Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jan 15, 2023; 15(1): 1-18
Published online Jan 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i1.1
Published online Jan 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i1.1
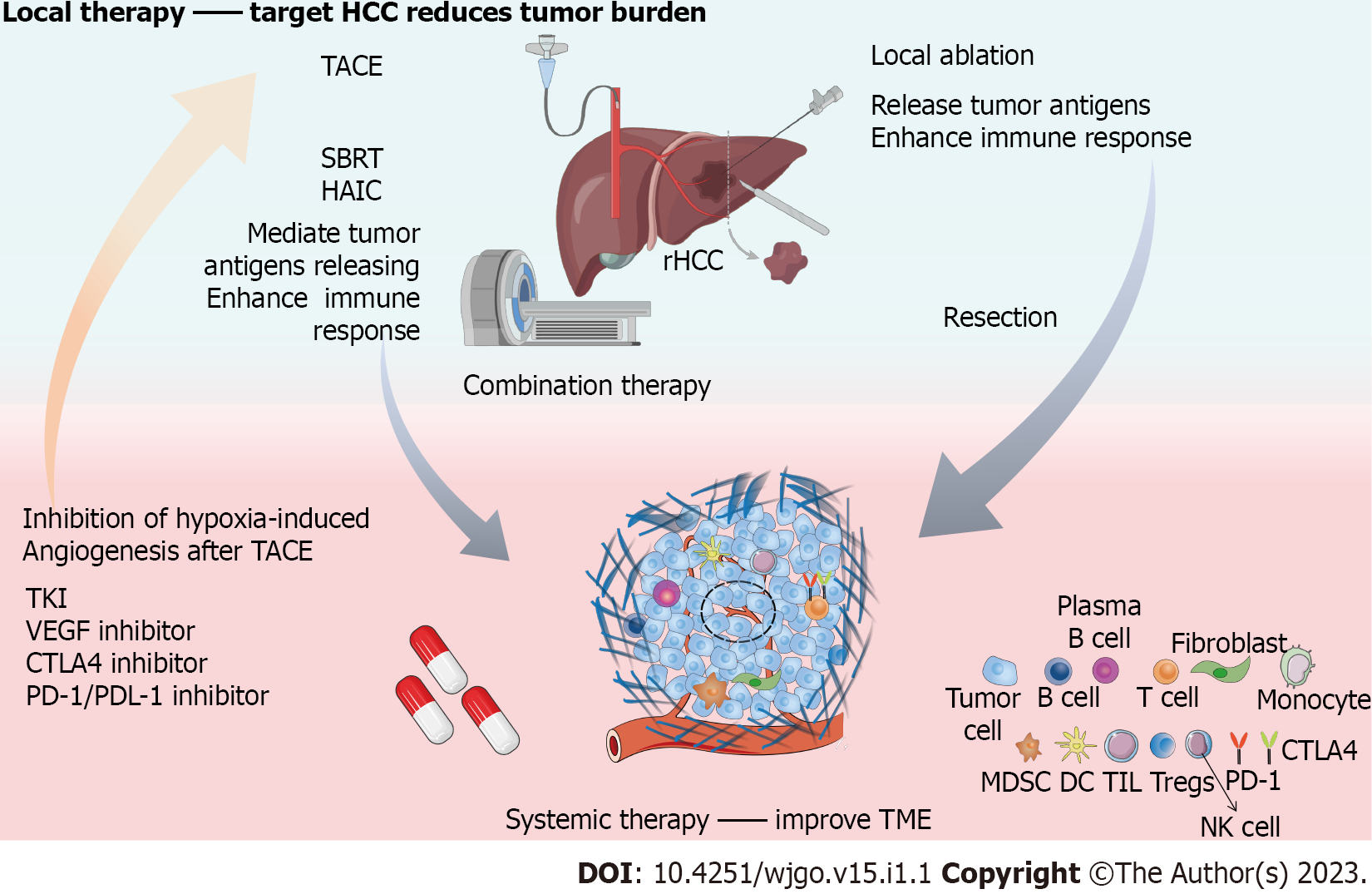
Figure 1 Complementary effects of local therapy combined with systemic therapy in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma.
Local therapies, including surgery, transhepatic arterial chemoembolization (TACE), ablation, hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy (HAIC), stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), are targeted-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) to reduce tumor load. Systematic therapy represented by tyrosine kinase inhibitor, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor, anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 inhibitor; programmed cell death protein-1/programmed cell death ligand-1 inhibitor is mainly aimed at improving tumor microenvironment. VEGF inhibitor can reduce hypoxia induced angiogenesis after TACE. Local ablation, HAIC and SBRT can promote or regulate the release of tumor antigens and enhance the response of immunotherapy. The combination of local therapy and systematic therapy is expected to improve the outcome of recurrent HCC. rHCC: Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma; TACE: Transhepatic arterial chemoembolization; SBRT: Stereotactic body radiotherapy; HAIC: Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy; TKI: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; CTLA4: Anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein-1; PDL-1: Programmed cell death ligand-1; TME: Tumor microenvironment.
- Citation: Liang J, Bai Y, Ha FS, Luo Y, Deng HT, Gao YT. Combining local regional therapy and systemic therapy: Expected changes in the treatment landscape of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(1): 1-18
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i1.1