Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2022; 14(10): 2077-2084
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.2077
Published online Oct 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.2077
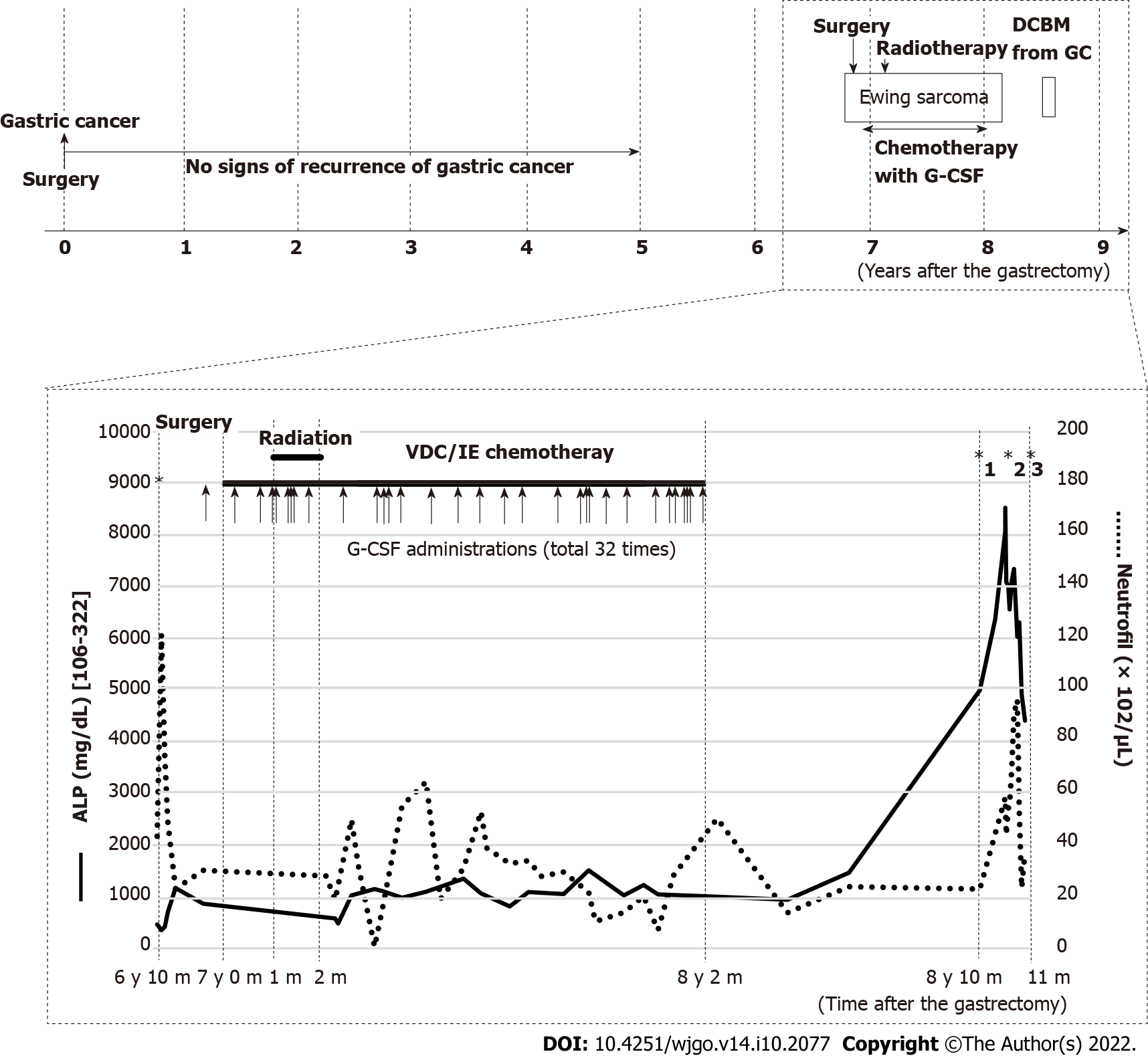
Figure 1 Clinical course after gastrectomy.
During the five-year follow-up of resected gastric cancer, there are no signs of recurrence based on tumor markers, computed tomography, and gastroduodenoscopy. Eight months after completing chemotherapy with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration for Ewing sarcoma, disseminated carcinomatosis of the bone marrow (DCBM) from gastric cancer is diagnosed. Alkaline phosphatase is moderately elevated during the treatment of Ewing sarcoma and remarkably increased when the patient complained of lumbar pain, which led to the diagnosis of DCBM.*1: Complaint of pain; *2: Bone marrow biopsy; *3: Died of DCBM. G-CSF: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; DCBM: Disseminated carcinomatosis of the bone marrow; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; VDC/IE: Vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide/ifosfamide, etoposide; GC: Gastric cancer.
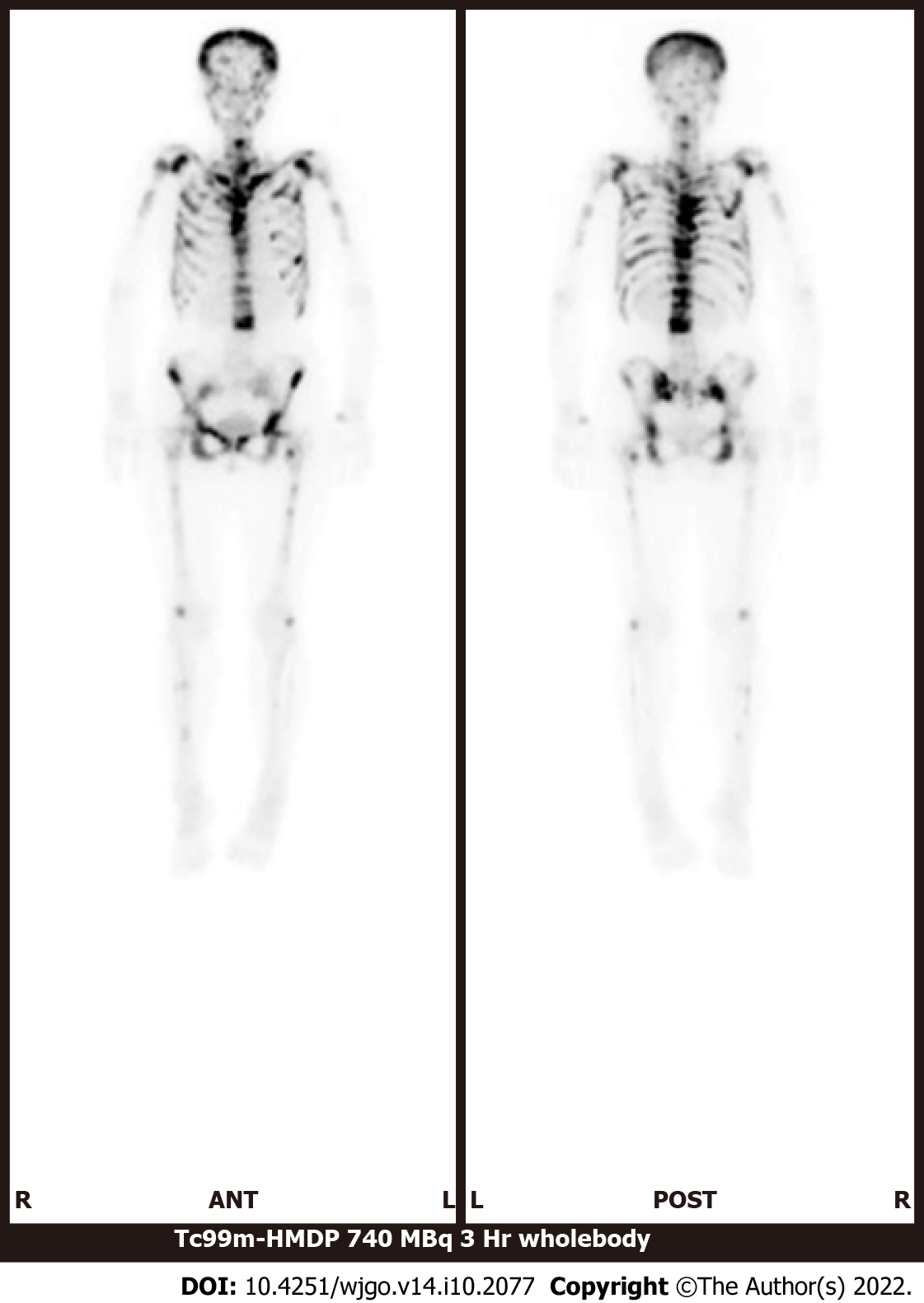
Figure 2 Bone scintigraphy using 99 m technetium-hydroxymethylene diphosphonate.
There is increased uptake in the spine, limbs, pelvis, and skull and decreased uptake in the kidneys.
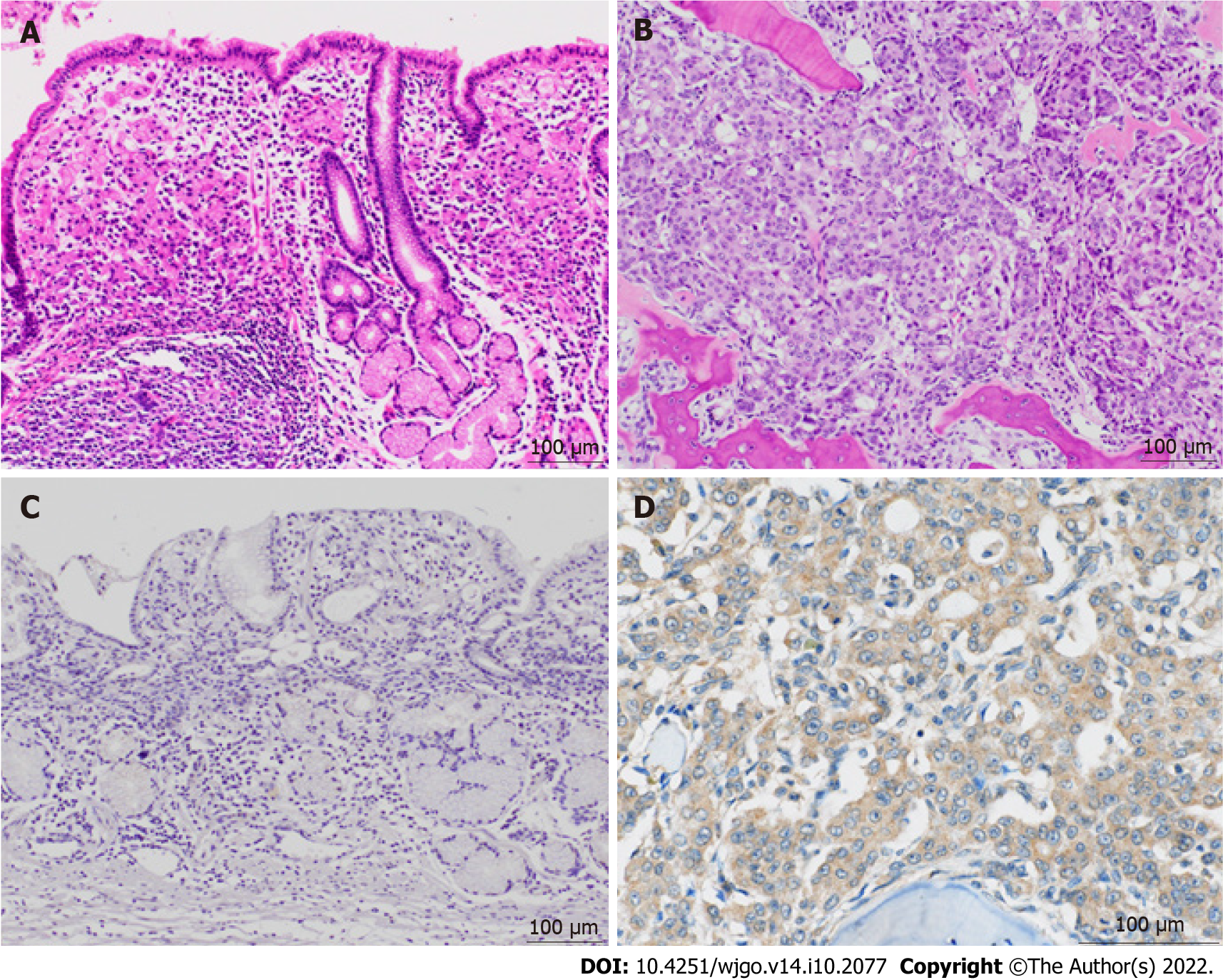
Figure 3 Histologic and immunohistochemical images of the primary and relapsed lesions.
A: Histology of the primary gastric specimen shows moderately to poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma and, partially, signet cell carcinoma (hematoxylin and eosin); B: On autopsy, the metastatic bone marrow lesion shows corresponding adenocarcinoma (hematoxylin and eosin); C: Immunohistochemical staining for granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor (G-CSFR) is negative in the primary lesion; D: Immunohistochemical staining for G-CSFR is diffusely positive in the bone marrow metastatic lesion.
- Citation: Fujita K, Okubo A, Nakamura T, Takeuchi N. Disseminated carcinomatosis of the bone marrow caused by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: A case report and review of literature. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(10): 2077-2084
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i10/2077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i10.2077