Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2021; 13(6): 550-559
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.550
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.550
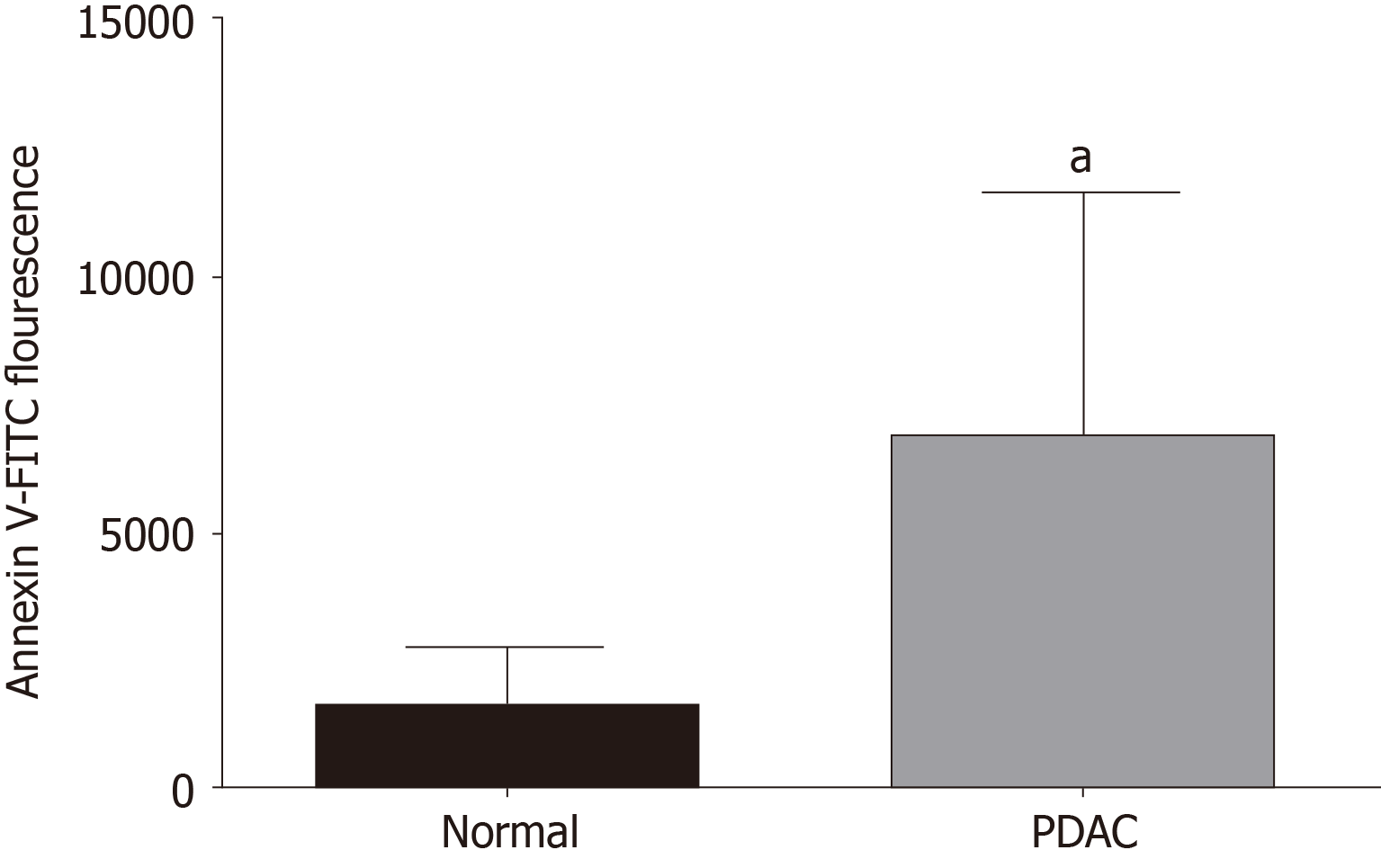
Figure 1 Surface phosphatidylserine on normal pancreata and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumors.
Pancreatic tumors and neighboring more normal tissue excised from treatment-naïve pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients were digested with collagenase IV or a Tumor Dissociation kit (Miltenyi). PDAC cells were co-stained with MUC-4-APC, a marker for epithelial cells and Annexin V-FITC, which binds cell surface phosphatidylserine (PS) and surface PS was quantified on MUC-4+ cells by flow cytometry (n = 5 for each). Data are presented as the mean ± SE of the mean, and were compared between two groups using t-test. aP < 0.05 vs normal group. PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
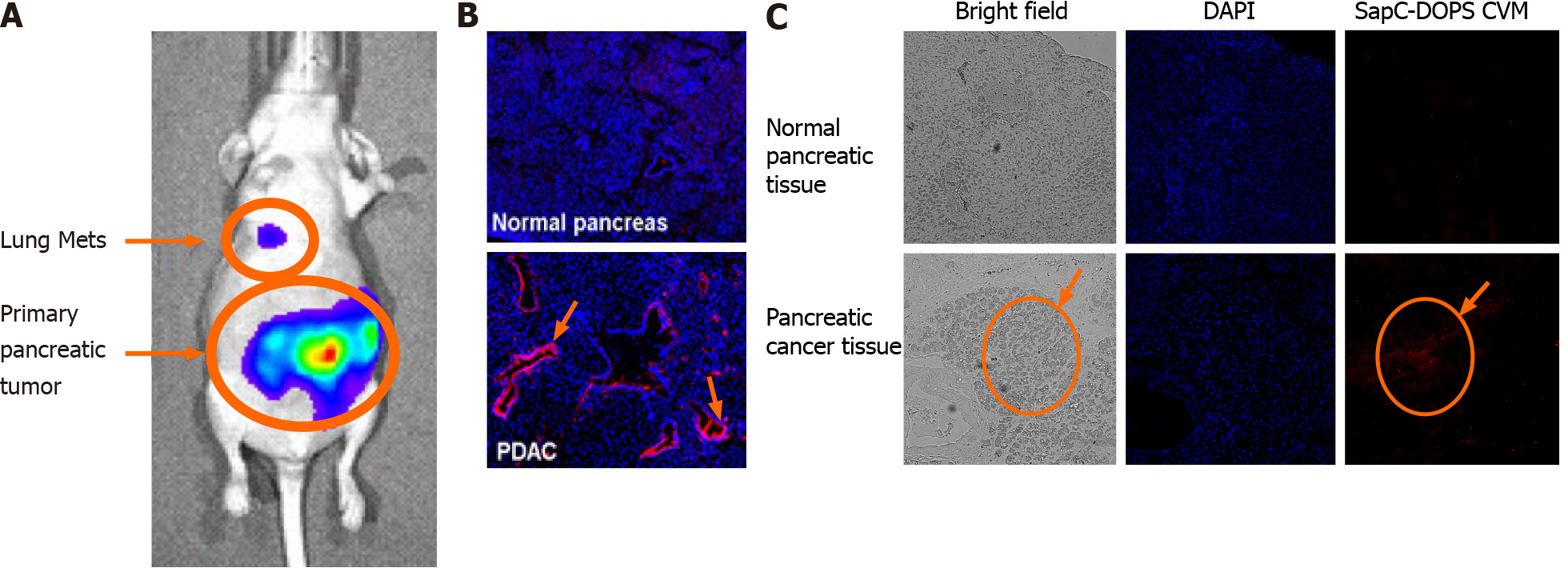
Figure 2 Saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine targets pancreatic tumors.
Saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine (SapC-DOPS) was fluorescently labeled with CellVue Maroon (CVM, a far red fluorescent probe) and injected into mice after pancreatic tumors were established from human cancer cells (cfPac-1-Luc3) (see details in reference 26)[26]. A: SapC-DOPS-CVM localized to the primary and lung metastatic tumors detected with intravascular ultrasound live animal imaging; B: Tumors, established from human MiaPaCa-2 cells, and normal pancreata of SapC-DOPS-CVM-injected mice were isolated and prepared for fluorescent microscopy. The slides, after staining with DAPI (blue) to detect nuclei, show accumulation of SapC-DOPS-CVM in the tumors. Note preferential SapC-DOPS labeling of ductal structures (arrows) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), and minimal binding to normal pancreas. SapC-DOPS is binding phosphatidylserine (PS) on the cancer cell surfaces as prior treatment with lactadherin, a PS binding protein, eliminates subsequent binding of SapC-DOPS; C: Frozen, unfixed sections from murine PDAC and matched normal pancreas tissues were incubated with SapC-DOPS-CVM nanovesicles for 20 min, counterstained with DAPI and mounted. The ovals localize the PDAC tumor. SapC-DOPS: Saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine; CVM: CellVue Maroon; Mets: Metastatic tumors; PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
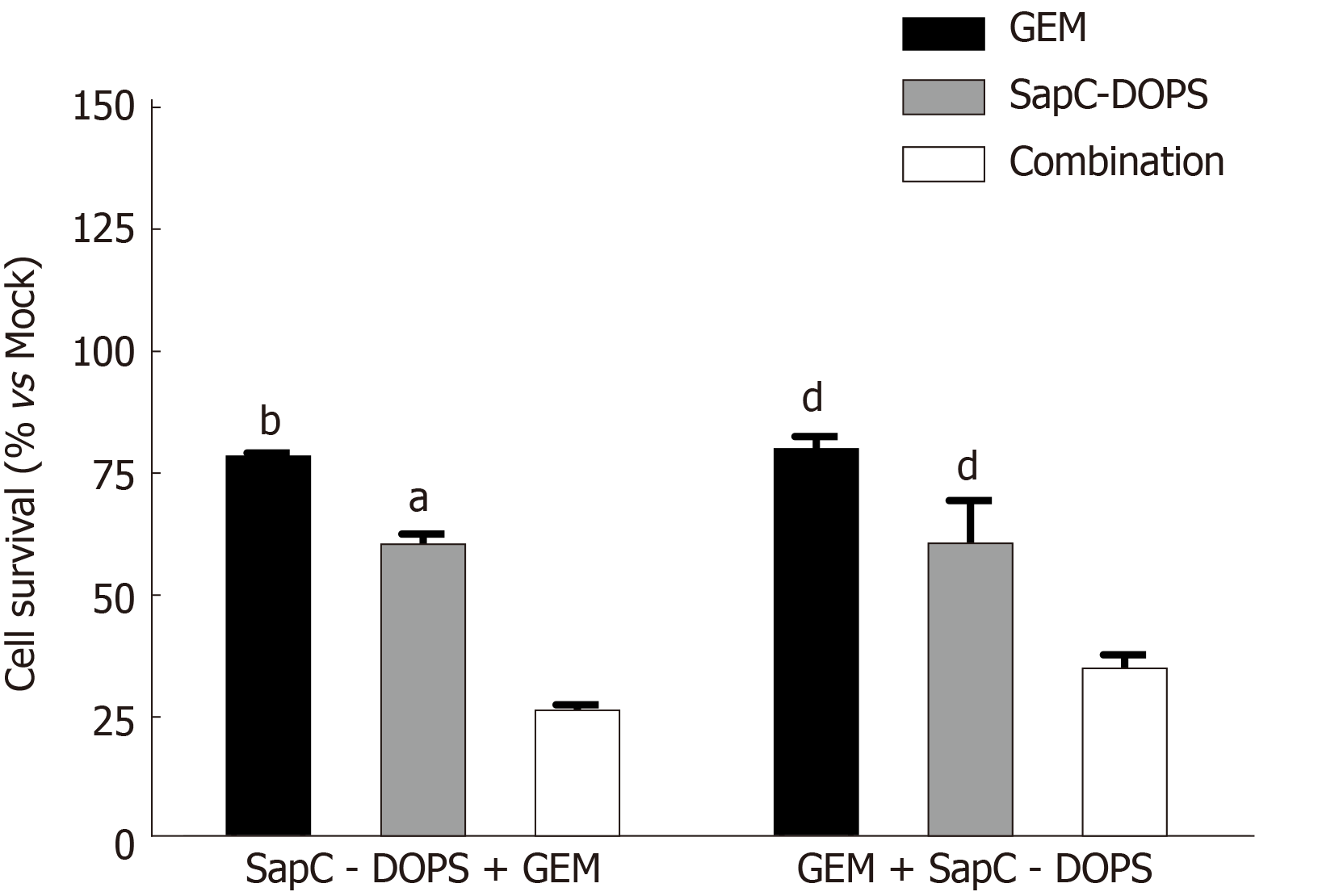
Figure 3 Sequential treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells with saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine nanodrug and gemcitabine.
MiaPaCa-2 cells were treated with saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine (SapC-DOPS) (25 µmol/L) alone, gemcitabine (GEM) (50 nmol/L) alone or in combination. Cells were seeded onto 96 well plates and the next day were exposed to drugs. In the left grouping SapC-DOPS was added for 48 h, the cells were washed twice then incubated with GEM for 24 h. In the right grouping the cells were treated with GEM for 24 h, washed twice and SapC-DOPS was added for 48 h. Untreated cells remained in the media for 72 h. After the 72 h incubation, the MTT cell viability assay was performed. Data are presented as the mean ± SE of the mean, and were compared between two groups using t-test. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs combination group; dP < 0.01 vs combination group. GEM: Gemcitabine; SapC-DOPS: Saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine.
Figure 4 Variable surface phosphatidylserine on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumor cells are sensitive to phosphatidylserine-selective treatments.
Chemotherapy and radiation target primarily low surface phosphatidylserine (PS) cells and may increase PS. Saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine (SapC-DOPS) hones in on high surface PS cells in the acidic tumor microenvironment. Thus, a combination of chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy and SapC-DOPS has the potential to eliminate the preponderance of tumor cells. PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
- Citation: Davis HW, Kaynak A, Vallabhapurapu SD, Qi X. Targeting of elevated cell surface phosphatidylserine with saposin C-dioleoylphosphatidylserine nanodrug as individual or combination therapy for pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(6): 550-559
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i6/550.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.550