Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2021; 12(5): 514-523
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.514
Published online May 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.514
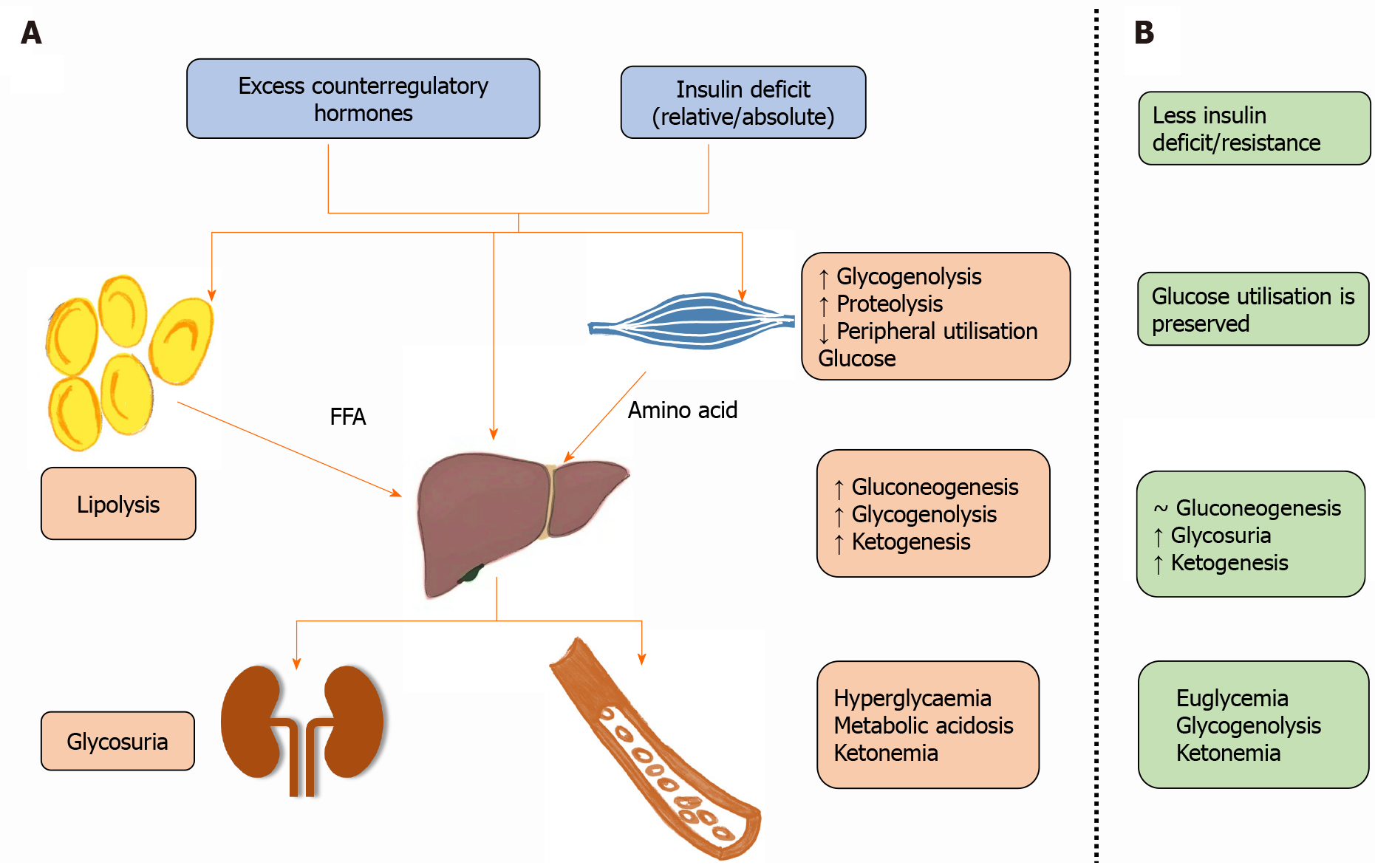
Figure 1 Ketone bodies (beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone) are responsible for metabolic acidosis, while hyperglycemia through glycosuria and osmotic diuresis causes dehydration and hypovolemia.
A: Pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis; B: Pathophysiology of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. FFA: Free fatty acids; ↑: Increase; ↓: Decrease; ~: No change.
- Citation: Nasa P, Chaudhary S, Shrivastava PK, Singh A. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: A missed diagnosis. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(5): 514-523
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i5/514.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.514