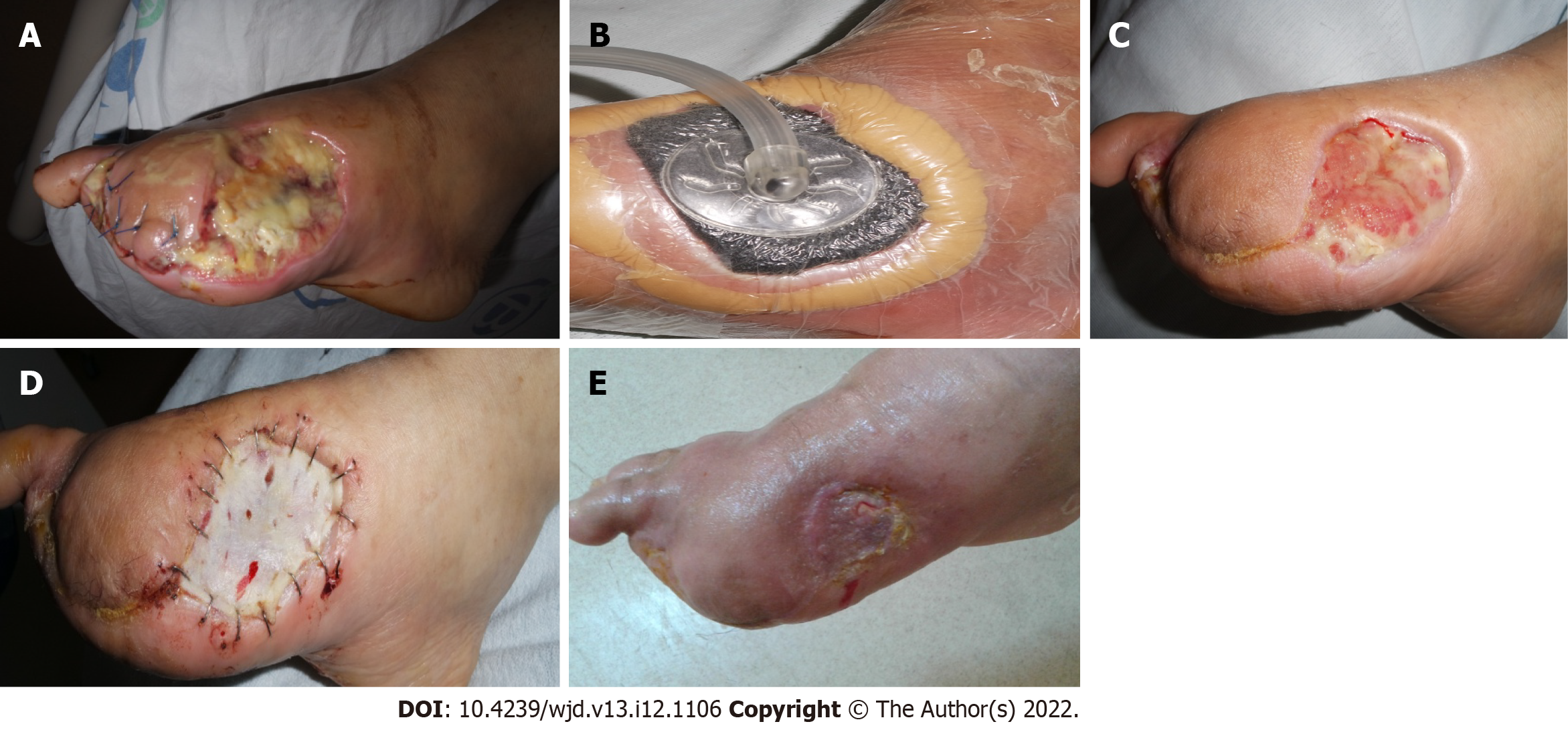
Figure 6 Negative pressure wound therapy is considered as a better alternative therapy for the management of diabetic foot ulcer.
A-E: This patient was treated with negative pressure wound therapy therapy after surgical therapy.
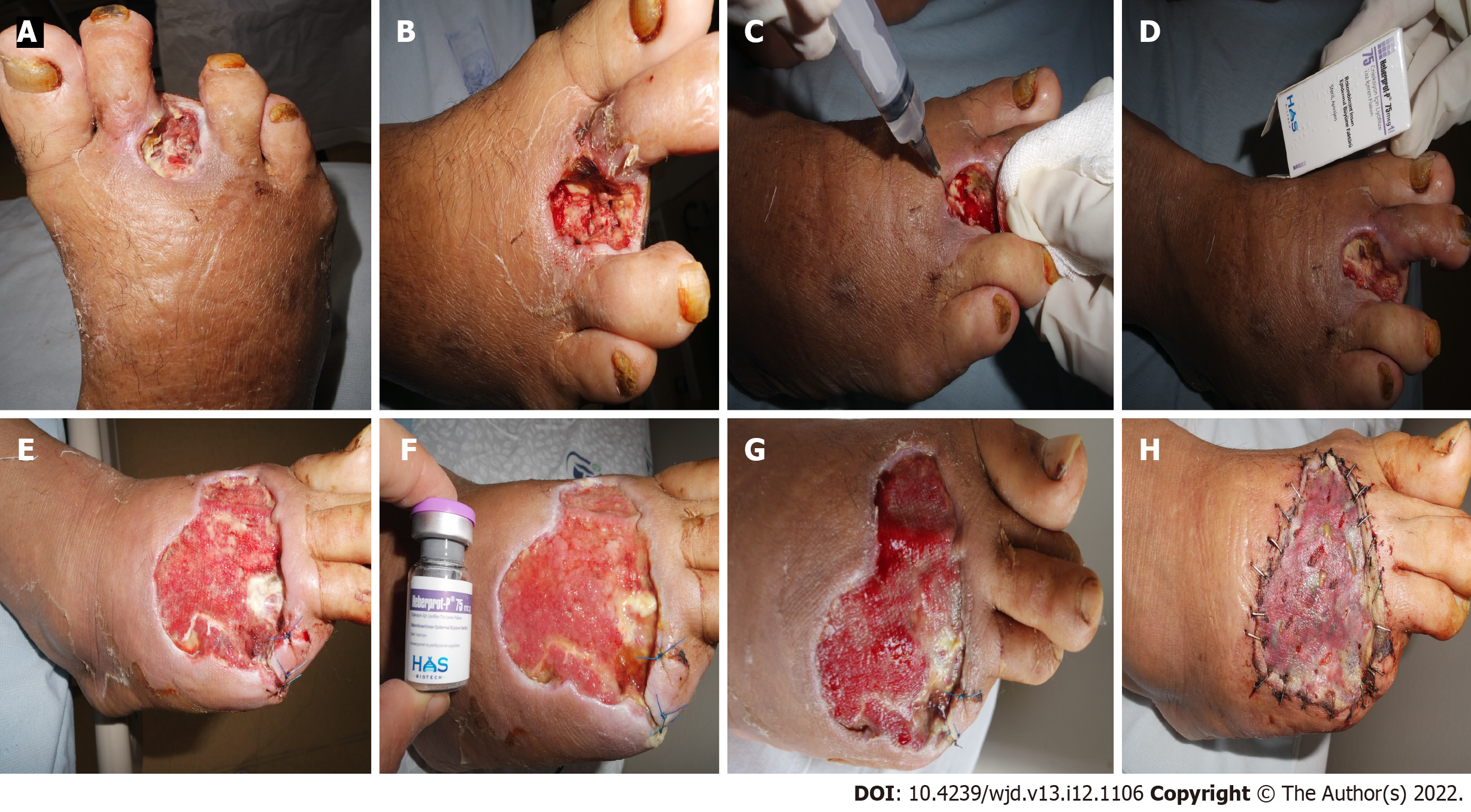
Figure 7 Epidermal growth factor is perhaps the most widely used method in diabetic foot.
A-D: Intralesional epidermal growth factor therapy into the wound bottom and contours encourages granulation tissue growth and wound closure; E-H: Before and after intralesional epidermal growth factor therapy.
- Citation: Akkus G, Sert M. Diabetic foot ulcers: A devastating complication of diabetes mellitus continues non-stop in spite of new medical treatment modalities. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(12): 1106-1121
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i12/1106.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1106