Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2023; 15(11): 1835-1851
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i11.1835
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i11.1835
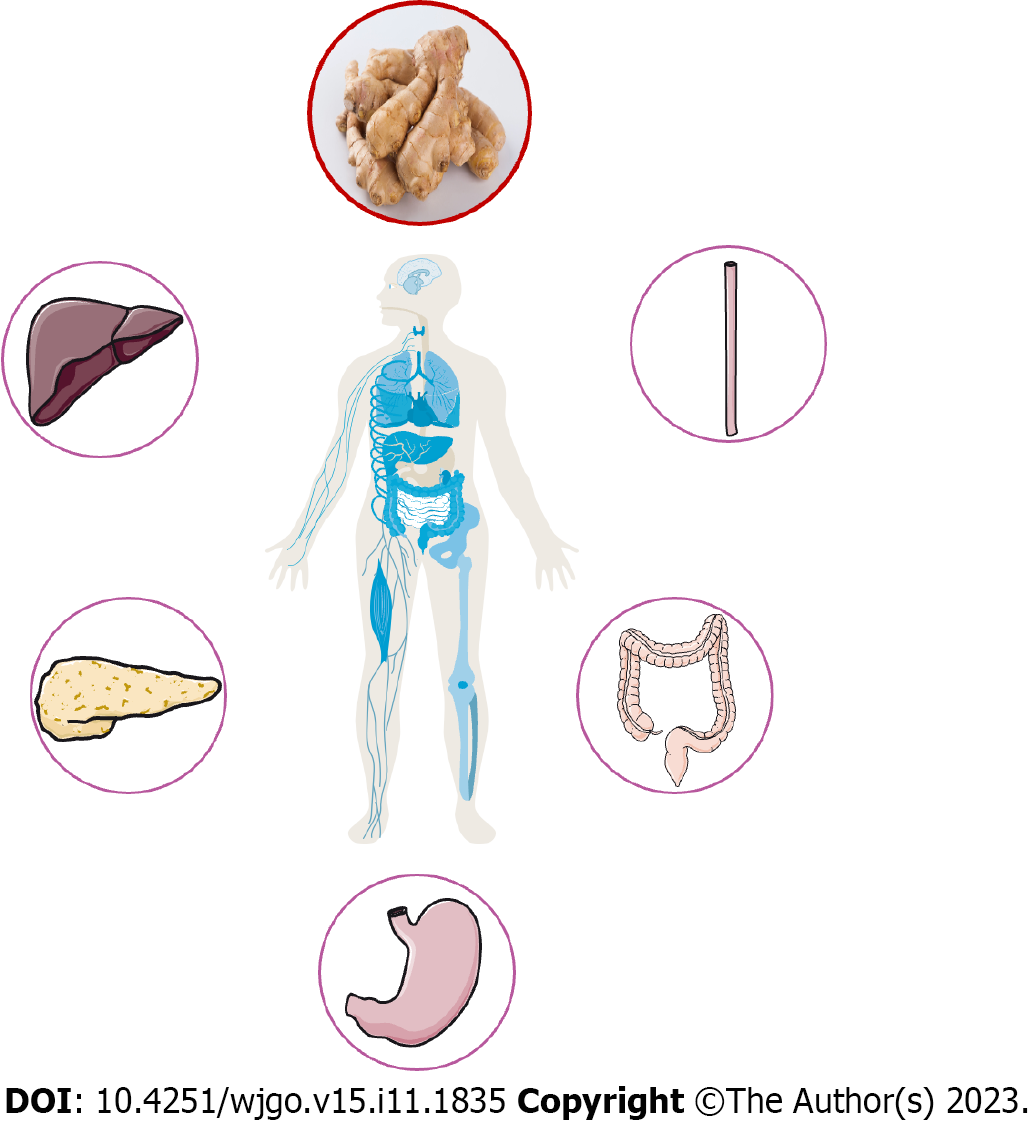
Figure 1 Types of tumors treated with ginger.
Ginger has excellent therapeutic effects on liver, pancreatic, stomach, colorectal and laryngeal cancers.
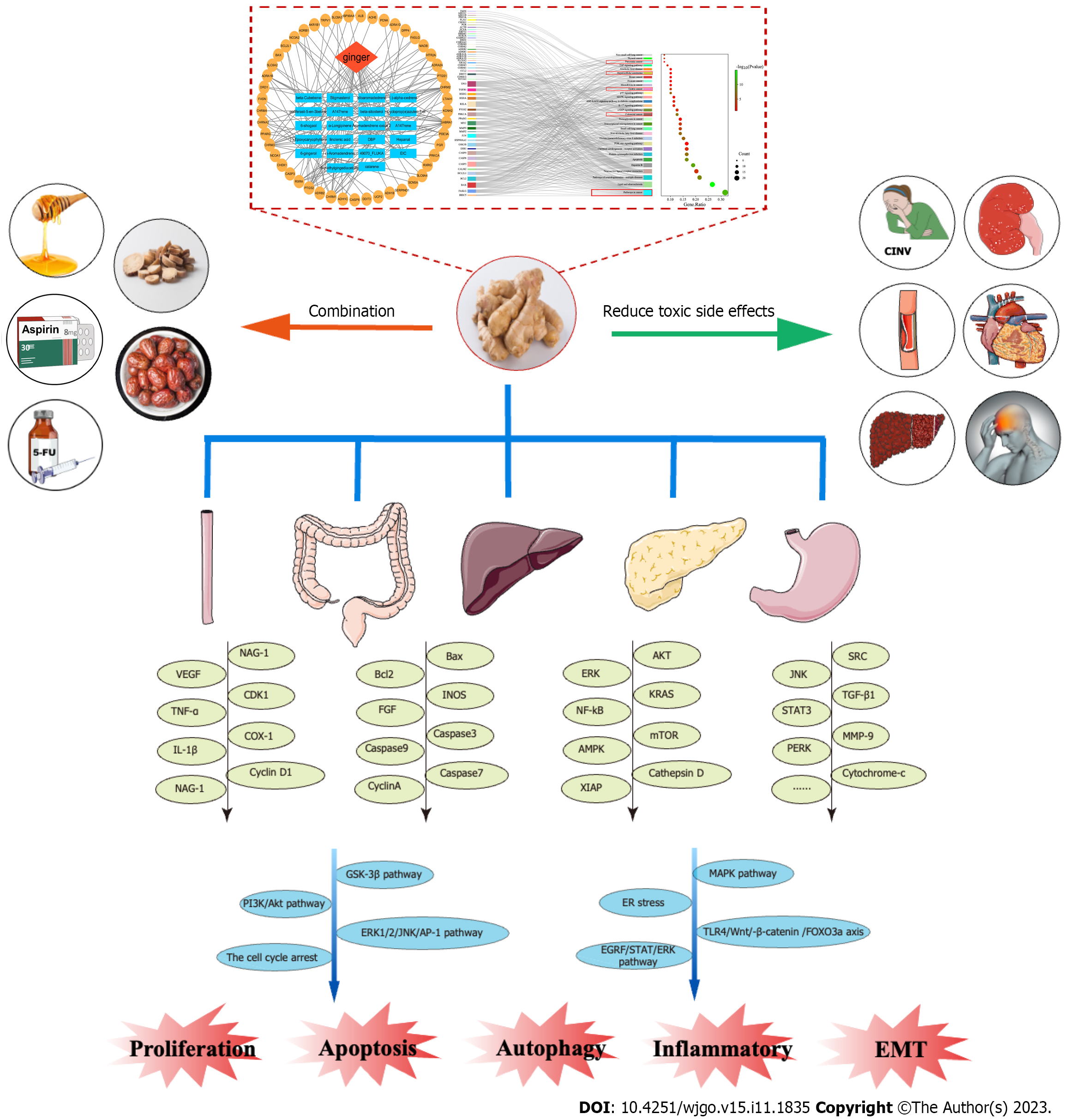
Figure 2 Flow diagram.
The anti-gastrointestinal tumor effect of ginger was verified by network pharmacological analysis of ginger. Literature search, review, and literature synthesis were performed to summarize ginger's anti-tumor combinations, reduction of toxicities, mechanisms of action, and related signaling pathways. In the red box are the pathways in the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway associated with gastrointestinal cancer. COX-1: Cyclooxygenase-1; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; IL-1β: Interleukin-1beta; MMP-9: Matrix metalloproteinase-9; NAG-1: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1; PI3K/AKT: Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase/protein kinase B; TLR4: Toll receptor 4; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
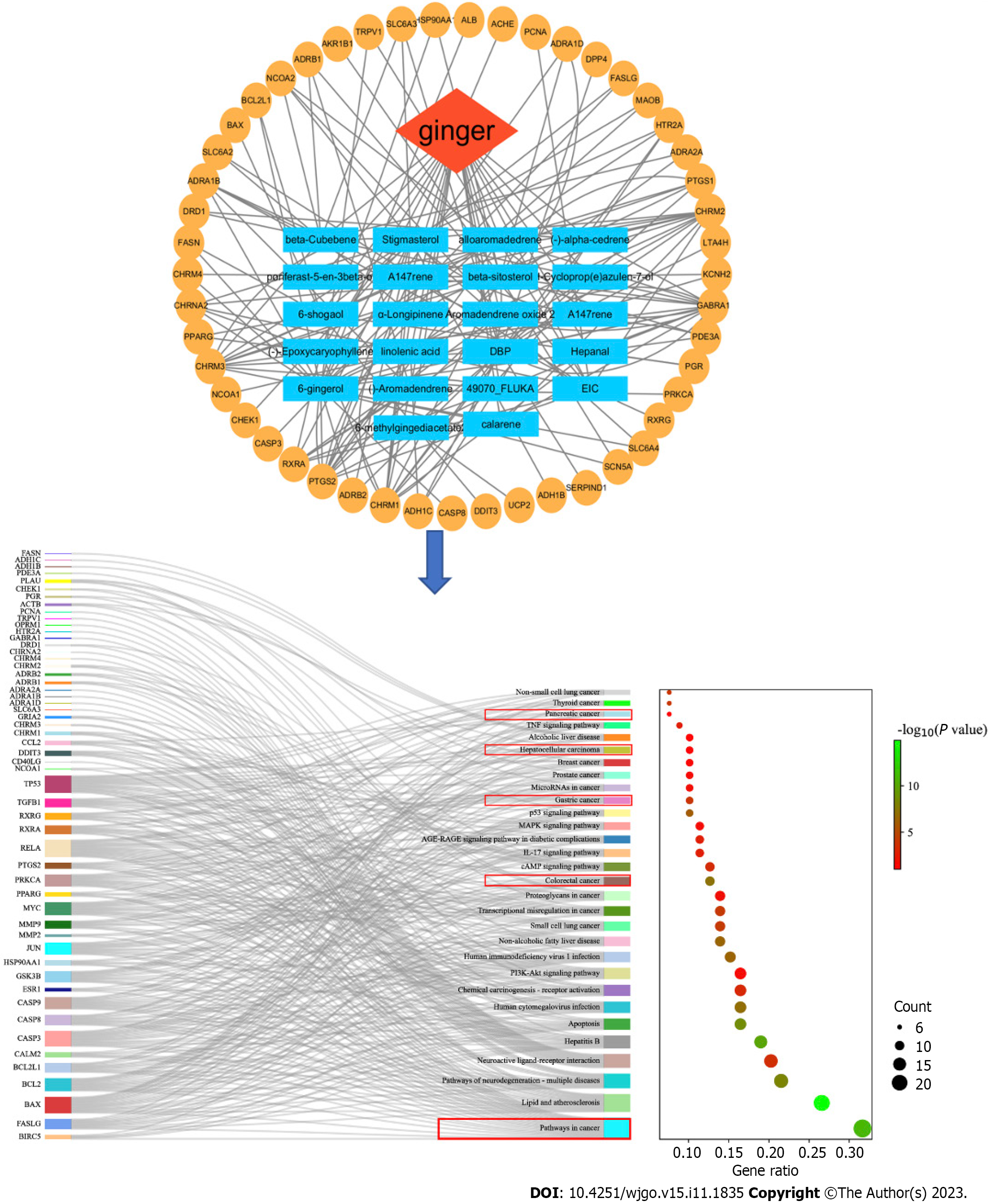
Figure 3 Ginger-active composition target plot and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analyses.
In the red box are the signaling pathways associated with gastrointestinal tumors in the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis.
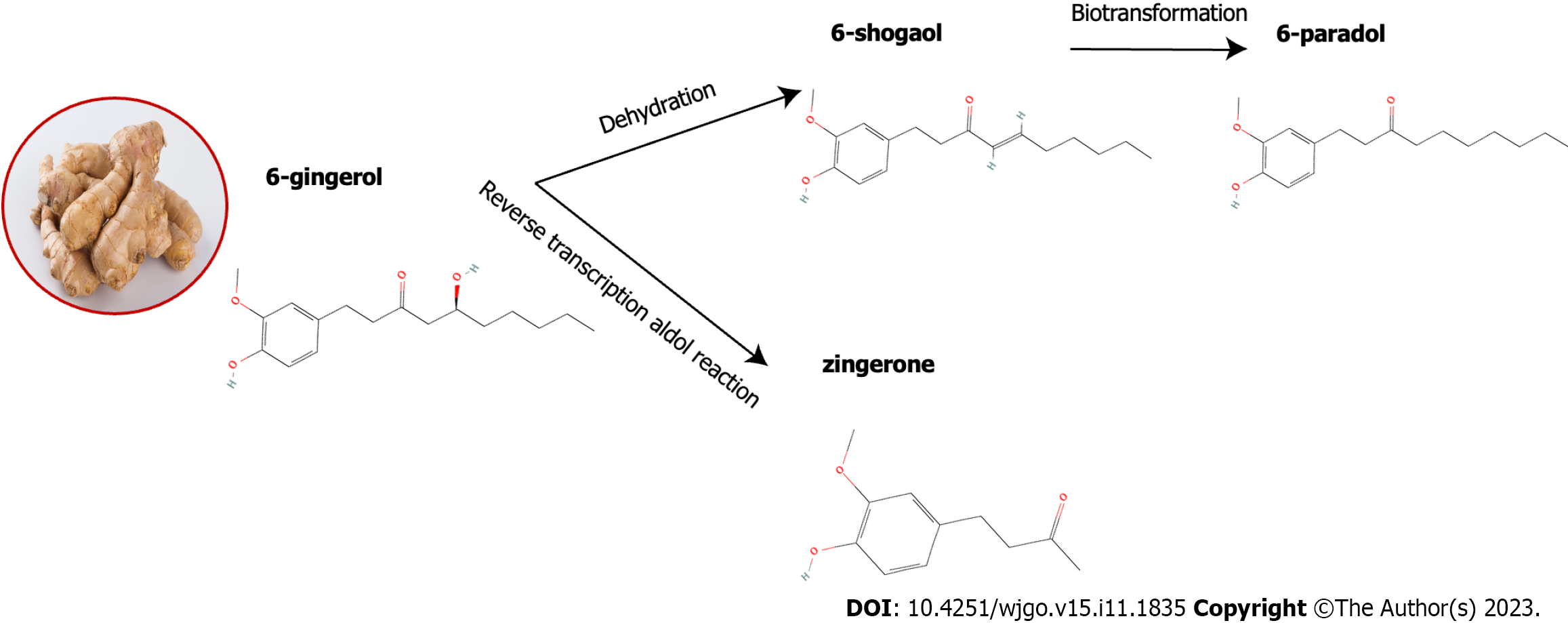
Figure 4 Structural formulae of the representative components of ginger and the transformation between them.
- Citation: Chen GQ, Nan Y, Huang SC, Ning N, Du YH, Lu DD, Yang YT, Meng FD, Yuan L. Research progress of ginger in the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(11): 1835-1851
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i11/1835.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i11.1835