Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2021; 13(6): 536-549
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.536
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.536
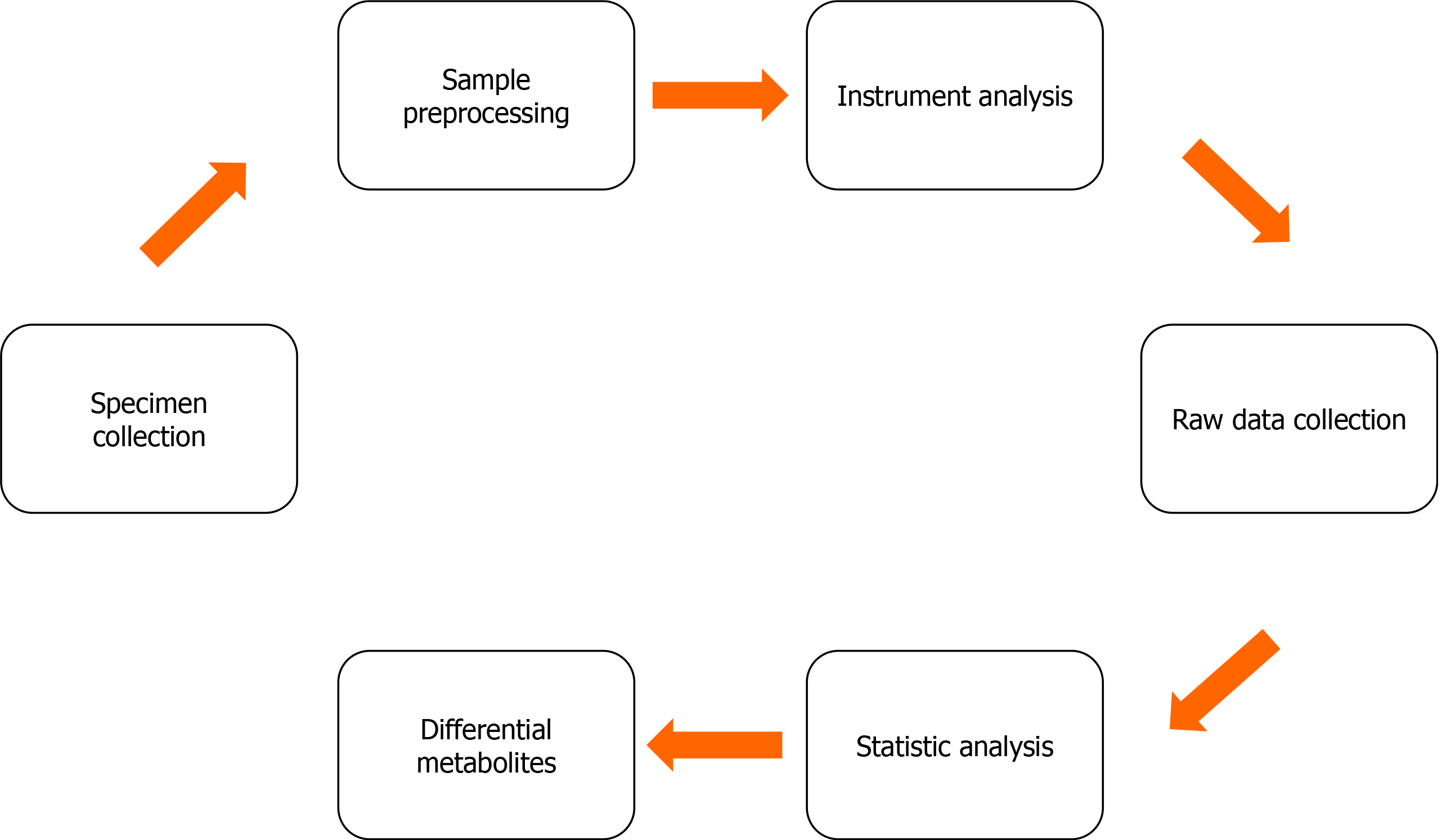
Figure 1 The basic workflow of metabolomics.
Samples aiming at different purposes are first collected. The applicable specimen types include blood, biopsy, biofluid, cell, and urine samples. Some specimens must be preprocessed before they are analyzed with various equipment. The manipulations include metabolite extraction, condensation, or derivatization as possible. The metabolomics data are usually collected with the corresponding software equipped with the instruments. Some software also provides data pre-procession (e.g., to remove noise signals) and statistical analysis functions. The differential metabolites are first screened out by statistical methods. These selected metabolites should be verified using another set of samples if possible. It is better to ascertain the concentration changes of each metabolite using a robust quantitation method.
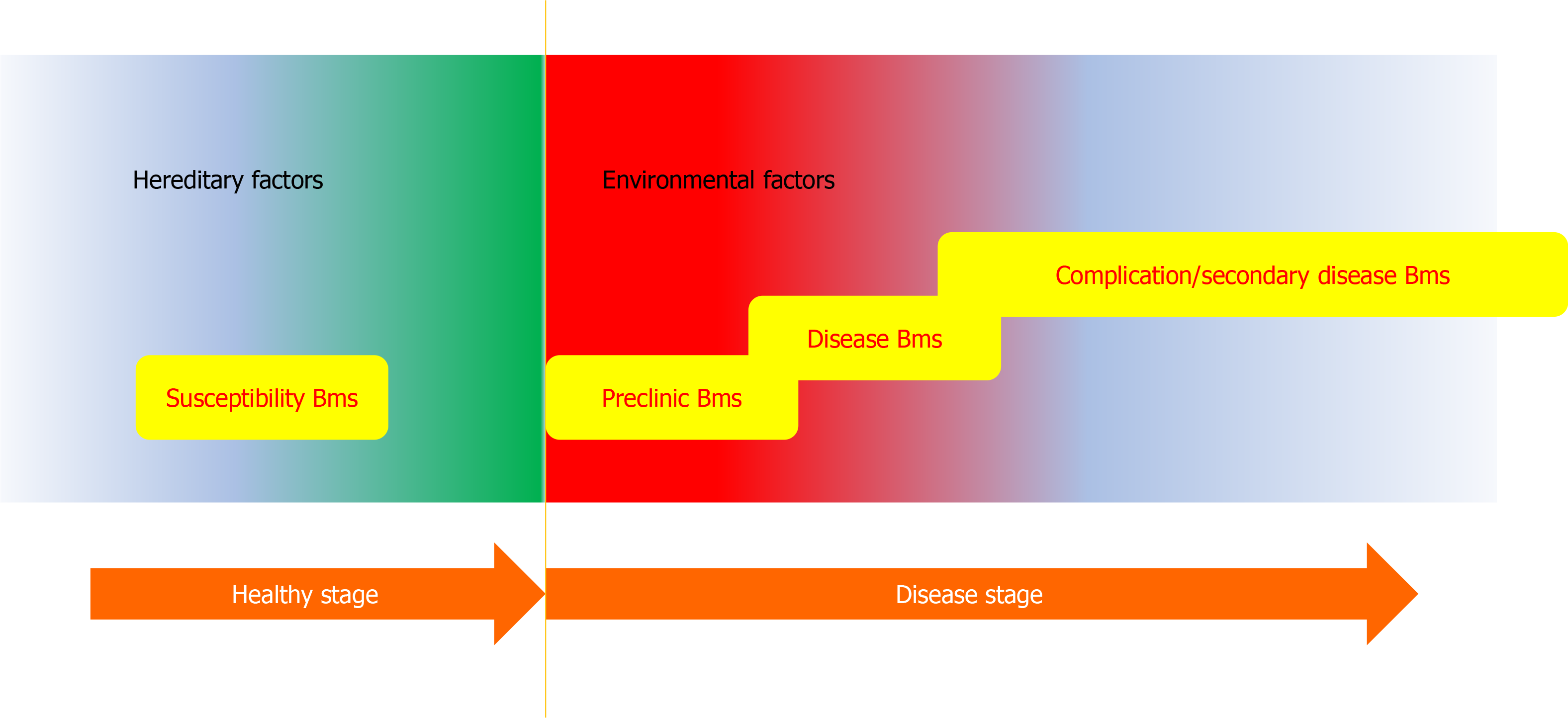
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the fluctuation of biomarker in the whole period of a disease.
Disease susceptibility is usually defined by the individual’s genetic background. The susceptibility biomarker (Bms) can be detected by genetic analysis most possibly. The onset of the disease would be triggered by many environmental factors. At the very beginning (preclinical stage), some prediction Bms appears. When a disease progresses to the clinical stage (with clear symptoms) the diagnosis Bms could be detected. If the disease advances further, some complications and secondary hurts would emerge. These end events give birth to the opportunities to develop the relevant Bms. Metabolomics could be applied to the whole disease period. Besides, prognosis and treatment efficacy Bms could also be explored by metabolomic analysis.
- Citation: Gao P, Huang X, Fang XY, Zheng H, Cai SL, Sun AJ, Zhao L, Zhang Y. Application of metabolomics in clinical and laboratory gastrointestinal oncology. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(6): 536-549
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i6/536.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.536