Published online May 16, 2023. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v15.i5.338
Peer-review started: December 28, 2022
First decision: February 8, 2023
Revised: February 24, 2023
Accepted: April 12, 2023
Article in press: April 12, 2023
Published online: May 16, 2023
Processing time: 138 Days and 22 Hours
A review of the development of the key performance metrics of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), learning from the experience of the establishment of widespread colonoscopy quality measurements. Potential future performance markers for both colonoscopy and EMR are also evaluated to ensure continued high quality performance is maintained with a focus service framework and predictors of patient outcome.
Core Tip: Colonoscopy quality and key performance indicators (KPIs) are a mainstay of endoscopy practice. Adherence to colonoscopy KPIs is important for trainees and consultant endoscopists and is closely linked to patient outcomes. High quality colonoscopy often yields complex polyps, the management of which is now primarily endoscopic. Endoscopic resection of complex polyps thus requires similar scrutiny to diagnostic colonoscopy, to ensure consistent standards are applied. In this review, we discuss existing colonoscopy quality indicators, evaluate some potential new markers and the evidence base for KPIs in the management of complex polyps.
- Citation: Keating E, Leyden J, O'Connor DB, Lahiff C. Unlocking quality in endoscopic mucosal resection. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2023; 15(5): 338-353
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v15/i5/338.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v15.i5.338
Colonoscopy has proven benefit in screening for colorectal cancer and pre-malignant polyps, as well as utility in symptomatic populations for the detection and management of significant non-malignant pathologies[1,2]. Providing access to high-quality colonoscopy is an ongoing challenge for health services internationally. Ensuring that colonoscopy is performed to an acceptable standard requires an open framework of assessment of service and endoscopist performance as well as feedback mechanisms and training supports to improve quality.
International guidelines recommend a range of key performance indicators (KPIs) for colonoscopy which are evidence based and aim to quality assure and standardise the delivery of colonoscopy to patients. Technological advances as well as adoption of KPI standards have resulted in consistent improvements in colonoscopy quality over time[3,4].
While quality assurance in colonoscopy has become part of routine clinical care and service development, equivalent quality assurance standards in therapeutic procedures have yet to be achieved. These procedures carry significantly increased risk of complications compared to diagnostic endoscopy.
The specialised field of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) has developed to allow safe management of complex or large non-pedunculated colorectal polyps (LNPCPs), which traditionally required surgery. Originally pioneered by Japanese endoscopists in the 1990s to facilitate resection of early gastric cancers[5], EMR was subsequently demonstrated to be effective in all areas of the gastrointestinal tract. An initial review on the efficacy of EMR in all areas of the gastrointestinal tract was conducted by the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) in 2008, followed by a second technical analysis in 2015[6,7]. The British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) also produced an initial guideline in 2015 to assess colonic EMR performance in Western populations and was the first to establish recommended key performance indicators to assess EMR practitioners[8]. This was followed by European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) recommendations in 2017, which included a framework for referral practices, equipment and peri-procedural management, in addition to strategies to improve performance, minimise complications and reduce the risk of recurrence for LNPCPs[9].
Quality assurance for EMR remains a challenge in day-to-day practice and the organisation of services in most settings has yet to allow for a robust framework to develop in a similar manner to diagnostic colonoscopy. In this article we will review the evidence for established and aspirational colonoscopy KPIs as well as discussing quality assurance metrics for endoscopic resection of LNPCPs, and training considerations.
Successful colonoscopic evaluation for colorectal pathology must adequately survey all anatomical areas of the colon. As the anatomical endpoint of the colon, intubation of the caecum confirms that the colonoscope has successfully traversed the remainder the colon. Caecal intubation has been demonstrated to significantly affect the detection of proximal colorectal cancers[10,11].
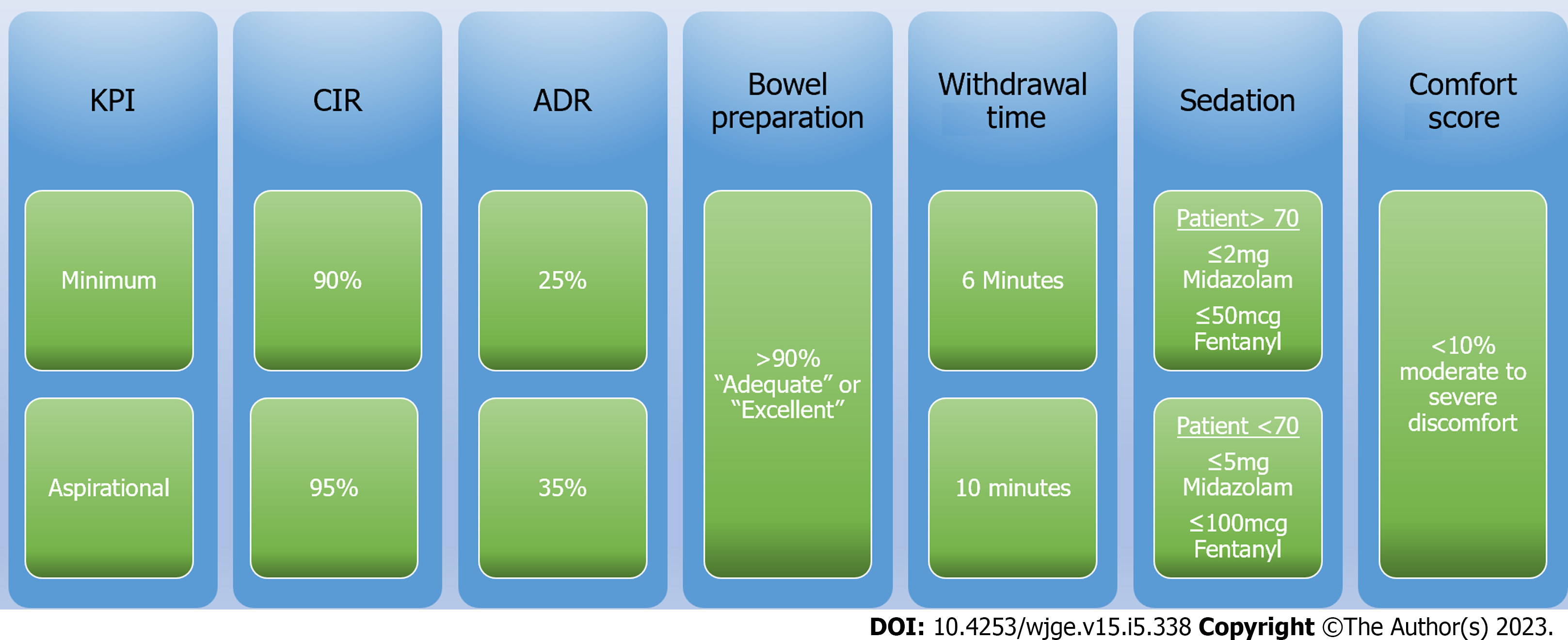
Current guidelines recommend a minimum caecal intubation rate (CIR) of greater than 90% for all intended full colonoscopies with an aspirational target of greater than 95%[12-14]. Caecal intubation is confirmed with the identification of the anatomical landmarks of the appendiceal orifice, tri-radiate fold and ileo-caecal valve. Photographic or video recording of these landmarks should be completed to document caecal intubation. Higher quality caecal landmark photographs, associated with higher quality endoscopy, have also been shown to have a higher polyp detection rate[15,16].
The adenoma detection rate (ADR) is defined as the proportion of patients where at least one adenoma is found among all patients examined by an endoscopist[14]. Higher ADR has an inverse relationship with interval colorectal cancer development[4,17]. ADR has thus been proposed as an important quality indicator for mucosal inspection[18].
While previous BSG guidelines had suggested a minimum ADR of 15% with an aspirational goal of 20%, the most recent 2021 American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) guidelines have suggested a target minimum ADR of 30% with an aspirational target of 35%[12,13]. Similar ESGE guidelines have offered a minimum ADR target of 25%[14]. ADR amongst endoscopists is known to vary significantly with reported overall adenoma miss rates of 17% to 26%[19-22]. Corley et al[17] demonstrated that achieving a 1% improvement in ADR correlates with a 3% decrease in the risk of post colonoscopy colorectal cancer. Therefore, strategies to even marginally improve ADR, particularly amongst endoscopists with lower ADRs, can potentially yield the greatest benefit for patients.
Adenoma rates are recognised to vary depending on patient demographics such as age and indication for colonoscopy[23]. Increasing age is consistently associated with increased adenoma occurrence, across all ethnicities, demonstrated in studies of black, Caucasian, Middle Eastern and Asian populations[23-26]. However adjustment to target ADRs is not generally required, but may be factored in to post-hoc reviews of endoscopist performance should this KPI fall short on an individual basis[27].
A concern has been raised at the potential for endoscopist manipulation of the binary mechanic of ADR through a “one and done” approach[28]. However, the prevalence of such behaviour was found to be infrequent and did not require a change to measuring ADR as a quality assurance indicator[29]. Suggested alternative quality metrics such as adenoma per colonoscopy (APC), have been considered to improve reliability[30-33] and are reported in parallel with ADR routinely in endoscopic trials.
To confidently assess the bowel mucosa, adequate bowel cleansing is required. Polyethylene Glycol is the bowel cleansing regimen most commonly prescribed, formulated into a high (> 3 L) or low (< 3 L) volumes depending on patient factors such as fluid balance restrictions. Suboptimal bowel preparation is associated with lower ADRs and increased hospital costs[34,35]. Published rates of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy approach 25%[36]. The causes of poor bowel preparation are multifactorial and include age, educational level and sex, in addition to hospital inpatient colonoscopies[37]. Adequate bowel preparation, defined as the ability of an endoscopist to detect adenomas > 5 mm in size[38], requires patient understanding of and adherence to strict dietary and medication regimens for up to 24 hours prior to a colonoscopy. Timing of procedures to align with bowel preparation is another factor with same-day administration encouraged and colonoscopies ideally scheduled not more than 5 hours after commencement of the final sachet of preparation.
Strategies to improve dietary compliance, encourage patient education and medication tolerance have been trialled, leading to ESGE guidelines on recommended practice[37,39]. A recommended target of over 90% ‘adequate’ or ‘excellent’ bowel preparation has been proposed to be measured as a unit KPI[4,14].
Colonic mucosal inspection is primarily completed during colonoscope withdrawal post caecal intubation. The time allocated from caecal examination to removal of colonoscope from the rectum is recorded as the colonoscopy withdrawal time (CWT). CWT > 6 min is associated with a significant increase in ADR[19,40,41]. Conversely a CWT of < 6 min is linked to increased risk of interval colorectal cancer[42].
For expert endoscopists, defined as over 3000 procedures[19], the increase in ADR plateaus at a CWR of > 10 min[43]. For trainee endoscopists however, a CWT of greater than 10 min may be beneficial[44]. Thus, the recommendation is for a minimum CWT of 6 minutes and an aspirational target of 10 min[12-14].
Artificial intelligence (AI) is likely to play a role here in the near future. The introduction of a CWT speedometer, warning endoscopists of rapid withdrawal, inserted into the overlay of the endoscopic image, was successful in significantly improving the ADR versus standard colonoscopy in a recent Chinese study (24.54% vs 14.76%)[45].
The majority of colonoscopies are completed using pharmacological sedatives. Standard practice targets conscious sedation achieved via a combination of benzodiazepine (most commonly midazolam or diazepam) and opioid (most commonly fentanyl or pethidine) administration. Acceptable sedation targets require factoring in the patient age, in addition to co-morbidities. The BSG has a recommended sedation of ≤ 2 mg of midazolam (or equivalent) and ≤ 50 micrograms of fentanyl (or equivalent) in patients over the age of 70. In patients under 70, the recommended sedative dose is ≤ 5 mg of midazolam and ≤ 100 mcg of fentanyl[12]. The ASGE guidelines also recommend the use of a combination of opioid and benzodiazepine but do not specify a recommended dose[46].
These targets for sedation were included in the Performance Indicator of Colonic Intubation (PICI) study as a collective indicator of endoscopist performance[47]. This devised a binary outcome based on caecal intubation, patient comfort and sedation administered. Valori et al[48] showed that a PICI positive colonoscopy was significantly associated with a higher polyp detection rate (PDR). However, the real world practice of sedation for colonoscopy has significant geographical variation and PICI outcomes may therefore be difficult to standardise internationally.
Digital rectal examination, or justification for omission is recommended in 100% of procedures by the BSG guidelines[12]. This prepares the anal canal for the entry of the colonoscope and may provide tactile information to the endoscopist of potential strictures or pathology which may impede colonoscope insertion.
Rectal retroflexion was demonstrated to be useful in the detection of low rectal pathology in the 1980s[49]. Consequently, it has been taught to all endoscopists and a target retroflexion rate of 90% has been proposed as a KPI[12]. However, the diagnostic yield of retroflexion has been demonstrated to be minimal[50,51]. Retroflexion can rarely cause perforation[52] and this needs to be considered in the context of patient factors.
An acceptable minimum volume of procedures to achieve colonoscopy proficiency has been suggested at 200 procedures[12,53]. However studies on competency curves have identified a range from 233 to 500 procedures to achieve reliable CIR of > 90%[54-57]. This suggests that the currently accepted volume is slightly below the mean number of procedures required for colonoscopy training.
Similarly, the volume of procedures required to maintain competence has been recommended at 100 procedure per year but evidence suggests a higher target of 200 procedures per year is beneficial[58]. Quality indicators including CIR and ADR are shown to be significantly associated with annual colonoscopy volume and would advocate for a higher competency maintenance target of 250 procedures[59].
Recording of accurate comfort scores is essential to maintaining a patient centred service. Patients with positive experiences during colonoscopy are more likely to return and re-engage with services[60]. The accurate estimation of comfort scores is challenging due to the subjective nature of discomfort[61,62]. Multiple endoscopic comfort-scoring systems are available. These include subjective reporting of discomfort (e.g., Modified Gloucester Comfort Scale) and objective scales (e.g., St Pauls Endoscopy Comfort Scale)[63,64]. Current BSG guidelines recommend frequent auditing of comfort scores in endoscopy and targeting < 10% moderate or severe discomfort in patients[12].
Comfort scores are recorded on the endoscopy reporting system and evidence suggests comfort scores are best provided by the endoscopy nurse. Inter-operator agreement on comfort scores is recognised to be inconsistent, particularly during periods of increased patient discomfort[65]. Nurse recorded comfort levels are strongly correlated with patient reported comfort scores[66].
Overall, endoscopists with lower average comfort scores have associated higher rates of CIR and lower sedation scores. Similarly, higher annual procedural volume are associated with lower comfort scores[66].
Colonoscopy has been considered to be more effective at preventing left sided colorectal cancers than right sided cancers[67]. The higher rate of post colonoscopy colorectal cancers occurring in the right colon is thought to relate to missed adenomas at the index colonoscopy[68-70]. This has led to evaluation of strategies considered to enhance right colon visualisation.
Prolonged examination of the right colon may occur in anterograde view or in retroflexion. Both methods are demonstrated to increase the ADR[71,72]. Research into the use of RCR in increasing ADR significantly over multiple anterograde views has had mixed results[73-76]. Case studies have demonstrated that RCR can also be associated with colonic perforation[77]. In the absence of significant benefit over 2nd anterograde colonic intubation, RCR has not yet been recommended as a standard approach. Second look antegrade examination is favoured by many, with potential benefit using image-enhancement to support the second withdrawal[78].
Anti-spasmodic agents such as hyoscine-n-butylbromide or glucagon are used by some endoscopists as smooth muscle relaxants to reduce mucosal folds and enhance colonic surface area exposure. Regular or intermittent usage of hyoscine during endoscopy as an has been reported by 86% of endoscopists in the United Kingdom[79].
Initial studies suggested that hyoscine use trends towards elevated ADR[80]. As such, it was included in the quality improvement in colonoscopy study bundle which showed a benefit when used with other adjuncts in colonoscopy[81,82]. Meta-analysis of the use of hyoscine in isolation however, has not been demonstrated to significantly affect the ADR[83-85]. Hyoscine is recognised to be associated with cardiac dysrhythmias and haemodynamic instability in patients with pre-existing cardiac conditions such as heart failure and its use in these patients is cautioned against.
Simethicone is an emulsifying agent often used to clear bubbles in the gastrointestinal tract[86]. It can be incorporated into the pre-procedural bowel preparation to improve endoscopic visibility[87]. Pre-procedural simethicone administration has shown mixed results on improving ADR[88-90].
Intra-procedural use of simethicone can result in suboptimal decontamination and[91]. Endoscope manufacturers have recommended against the use of intra-procedural simethicone[92]. Position statements from international endoscopic guidelines have cautioned against the intraprocedural use of simethicone whilst advocating for pre-procedural use[93,94].
Patient positional changes during colonoscopy, described as dynamic colonoscopy, refer to rotating the patient, from the left lateral position to a supine, right lateral or prone position intra-procedure. This is facilitated by the endoscopy nurse to ensure a safe positional change occurs. This is a cost neutral, safe and very quick technique, consistently associated with improved CIR, ADR and mucosal views[95-98]. Barriers to positional changes during colonoscopy include patients with arthropathy, spinal injuries or external adjuncts such as percutaneous drains.
Dynamic colonoscopy is recognised to be an effective and achievable adjunct to colonoscopy. At present, it does not feature in endoscopist KPIs, likely due to inability to record and verify accurately.
The image quality of modern colonoscopes has increased dramatically in recent years to incorporate the second generation high definition instruments available today. Magnification is now widely available and further enhances their diagnostic capability. Improved image quality from high definition colonoscopes has been proven to increase ADR[99-101] and also provides in advantages in other areas, including surveillance for Inflammatory Bowel Disease[102]. Virtual chromoendoscopy, such as the use of Narrow Band Imaging (NBI), facilitated by high definition colonoscopes has been shown in meta-analysis to improve ADR[78]. Similar to NBI, blue laser imaging and i-scan have been shown to improve ADR when compared to white light imaging[103-105].
Meta-analysis of CAC versus standard colonoscopy (SC) has demonstrated increased PDR and reduced procedural time[106,107]. CAC has been consistently to achieve higher ADR yields vs SC[108-110], although studies comparing CAC with cheaper adjuncts such as position changes or NBI are lacking. As in many areas of endoscopic research, further head-to-head trials of distal attachment devices would be welcome[111].
While first generation Endocuff can be considered to have equivocal benefit in terms of ADR, with most advantages over SC relating to diminutive polyps, the second generation endocuff vision has shown benefit within screening populations. The well-conducted ADENOMA trial showed a significant improvement in ADR and MAP, without improved detection per unit withdrawal time, suggesting a value in supporting more efficient colonoscopy[112]. Cuff devices have also been shown to be superior to cap-assisted colonoscopy for ADR and lower adenoma miss rates and have particular utility in colon cancer screening[113,114].
Initial single centre trials of CADe have demonstrated positive results with reported increase in ADR with the addition of CADe[115]. However, the increased ADR was primarily due to the detection of non-advanced diminutive and hyperplastic polyps. Recent multi-centre studies indicated a significant improvement in APC and a non-significant trend towards greater ADR with the addition of CADe vs standard colonoscopy[116]. A potential adverse effect of CADe adoption will be the workload associated with diminutive and hyperplastic polyp assessment and removal[117], which can be offset by adoption of a resect and discard strategy, which has proven utility in the hands of specialist endoscopists using AI (CADx) support[118,119].
The ESGE comprehensively assessed both the potential benefits and concerns relating to AI In GI endoscopy and machine learning. Risk of external interference (hacking), endoscopist deskilling, over-reliance on AI and the impact of biased datasets are all raised as concerns regarding AI adoption[120] and mitigation strategies will need to be incorporated as this field develops.
EMR has been demonstrated to be a safe and effective alternative to surgery in the management of LNPCPs. However, early adenoma recurrence post EMR is recognised to occur in 15%-30% of patients[121,122] and necessitates a strict surveillance programme for early identification and resection of residual adenoma.
Recurrence rates are also shown to be dependent on the index resection method. En-bloc resections have a significant lower rate of adenoma recurrence compared to piecemeal[121]. Other factors with regard to recurrence rates include increased adenoma size[123], intra-procedural bleeding (IPB) at time of resection[123] and endoscopist experience[124]. Recurrence rates according to colonic location have demonstrated mixed results, with some studies indicating elevated recurrence rates in proximal locations[125,126], possibly reflecting increased resection difficulty in the right colon. Conversely, Lim et al[127] indicated significantly higher recurrence rates in the distal colon and rectum.
Endoscopic thermal strategies such as snare-tip soft coagulation (STSC) have consistently demo
Recurrence analysis may need to consider the mode of initial resection, with different recurrence rates likely for conventional EMR when compared with other modalities such as underwater EMR[130] and cold piecemeal EMR[131], which is primarily employed for resection of sessile serrated lesions.
Acknowledging the high rates of adenoma recurrence post EMR emphasises the requirement for a reliable surveillance programme. Meta-analysis indicates that 90% of recurrence is detectable by site check colonoscopy 6 months post EMR procedure[121]. Prospective studies, similarly examining surveillance intervals have confirmed the optimal timing of initial surveillance to be 6 months post resection[132]. Recurrence detected at initial surveillance colonoscopy is most commonly unifocal and diminutive[123]. The vast majority of early detected recurrence is suitable for endoscopic management[123,133].
Consolidating the information above, the 2015 BSG guidelines agreed a KPI threshold for recurrence of < 10% at 12 months post EMR with an aspirational target of < 5%[8]. This acknowledges the occurrence of early recurrence which can be managed endoscopically, while also accounting for cases of “late recurrence”, not detected at the initial post-EMR surveillance colonoscopy.
Standard colonoscopy and polypectomy confers an accepted perforation risk of 0.07%-0.19%[134,135]. Although rare, colonic perforation carries a considerable morbidity and mortality burden[136]. Perforation during EMR remains rare, but is higher than standard colonoscopy, and must be addressed specifically during the informed patient consent process. Perforation rates during EMR range from 0.3%-1.3%[7,137,138].
Recognition and early intervention in the management of colonic perforation is essential to optimise patient outcomes[135]. Swan et al[139] described routine close inspection of the mucosal defect to examine for deep muscle injury. The benefit of immediate recognition of a potential MP injury affords the opportunity to apply endoscopic therapies such as clip placement to close defects with a view to minimising further complications[140,141].
Consequently, the BSG workgroup adopted a minimum standard of < 2% perforation rate with an aspirational standard of < 0.5%[8].
The reported incidence of PPB ranges from 2.6%-9.7%[142] but is limited by a lack of consensus definition for PPB. 65% of PPB is apparent within 24 hours of EMR, increasing to 88% at 48 hours[143]. Post procedural bleeding was defined by the BSG working group as rectal bleeding occurring up to 30 days post EMR and could be further subcategorised as minor/intermediate/major or fatal according to the severity. PPB is accepted to be the most common serious complication of EMR procedures and is differentiated from IPB which can be managed endoscopically at the time of EMR.
Risk factors to predict clinically significant PPB were examined by Metz et al[143] in 2011, demonstrating that proximal (right) colonic location compared to distal colon (11.3% vs 3.5%) and antiplatelet therapy were significantly associated with increased risk of PPB.
Electrocautery at the time of EMR, has also been shown to affect the rates and timing of PPB. Higher rates of IPB is associated with the use of pure cutting current as demonstrated by Kim et al[144]. Conversely, a pure coagulation current, with lower risk of intra-procedural bleeding, confers additional risk of delayed-bleeding and potentially also perforation due to transmitted deep thermal injury[145]. The ESGE recommends the use of a blended coagulation/cutting diathermy current for EMR[9].
Heterogeneity amongst study outcomes on the benefit of prophylactic clipping (through the scope clips, TTSC) in preventing PPB led to a meta-analysis which indicated no significant benefit to additional clip placement on PPB rates[146]. Citing the low rate of PPB in the control group of this meta-analysis (2.7%), Albeniz et al[142] conducted a RCT of prophylactic clipping in high risk lesions and demonstrated a non-significant trend towards less PPB. Further investigation by Pohl et al confirmed that prophylactic clipping was beneficial for proximal, large lesions, especially in patients on antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications[147]. The ongoing use of prophylactic clips to prevent TTSC should be patient-specific with recent studies favouring efficacy in clipping to reduce risk of PPB in the right colon[148]. Cost-analysis in this area will by driven by the relative costs of TTSCs and hospital admission costs in different countries, with high levels of variability evident[149].
The ESGE guidelines do not recommend prophylactic clipping as standard post EMR management[9]. However, their guidelines do recognise the need for prophylactic clipping in a subset of high risk patients. A clinical predictive score, “clinically significant bleeding” (CSPEB) was developed by Bahin et al[150], finding lesions > 30 mm in size, proximal location and additional co-morbidities warranted consideration for prophylactic clipping.
With regard to PPB as a performance indicator, the BSG guidelines have set a minimum PPB rate of < 5% to be analysed at both an endoscopist and unit level[8].
Recognising the high risk of potential malignant transformation of LNPCPs, a 28 day cut-off for referral for consideration for EMR has been proposed by the BSG guidelines[8]. This 28 day standard was proposed but no minimum proportional standard has been published or disseminated. There is limited published data indicating compliance with this KPI, making interpretation of its impact challenging. A recommended 56 day period was allocated from referral to definitive endoscopic therapy with no minimum standard suggested as yet.
Audit data on real world clinical practice achievement of these EMR guidelines is necessary to establish the feasibility of the 28 and 56 day rule, respectively.
As discussed above, procedural volume and clinical exposure are recognised contributory factors in colonoscopy performance. Bowel cancer screening programmes require an annual minimum volume of 150 procedures to ensure competency standards are maintained[151,152] although based on evidence discussed above, this may be a conservative Figure 1. Reviewing available literature, an initial training volume of 50 EMRs to establish proficiency with a minimum annual volume of 30 procedures to maintain competency are suggested[153].
Traditionally polyp complexity has been inferred by size, conventionally > 20 mm. Recognising polyp complexity as multifactorial, Gupta et al[154] developed the Size-Morphology-Site-Access (SMSA) score. This score assigns each component a difficulty rating, forming a composite polyp score (SMSA Score), reflecting overall complexity and was evaluated by ESGE. Increased SMSA score accurately predicts recurrence, adverse events and incomplete resection[155]. We suggest that the SMSA score should be reported by all endoscopists when they encounter complex polyps, as they can be useful in planning resection approach, time slots for lists as well as predicting outcome.
STSC is a safe and effective procedural method in reducing recurrence post piecemeal EMR[128] and has been revalidated by a recent 2022 meta-analysis[156]. Due to the strong evidence in favour of STSC use, the majority of endoscopists now employ this method to minimise recurrence. Consequently, the recording of a unit STSC rate as a KPI should be considered.
A reliable surveillance programme is an essential component of an EMR service. Optimal surveillance intervals are established and discussed above but the proportion of patients who successfully complete timely surveillance can vary. Measuring the proportion of patients achieving site checks at appropriate intervals would underline adherence to surveillance programmes and support management of EMR recurrences. Based off the meta-analysis findings of Belderbos et al[121] that 90% of recurrence is detectable at 6 months, we suggest an interval of less than 180 days from date of resection for first site check (SC1) and 18 months from index for SC2, provided SC1 is clear. We further suggest that recurrences should be managed appropriately and in this scenario the next SC interval should again be < 180 days.
EMR has less morbidity, lower complication rates and is associated with shorter hospital stays compared to surgical resection[157] for benign polyps. However, recognising that EMR may not be possible in a proportion of referred patients, measurement of surgical referral rates were recommended by the BSG guidelines in 2015[8]. This is another area which may benefit from accurate SMSA assessment at index referral. Similarly, the rate of incomplete resection and subsequent surgical referral are a necessary performance indicator of EMR quality. This metric needs to incorporate the complexity of EMRs undertaken and should be subject to regular audit.
The focus on gastrointestinal endoscopy quality assurance and improvement has led to the development of standardised colonoscopy key performance indicators such as caecal intubation rate and adenoma detection rates[158]. The rapid endorsement of KPIs by international endoscopy societies[159] led to the widespread adoption of these benchmarks. New candidates for colonoscopy KPIs have since emerged and the arrival of artificial intelligence to general colonoscopy practice is likely to influence the field over the coming years.
Today, colonoscopy KPIs are valuable to ensure adequate endoscopist performance, identify underperforming practitioners and to target training interventions. Colonoscopy KPI monitoring and awareness is now instituted from the beginning of endoscopy training and regular audits are completed to ensure unit performance is adequate.
However, the adoption and widespread acceptance of endoscopic performance metrics has not permeated equally through all fields of endoscopy. Guidelines examining performance in gastroscopy have been detailed but adherence to these KPIs is suboptimal[160,161]. Specifically with regard to advanced endoscopic procedures, although publications recommending minimum standard practices have been available since 2015 for EMR, there is yet to be a similar consensus push towards outcome monitoring.
One of the challenges to KPI implementation for EMR is the limitation of endoscopy reporting systems. Continuous monitoring of complex data and surveillance metrics requires significant resource and it is not yet clear how we might achieve this. The collation and review of complication and, recurrence rates as well as referral timelines requires significant time, adding to endoscopist workload.
Quality assurance in endoscopy will always require practitioner performance measurement through KPIs. Both patients and the endoscopy community have benefited from the introduction and participation in colonoscopy KPIs. Replicating these enhanced standards of performance measurement in therapeutic endoscopy is therefore a logical next step in the evolution of endoscopy.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Corresponding Author's Membership in Professional Societies: Irish Society of Gastroenterology.
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Ireland
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Castro FJ, United States; Okasha H, Egypt S-Editor: Ma YJ L-Editor: A P-Editor: Cai YX
| 1. | Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Ho MN, O'Brien MJ, Gottlieb LS, Sternberg SS, Waye JD, Schapiro M, Bond JH, Panish JF. Prevention of colorectal cancer by colonoscopic polypectomy. The National Polyp Study Workgroup. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1977-1981. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3107] [Cited by in RCA: 3128] [Article Influence: 97.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 2. | Leighton JA, Shen B, Baron TH, Adler DG, Davila R, Egan JV, Faigel DO, Gan SI, Hirota WK, Lichtenstein D, Qureshi WA, Rajan E, Zuckerman MJ, VanGuilder T, Fanelli RD; Standards of Practice Committee, American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. ASGE guideline: endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:558-565. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 173] [Cited by in RCA: 161] [Article Influence: 8.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Rees CJ, Bevan R, Zimmermann-Fraedrich K, Rutter MD, Rex D, Dekker E, Ponchon T, Bretthauer M, Regula J, Saunders B, Hassan C, Bourke MJ, Rösch T. Expert opinions and scientific evidence for colonoscopy key performance indicators. Gut. 2016;65:2045-2060. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Kaminski MF, Regula J, Kraszewska E, Polkowski M, Wojciechowska U, Didkowska J, Zwierko M, Rupinski M, Nowacki MP, Butruk E. Quality indicators for colonoscopy and the risk of interval cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1795-1803. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1287] [Cited by in RCA: 1468] [Article Influence: 97.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Soetikno RM, Gotoda T, Nakanishi Y, Soehendra N. Endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57:567-579. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 406] [Cited by in RCA: 378] [Article Influence: 17.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | ASGE Technology Committee; Kantsevoy SV, Adler DG, Conway JD, Diehl DL, Farraye FA, Kwon R, Mamula P, Rodriguez S, Shah RJ, Wong Kee Song LM, Tierney WM. Endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:11-18. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 236] [Cited by in RCA: 220] [Article Influence: 12.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | ASGE Technology Committee; Hwang JH, Konda V, Abu Dayyeh BK, Chauhan SS, Enestvedt BK, Fujii-Lau LL, Komanduri S, Maple JT, Murad FM, Pannala R, Thosani NC, Banerjee S. Endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:215-226. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 110] [Cited by in RCA: 126] [Article Influence: 12.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Rutter MD, Chattree A, Barbour JA, Thomas-Gibson S, Bhandari P, Saunders BP, Veitch AM, Anderson J, Rembacken BJ, Loughrey MB, Pullan R, Garrett WV, Lewis G, Dolwani S. British Society of Gastroenterology/Association of Coloproctologists of Great Britain and Ireland guidelines for the management of large non-pedunculated colorectal polyps. Gut. 2015;64:1847-1873. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 126] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 12.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Ferlitsch M, Moss A, Hassan C, Bhandari P, Dumonceau JM, Paspatis G, Jover R, Langner C, Bronzwaer M, Nalankilli K, Fockens P, Hazzan R, Gralnek IM, Gschwantler M, Waldmann E, Jeschek P, Penz D, Heresbach D, Moons L, Lemmers A, Paraskeva K, Pohl J, Ponchon T, Regula J, Repici A, Rutter MD, Burgess NG, Bourke MJ. Colorectal polypectomy and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy. 2017;49:270-297. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 559] [Cited by in RCA: 766] [Article Influence: 95.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Brenner H, Chang-Claude J, Seiler CM, Hoffmeister M. Interval cancers after negative colonoscopy: population-based case-control study. Gut. 2012;61:1576-1582. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 131] [Cited by in RCA: 141] [Article Influence: 10.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Hilsden RJ, Dube C, Heitman SJ, Bridges R, McGregor SE, Rostom A. The association of colonoscopy quality indicators with the detection of screen-relevant lesions, adverse events, and postcolonoscopy cancers in an asymptomatic Canadian colorectal cancer screening population. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:887-894. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Rees CJ, Thomas Gibson S, Rutter MD, Baragwanath P, Pullan R, Feeney M, Haslam N; British Society of Gastroenterology, the Joint Advisory Group on GI Endoscopy, the Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland. UK key performance indicators and quality assurance standards for colonoscopy. Gut. 2016;65:1923-1929. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 169] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 25.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Keswani RN, Crockett SD, Calderwood AH. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Strategies to Improve Quality of Screening and Surveillance Colonoscopy: Expert Review. Gastroenterology. 2021;161:701-711. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 24.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Kaminski MF, Thomas-Gibson S, Bugajski M, Bretthauer M, Rees CJ, Dekker E, Hoff G, Jover R, Suchanek S, Ferlitsch M, Anderson J, Roesch T, Hultcranz R, Racz I, Kuipers EJ, Garborg K, East JE, Rupinski M, Seip B, Bennett C, Senore C, Minozzi S, Bisschops R, Domagk D, Valori R, Spada C, Hassan C, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Rutter MD. Performance measures for lower gastrointestinal endoscopy: a European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Quality Improvement Initiative. Endoscopy. 2017;49:378-397. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 337] [Cited by in RCA: 486] [Article Influence: 60.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Thoufeeq MH, Rembacken BJ. Meticulous cecal image documentation at colonoscopy is associated with improved polyp detection. Endosc Int Open. 2015;3:E629-E633. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Rees C, Neilson L. Demonstrating that colonoscopy is high quality. Endosc Int Open. 2015;3:E634-E635. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Corley DA, Jensen CD, Marks AR, Zhao WK, Lee JK, Doubeni CA, Zauber AG, de Boer J, Fireman BH, Schottinger JE, Quinn VP, Ghai NR, Levin TR, Quesenberry CP. Adenoma detection rate and risk of colorectal cancer and death. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1298-1306. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1251] [Cited by in RCA: 1561] [Article Influence: 141.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Rex DK, Schoenfeld PS, Cohen J, Pike IM, Adler DG, Fennerty MB, Lieb JG 2nd, Park WG, Rizk MK, Sawhney MS, Shaheen NJ, Wani S, Weinberg DS. Quality indicators for colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:72-90. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 289] [Cited by in RCA: 357] [Article Influence: 35.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Barclay RL, Vicari JJ, Doughty AS, Johanson JF, Greenlaw RL. Colonoscopic withdrawal times and adenoma detection during screening colonoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2533-2541. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 911] [Cited by in RCA: 951] [Article Influence: 50.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Atkin W, Rogers P, Cardwell C, Cook C, Cuzick J, Wardle J, Edwards R. Wide variation in adenoma detection rates at screening flexible sigmoidoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:1247-1256. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 119] [Cited by in RCA: 123] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Zhao S, Wang S, Pan P, Xia T, Chang X, Yang X, Guo L, Meng Q, Yang F, Qian W, Xu Z, Wang Y, Wang Z, Gu L, Wang R, Jia F, Yao J, Li Z, Bai Y. Magnitude, Risk Factors, and Factors Associated With Adenoma Miss Rate of Tandem Colonoscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1661-1674.e11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 205] [Cited by in RCA: 376] [Article Influence: 62.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | van Rijn JC, Reitsma JB, Stoker J, Bossuyt PM, van Deventer SJ, Dekker E. Polyp miss rate determined by tandem colonoscopy: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:343-350. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 878] [Cited by in RCA: 917] [Article Influence: 48.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Corley DA, Jensen CD, Marks AR, Zhao WK, de Boer J, Levin TR, Doubeni C, Fireman BH, Quesenberry CP. Variation of adenoma prevalence by age, sex, race, and colon location in a large population: implications for screening and quality programs. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:172-180. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 146] [Cited by in RCA: 190] [Article Influence: 15.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Hemmasi G, Sohrabi M, Zamani F, Ajdarkosh H, Rakhshani N, Khoonsari M, Ameli M, Hatami K. Prevalence of colorectal adenoma in an average-risk population aged 40-50 versus 50-60 years. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2015;24:386-390. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Hussein Kamareddine M, Ghosn Y, Karam K, Nader AA, El-Mahmoud A, Bou-Ayash N, El-Khoury M, Farhat S. Adenoma Detection before and after the age of 50: a retrospective analysis of Lebanese outpatients. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2018;5:e000253. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Pommergaard HC, Burcharth J, Rosenberg J, Raskov H. The association between location, age and advanced colorectal adenoma characteristics: a propensity-matched analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2017;52:1-4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Jensen CD, Doubeni CA, Quinn VP, Levin TR, Zauber AG, Schottinger JE, Marks AR, Zhao WK, Lee JK, Ghai NR, Schneider JL, Fireman BH, Quesenberry CP, Corley DA. Adjusting for patient demographics has minimal effects on rates of adenoma detection in a large, community-based setting. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:739-746. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Wang HS, Pisegna J, Modi R, Liang LJ, Atia M, Nguyen M, Cohen H, Ohning G, van Oijen M, Spiegel BM. Adenoma detection rate is necessary but insufficient for distinguishing high versus low endoscopist performance. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:71-78. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 109] [Cited by in RCA: 112] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Fedewa SA, Anderson JC, Robinson CM, Weiss JE, Smith RA, Siegel RL, Jemal A, Butterly LF. Prevalence of 'one and done' in adenoma detection rates: results from the New Hampshire Colonoscopy Registry. Endosc Int Open. 2019;7:E1344-E1354. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Wang S, Kim AS, Church TR, Perdue DG, Shaukat A. Adenomas per colonoscopy and adenoma per positive participant as quality indicators for screening colonoscopy. Endosc Int Open. 2020;8:E1560-E1565. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Park SK, Kim HY, Lee CK, Cha JM, Eun CS, Han DS, Lee BI, Shin JE, Park DI. Comparison of adenoma detection rate and adenoma per colonoscopy as a quality indicator of colonoscopy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016;51:886-890. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Wieszczy P, Bugajski M, Januszewicz W, Rupinska M, Szlak J, Pisera M, Turkot MH, Rupinski M, Wojciechowska U, Didkowska J, Regula J, Kaminski MF. Comparison of Quality Measures for Detection of Neoplasia at Screening Colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;21:200-209.e6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 12.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Gessl I, Waldmann E, Penz D, Majcher B, Dokladanska A, Hinterberger A, Szymanska A, Ferlitsch A, Trauner M, Ferlitsch M. Evaluation of adenomas per colonoscopy and adenomas per positive participant as new quality parameters in screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89:496-502. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0154149. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 91] [Article Influence: 10.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 35. | Rex DK, Imperiale TF, Latinovich DR, Bratcher LL. Impact of bowel preparation on efficiency and cost of colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:1696-1700. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 395] [Cited by in RCA: 471] [Article Influence: 20.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Harewood GC, Sharma VK, de Garmo P. Impact of colonoscopy preparation quality on detection of suspected colonic neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:76-79. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 524] [Cited by in RCA: 560] [Article Influence: 25.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Hernández G, Gimeno-García AZ, Quintero E. Strategies to Improve Inadequate Bowel Preparation for Colonoscopy. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019;6:245. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, Imaeda A, Ciarleglio MM, Deng Y, Laine L. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:396-405; quiz e14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 108] [Cited by in RCA: 154] [Article Influence: 17.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Hassan C, East J, Radaelli F, Spada C, Benamouzig R, Bisschops R, Bretthauer M, Dekker E, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Ferlitsch M, Fuccio L, Awadie H, Gralnek I, Jover R, Kaminski MF, Pellisé M, Triantafyllou K, Vanella G, Mangas-Sanjuan C, Frazzoni L, Van Hooft JE, Dumonceau JM. Bowel preparation for colonoscopy: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline - Update 2019. Endoscopy. 2019;51:775-794. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 407] [Cited by in RCA: 353] [Article Influence: 58.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (4)] |
| 40. | Simmons DT, Harewood GC, Baron TH, Petersen BT, Wang KK, Boyd-Enders F, Ott BJ. Impact of endoscopist withdrawal speed on polyp yield: implications for optimal colonoscopy withdrawal time. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:965-971. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 153] [Cited by in RCA: 157] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Overholt BF, Brooks-Belli L, Grace M, Rankin K, Harrell R, Turyk M, Rosenberg FB, Barish RW, Gilinsky NH; Benchmark Colonoscopy Group. Withdrawal times and associated factors in colonoscopy: a quality assurance multicenter assessment. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;44:e80-e86. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Shaukat A, Rector TS, Church TR, Lederle FA, Kim AS, Rank JM, Allen JI. Longer Withdrawal Time Is Associated With a Reduced Incidence of Interval Cancer After Screening Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:952-957. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 144] [Cited by in RCA: 181] [Article Influence: 18.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. |
Lee TJW, Blanks RG, Rees CJ, Wright KC, Nickerson C, Moss SM, Chilton A, Goddard AF, Patnick J, McNally RJQ, Rutter MD, Colonoscopy withdrawal time and adenoma detection rate in screening colonoscopy: the optimum average withdrawal time is 10 min.
|
| 44. | Gromski MA, Miller CA, Lee SH, Park ES, Lee TH, Park SH, Chung IK, Kim SJ, Hwangbo Y. Trainees' adenoma detection rate is higher if ≥ 10 minutes is spent on withdrawal during colonoscopy. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:1337-1342. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Yao L, Zhang L, Liu J, Zhou W, He C, Zhang J, Wu L, Wang H, Xu Y, Gong D, Xu M, Li X, Bai Y, Gong R, Sharma P, Yu H. Effect of an artificial intelligence-based quality improvement system on efficacy of a computer-aided detection system in colonoscopy: a four-group parallel study. Endoscopy. 2022;54:757-768. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 20.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | ASGE Standards of Practice Committee; Early DS, Lightdale JR, Vargo JJ 2nd, Acosta RD, Chandrasekhara V, Chathadi KV, Evans JA, Fisher DA, Fonkalsrud L, Hwang JH, Khashab MA, Muthusamy VR, Pasha SF, Saltzman JR, Shergill AK, Cash BD, DeWitt JM. Guidelines for sedation and anesthesia in GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:327-337. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 247] [Cited by in RCA: 363] [Article Influence: 51.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Valori RM, Damery S, Gavin DR, Anderson JT, Donnelly MT, Williams JG, Swarbrick ET. A new composite measure of colonoscopy: the Performance Indicator of Colonic Intubation (PICI). Endoscopy. 2018;50:40-51. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Nass KJ, van Doorn SC, van der Vlugt M, Fockens P, Dekker E. Impact of sedation on the Performance Indicator of Colonic Intubation. Endoscopy. 2021;53:619-626. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Grobe JL, Kozarek RA, Sanowski RA. Colonoscopic retroflexion in the evaluation of rectal disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1982;77:856-858. [PubMed] |
| 50. | Saad A, Rex DK. Routine rectal retroflexion during colonoscopy has a low yield for neoplasia. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:6503-6505. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 51. | Téllez-Ávila F, Barahona-Garrido J, García-Osogobio S, López-Arce G, Camacho-Escobedo J, Saúl A, Herrera-Gómez S, Elizondo-Rivera J, Barreto-Zúñiga R. Diagnostic yield and therapeutic impact of rectal retroflexion: a prospective, single-blind study conducted in three centers. Clin Endosc. 2014;47:79-83. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 52. | Quallick MR, Brown WR. Rectal perforation during colonoscopic retroflexion: a large, prospective experience in an academic center. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:960-963. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Joint Advisory Group on Gastrointestinal. JAG Certification criteria and application process. 2021. Available from: https://www.thejag.org.uk/Downloads/JAG/JAG%20certification/JETS%20certification%20pathways%20-%202022%20update.pdf. |
| 54. | Ward ST, Mohammed MA, Walt R, Valori R, Ismail T, Dunckley P. An analysis of the learning curve to achieve competency at colonoscopy using the JETS database. Gut. 2014;63:1746-1754. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 98] [Cited by in RCA: 117] [Article Influence: 10.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 55. | Spier BJ, Benson M, Pfau PR, Nelligan G, Lucey MR, Gaumnitz EA. Colonoscopy training in gastroenterology fellowships: determining competence. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71:319-324. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 118] [Cited by in RCA: 134] [Article Influence: 8.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | Sedlack RE. Training to competency in colonoscopy: assessing and defining competency standards. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74:355-366.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 98] [Cited by in RCA: 110] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 57. | Stanford SB, Lee S, Masaquel C, Lee RH. Achieving competence in colonoscopy: Milestones and the need for a new endoscopic curriculum in gastroenterology training. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;7:1279-1286. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 58. | Harewood GC. Relationship of colonoscopy completion rates and endoscopist features. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:47-51. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 59. | Pace D, Borgaonkar M, Lougheed M, Marcoux C, Evans B, Hickey N, O'Leary M, Boone D, McGrath J. Effect of Colonoscopy Volume on Quality Indicators. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;2016:2580894. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 60. | Ko HH, Zhang H, Telford JJ, Enns R. Factors influencing patient satisfaction when undergoing endoscopic procedures. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:883-891, quiz 891.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 88] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Rafferty H, Hutchinson J, Ansari S, Smith LA. PWE-040 Comfort scoring for endoscopic procedures: who is right – the endoscopist, the nurse or the patient? Gut. 2014;63:139-140. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 62. | Rostom A, Ross ED, Dubé C, Rutter MD, Lee T, Valori R, Bridges RJ, Pontifex D, Webbink V, Rees C, Brown C, Whetter DH, Kelsey SG, Hilsden RJ. Development and validation of a nurse-assessed patient comfort score for colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:255-261. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 63. | Telford J, Tavakoli I, Takach O, Kwok R, Harris N, Yonge J, Galorpart C, Whittaker S, Amar J, Rosenfeld G, Ko HH, Lam E, Ramji A, Bressler B, Enns R. Validation of the St. Paul's Endoscopy Comfort Scale (SPECS) for Colonoscopy. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2020;3:91-95. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 64. | Ball AJ, Rees CJ, Corfe BM, Riley SA. Sedation practice and comfort during colonoscopy: lessons learnt from a national screening programme. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;27:741-746. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 65. | Naumann DN, Potter-Concannon S, Karandikar S. Interobserver variability in comfort scores for screening colonoscopy. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2019;10:372-378. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 66. | Ekkelenkamp VE, Dowler K, Valori RM, Dunckley P. Patient comfort and quality in colonoscopy. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:2355-2361. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 54] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 67. | Brenner H, Hoffmeister M, Arndt V, Stegmaier C, Altenhofen L, Haug U. Protection from right- and left-sided colorectal neoplasms after colonoscopy: population-based study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102:89-95. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 409] [Cited by in RCA: 419] [Article Influence: 27.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 68. | Bressler B, Paszat LF, Chen Z, Rothwell DM, Vinden C, Rabeneck L. Rates of new or missed colorectal cancers after colonoscopy and their risk factors: a population-based analysis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:96-102. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 442] [Cited by in RCA: 449] [Article Influence: 24.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Singh H, Nugent Z, Demers AA, Kliewer EV, Mahmud SM, Bernstein CN. The reduction in colorectal cancer mortality after colonoscopy varies by site of the cancer. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1128-1137. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 341] [Cited by in RCA: 373] [Article Influence: 24.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 70. | Rabeneck L, Davila JA, El-Serag HB. Is there a true "shift" to the right colon in the incidence of colorectal cancer? Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1400-1409. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 90] [Cited by in RCA: 97] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Desai M, Bilal M, Hamade N, Gorrepati VS, Thoguluva Chandrasekar V, Jegadeesan R, Gupta N, Bhandari P, Repici A, Hassan C, Sharma P. Increasing adenoma detection rates in the right side of the colon comparing retroflexion with a second forward view: a systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89:453-459.e3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 9.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 72. | Harrison M, Singh N, Rex DK. Impact of proximal colon retroflexion on adenoma miss rates. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:519-522. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 106] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 73. | Miyamoto H, Naoe H, Oda Y, Shono T, Narita R, Oyama S, Hashigo S, Okuda A, Hasuda K, Tanaka M, Sakurai K, Murakami Y, Sasaki Y. Impact of retroflexion in the right colon after repeated forward-view examinations. JGH Open. 2018;2:282-287. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 74. | Nogales O, de la Maza J, Martos E, Carrión L, Borobia R, Lucendo L, López-Ibáñez M, García-Lledó J, Pérez-Carazo L, Merino B. Success, safety, and usefulness of right colon retroflexion for the detection of additional colonic lesions not visualized with standard frontal view. Surg Endosc. 2021;35:620-625. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 75. | Michopoulos S, Axiaris G, Baxevanis P, Stoupaki M, Gkagkari V, Leonidakis G, Zampeli E, Sotiropoulou M, Petraki K. Retroflexion, a costless endoscopic maneuver, increases adenoma detection rate in the ascending colon. Ann Gastroenterol. 2021;34:53-60. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 76. | Kushnir VM, Oh YS, Hollander T, Chen CH, Sayuk GS, Davidson N, Mullady D, Murad FM, Sharabash NM, Ruettgers E, Dassopoulos T, Easler JJ, Gyawali CP, Edmundowicz SA, Early DS. Impact of retroflexion vs. second forward view examination of the right colon on adenoma detection: a comparison study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:415-422. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 90] [Cited by in RCA: 88] [Article Influence: 8.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 77. | Geng Z, Agrawal D, Singal AG, Kircher S, Gupta S. Contained colonic perforation due to cecal retroflexion. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:3285-3288. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 78. | Atkinson NSS, Ket S, Bassett P, Aponte D, De Aguiar S, Gupta N, Horimatsu T, Ikematsu H, Inoue T, Kaltenbach T, Leung WK, Matsuda T, Paggi S, Radaelli F, Rastogi A, Rex DK, Sabbagh LC, Saito Y, Sano Y, Saracco GM, Saunders BP, Senore C, Soetikno R, Vemulapalli KC, Jairath V, East JE. Narrow-Band Imaging for Detection of Neoplasia at Colonoscopy: A Meta-analysis of Data From Individual Patients in Randomized Controlled Trials. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:462-471. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 19.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 79. | Bedford MR, Reuser T, Wilson P, Karandikar S, Bowley D. Administration of hyoscine- n-butylbromide during colonoscopy: a survey of current UK practice. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2012;3:238-241. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 80. | Lee JM, Cheon JH, Park JJ, Moon CM, Kim ES, Kim TI, Kim WH. Effects of Hyosine N-butyl bromide on the detection of polyps during colonoscopy. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57:90-94. [PubMed] |
| 81. | Rajasekhar PT, Rees CJ, Bramble MG, Wilson DW, Rutter MD, Saunders BP, Hungin AP, East JE. A multicenter pragmatic study of an evidence-based intervention to improve adenoma detection: the Quality Improvement in Colonoscopy (QIC) study. Endoscopy. 2015;47:217-224. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 82. | Neilson LJ, East JE, Rajasekhar PT, Bassett P, Dunn S, Bevan R, Paremal S, Esmaily S, Rees CJ. Sustained colonoscopy quality improvement using a simple intervention bundle. Endoscopy. 2020;52:285-292. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 83. | Cui PJ, Yao J, Han HZ, Zhao YJ, Yang J. Does hyoscine butylbromide really improve polyp detection during colonoscopy? World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:7034-7039. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 84. | de Brouwer EJ, Arbouw ME, van der Zwet WC, van Herwaarden MA, Ledeboer M, Jansman FG, ter Borg F. Hyoscine N-butylbromide does not improve polyp detection during colonoscopy: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:835-840. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 85. | Corte C, Dahlenburg L, Selby W, Griffin S, Byrne C, Chua T, Kaffes A. Hyoscine butylbromide administered at the cecum increases polyp detection: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2012;44:917-922. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 86. | McDonald GB, O'Leary R, Stratton C. Pre-endoscopic use of oral simethicone. Gastrointest Endosc. 1978;24:283. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 87. | Tongprasert S, Sobhonslidsuk A, Rattanasiri S. Improving quality of colonoscopy by adding simethicone to sodium phosphate bowel preparation. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:3032-3037. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 88. | Bai Y, Fang J, Zhao SB, Wang D, Li YQ, Shi RH, Sun ZQ, Sun MJ, Ji F, Si JM, Li ZS. Impact of preprocedure simethicone on adenoma detection rate during colonoscopy: a multicenter, endoscopist-blinded randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2018;50:128-136. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 89. | Yeh JH, Hsu MH, Tseng CM, Chen TH, Huang RY, Lee CT, Lin CW, Wang WL. The benefit of adding oral simethicone in bowel preparation regimen for the detection of colon adenoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34:830-836. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 90. | Moraveji S, Casner N, Bashashati M, Garcia C, Dwivedi A, Zuckerman MJ, Carrion A, Ladd AM. The role of oral simethicone on the adenoma detection rate and other quality indicators of screening colonoscopy: a randomized, controlled, observer-blinded clinical trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;90:141-149. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 91. | Kovaleva J, Peters FT, van der Mei HC, Degener JE. Transmission of infection by flexible gastrointestinal endoscopy and bronchoscopy. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:231-254. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 283] [Cited by in RCA: 313] [Article Influence: 26.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 92. | Olympus, Use of simethicone and other non-water soluble additives with Olympus flexible endoscopes. 2018.. |
| 93. | Benmassaoud A, Parent J. Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Position Statement on the Impact of Simethicone on Endoscope Reprocessing. J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2018;1:40-42. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 94. | Day LW, Muthusamy VR, Collins J, Kushnir VM, Sawhney MS, Thosani NC, Wani S. Multisociety guideline on reprocessing flexible GI endoscopes and accessories. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93:11-33.e6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 95] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 19.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 95. | Arya V, Singh S, Agarwal S, Valluri A, Dowling O, Sison C, Gupta KA. Position change during colonoscopy improves caecal intubation rate, mucosal visibility, and adenoma detection in patients with suboptimal caecal preparation. Prz Gastroenterol. 2017;12:296-302. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 96. | East JE, Bassett P, Arebi N, Thomas-Gibson S, Guenther T, Saunders BP. Dynamic patient position changes during colonoscope withdrawal increase adenoma detection: a randomized, crossover trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:456-463. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 94] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 97. | Wilson A, Saunders BP. Position change during colonoscopy: the oldest and best trick in the book. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:495-496. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 98. | Köksal AŞ, Kalkan IH, Torun S, Taşkıran I, Öztaş E, Kayaçetin E, Şaşmaz N. A simple method to improve adenoma detection rate during colonoscopy: altering patient position. Can J Gastroenterol. 2013;27:509-512. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 99. | Banks MR, Haidry R, Butt MA, Whitley L, Stein J, Langmead L, Bloom SL, O'Bichere A, McCartney S, Basherdas K, Rodriguez-Justo M, Lovat LB. High resolution colonoscopy in a bowel cancer screening program improves polyp detection. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:4308-4313. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 100. | Buchner AM, Shahid MW, Heckman MG, McNeil RB, Cleveland P, Gill KR, Schore A, Ghabril M, Raimondo M, Gross SA, Wallace MB. High-definition colonoscopy detects colorectal polyps at a higher rate than standard white-light colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:364-370. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 88] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 101. | Tziatzios G, Gkolfakis P, Lazaridis LD, Facciorusso A, Antonelli G, Hassan C, Repici A, Sharma P, Rex DK, Triantafyllou K. High-definition colonoscopy for improving adenoma detection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:1027-1036.e9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 102. | Laine L, Kaltenbach T, Barkun A, McQuaid KR, Subramanian V, Soetikno R; SCENIC Guideline Development Panel. SCENIC international consensus statement on surveillance and management of dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81:489-501.e26. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 244] [Cited by in RCA: 271] [Article Influence: 27.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 103. | Shimoda R, Sakata Y, Fujise T, Yamanouchi K, Tsuruoka N, Hara M, Nakayama A, Yamaguchi D, Akutagawa T, Fujimoto K, Iwakiri R. The adenoma miss rate of blue-laser imaging vs. white-light imaging during colonoscopy: a randomized tandem trial. Endoscopy. 2017;49:186-190. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 104. | Ikematsu H, Sakamoto T, Togashi K, Yoshida N, Hisabe T, Kiriyama S, Matsuda K, Hayashi Y, Matsuda T, Osera S, Kaneko K, Utano K, Naito Y, Ishihara H, Kato M, Yoshimura K, Ishikawa H, Yamamoto H, Saito Y. Detectability of colorectal neoplastic lesions using a novel endoscopic system with blue laser imaging: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:386-394. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 82] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 10.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 105. | Aziz M, Ahmed Z, Haghbin H, Pervez A, Goyal H, Kamal F, Kobeissy A, Nawras A, Adler DG. Does i-scan improve adenoma detection rate compared to high-definition colonoscopy? Endosc Int Open. 2022;10:E824-E831. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 106. | Mir FA, Boumitri C, Ashraf I, Matteson-Kome ML, Nguyen DL, Puli SR, Bechtold ML. Cap-assisted colonoscopy versus standard colonoscopy: is the cap beneficial? Ann Gastroenterol. 2017;30:640-648. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 107. | Westwood DA, Alexakis N, Connor SJ. Transparent cap-assisted colonoscopy versus standard adult colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2012;55: 218-225. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 108. | Nutalapati V, Kanakadandi V, Desai M, Olyaee M, Rastogi A. Cap-assisted colonoscopy: a meta-analysis of high-quality randomized controlled trials. Endosc Int Open. 2018;6:E1214-E1223. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 109. | Rastogi A, Bansal A, Rao DS, Gupta N, Wani SB, Shipe T, Gaddam S, Singh V, Sharma P. Higher adenoma detection rates with cap-assisted colonoscopy: a randomised controlled trial. Gut. 2012;61:402-408. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 96] [Cited by in RCA: 110] [Article Influence: 8.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 110. | de Wijkerslooth TR, Stoop EM, Bossuyt PM, Mathus-Vliegen EM, Dees J, Tytgat KM, van Leerdam ME, Fockens P, Kuipers EJ, Dekker E. Adenoma detection with cap-assisted colonoscopy versus regular colonoscopy: a randomised controlled trial. Gut. 2012;61:1426-1434. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 89] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 111. | Lahiff C, East JE. Distal attachments for adenoma detection go head-to-head: Cap or cuff? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34:1471-1473. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 112. | Ngu WS, Bevan R, Tsiamoulos ZP, Bassett P, Hoare Z, Rutter MD, Clifford G, Totton N, Lee TJ, Ramadas A, Silcock JG, Painter J, Neilson LJ, Saunders BP, Rees CJ. Improved adenoma detection with Endocuff Vision: the ADENOMA randomised controlled trial. Gut. 2019;68:280-288. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 99] [Article Influence: 16.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 113. | Rameshshanker R, Tsiamoulos Z, Wilson A, Rajendran A, Bassett P, Tekkis P, Saunders BP. Endoscopic cuff-assisted colonoscopy versus cap-assisted colonoscopy in adenoma detection: randomized tandem study-DEtection in Tandem Endocuff Cap Trial (DETECT). Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:894-904.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 114. | Lahiff C. Distal attachment device is mandatory for screening-related colonoscopy. Endosc Int Open. 2021;9:E1593-E1594. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 115. | Liu P, Wang P, Glissen Brown JR, Berzin TM, Zhou G, Liu W, Xiao X, Chen Z, Zhang Z, Zhou C, Lei L, Xiong F, Li L, Liu X. The single-monitor trial: an embedded CADe system increased adenoma detection during colonoscopy: a prospective randomized study. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2020;13:1756284820979165. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 11.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 116. | Shaukat A, Lichtenstein DR, Somers SC, Chung DC, Perdue DG, Gopal M, Colucci DR, Phillips SA, Marka NA, Church TR, Brugge WR; SKOUT™ Registration Study Team. Computer-Aided Detection Improves Adenomas per Colonoscopy for Screening and Surveillance Colonoscopy: A Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology. 2022;163:732-741. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 76] [Article Influence: 25.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 117. | Hann A, Troya J, Fitting D. Current status and limitations of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy. United European Gastroenterol J. 2021;9:527-533. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 8.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 118. | van der Zander QEW, Schreuder RM, Fonollà R, Scheeve T, van der Sommen F, Winkens B, Aepli P, Hayee B, Pischel AB, Stefanovic M, Subramaniam S, Bhandari P, de With PHN, Masclee AAM, Schoon EJ. Optical diagnosis of colorectal polyp images using a newly developed computer-aided diagnosis system (CADx) compared with intuitive optical diagnosis. Endoscopy. 2021;53:1219-1226. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 119. | Biffi C, Salvagnini P, Dinh NN, Hassan C, Sharma P; GI Genius CADx Study Group, Cherubini A. A novel AI device for real-time optical characterization of colorectal polyps. NPJ Digit Med. 2022;5:84. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 8.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 120. | Bisschops R, East JE, Hassan C, Hazewinkel Y, Kamiński MF, Neumann H, Pellisé M, Antonelli G, Bustamante Balen M, Coron E, Cortas G, Iacucci M, Yuichi M, Longcroft-Wheaton G, Mouzyka S, Pilonis N, Puig I, van Hooft JE, Dekker E. Advanced imaging for detection and differentiation of colorectal neoplasia: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline - Update 2019. Endoscopy. 2019;51:1155-1179. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 152] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 38.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 121. | Belderbos TD, Leenders M, Moons LM, Siersema PD. Local recurrence after endoscopic mucosal resection of nonpedunculated colorectal lesions: systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2014;46:388-402. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 293] [Cited by in RCA: 275] [Article Influence: 25.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 122. | Knabe M, Pohl J, Gerges C, Ell C, Neuhaus H, Schumacher B. Standardized long-term follow-up after endoscopic resection of large, nonpedunculated colorectal lesions: a prospective two-center study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:183-189. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 102] [Cited by in RCA: 119] [Article Influence: 10.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 123. | Moss A, Williams SJ, Hourigan LF, Brown G, Tam W, Singh R, Zanati S, Burgess NG, Sonson R, Byth K, Bourke MJ. Long-term adenoma recurrence following wide-field endoscopic mucosal resection (WF-EMR) for advanced colonic mucosal neoplasia is infrequent: results and risk factors in 1000 cases from the Australian Colonic EMR (ACE) study. Gut. 2015;64:57-65. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 393] [Cited by in RCA: 367] [Article Influence: 36.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 124. | Brooker JC, Saunders BP, Shah SG, Williams CB. Endoscopic resection of large sessile colonic polyps by specialist and non-specialist endoscopists. Br J Surg. 2002;89:1020-1024. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 125. | Briedigkeit A, Sultanie O, Sido B, Dumoulin FL. Endoscopic mucosal resection of colorectal adenomas > 20 mm: Risk factors for recurrence. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;8:276-281. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 126. | Cipolletta L, Rotondano G, Bianco MA, Buffoli F, Gizzi G, Tessari F; Italian Colorectal Endoscopic Resection (ICER) Study Group. Endoscopic resection for superficial colorectal neoplasia in Italy: a prospective multicentre study. Dig Liver Dis. 2014;46:146-151. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 127. | Lim TR, Mahesh V, Singh S, Tan BH, Elsadig M, Radhakrishnan N, Conlong P, Babbs C, George R. Endoscopic mucosal resection of colorectal polyps in typical UK hospitals. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:5324-5328. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 128. | Klein A, Tate DJ, Jayasekeran V, Hourigan L, Singh R, Brown G, Bahin FF, Burgess N, Williams SJ, Lee E, Sidhu M, Byth K, Bourke MJ. Thermal Ablation of Mucosal Defect Margins Reduces Adenoma Recurrence After Colonic Endoscopic Mucosal Resection. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:604-613.e3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 211] [Cited by in RCA: 189] [Article Influence: 31.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 129. | Kandel P, Werlang ME, Ahn IR, Woodward TA, Raimondo M, Bouras EP, Wallace MB, Gómez V. Prophylactic Snare Tip Soft Coagulation and Its Impact on Adenoma Recurrence After Colonic Endoscopic Mucosal Resection. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:3300-3306. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 130. | Yamashina T, Uedo N, Akasaka T, Iwatsubo T, Nakatani Y, Akamatsu T, Kawamura T, Takeuchi Y, Fujii S, Kusaka T, Shimokawa T. Comparison of Underwater vs Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Intermediate-Size Colorectal Polyps. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:451-461.e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 88] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 22.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 131. | van Hattem WA, Shahidi N, Vosko S, Hartley I, Britto K, Sidhu M, Bar-Yishay I, Schoeman S, Tate DJ, Byth K, Hewett DG, Pellisé M, Hourigan LF, Moss A, Tutticci N, Bourke MJ. Piecemeal cold snare polypectomy versus conventional endoscopic mucosal resection for large sessile serrated lesions: a retrospective comparison across two successive periods. Gut. 2021;70:1691-1697. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 22.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 132. | Nakajima T, Sakamoto T, Hori S, Yamada S, Ikematsu H, Harada K, Chiu HM, Kiriyama S, Michida T, Hotta K, Sakamoto N, Abe T, Chino A, Fukuzawa M, Kobayashi N, Fukase K, Matsuda T, Murakami Y, Ishikawa H, Saito Y. Optimal surveillance interval after piecemeal endoscopic mucosal resection for large colorectal neoplasia: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc. 2022;36:515-525. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 133. | Rashid MU, Khetpal N, Zafar H, Ali S, Idrisov E, Du Y, Stein A, Jain D, Hasan MK. Colon mucosal neoplasia referred for endoscopic mucosal resection: Recurrence of adenomas and prediction of submucosal invasion. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;12:198-211. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 134. | Gatto NM, Frucht H, Sundararajan V, Jacobson JS, Grann VR, Neugut AI. Risk of perforation after colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy: a population-based study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:230-236. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 354] [Cited by in RCA: 338] [Article Influence: 15.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 135. | Iqbal CW, Cullinane DC, Schiller HJ, Sawyer MD, Zietlow SP, Farley DR. Surgical management and outcomes of 165 colonoscopic perforations from a single institution. Arch Surg. 2008;143:701-6; discussion 706. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 140] [Cited by in RCA: 144] [Article Influence: 8.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 136. | Lohsiriwat V. Colonoscopic perforation: incidence, risk factors, management and outcome. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:425-430. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 173] [Cited by in RCA: 158] [Article Influence: 10.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (4)] |
| 137. | Moss A, Bourke MJ, Williams SJ, Hourigan LF, Brown G, Tam W, Singh R, Zanati S, Chen RY, Byth K. Endoscopic mucosal resection outcomes and prediction of submucosal cancer from advanced colonic mucosal neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1909-1918. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 479] [Cited by in RCA: 439] [Article Influence: 31.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 138. | Pissas D, Ypsilantis E, Papagrigoriadis S, Hayee B, Haji A. Endoscopic management of iatrogenic perforations during endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for colorectal polyps: a case series. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2015;8:176-181. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 139. | Swan MP, Bourke MJ, Moss A, Williams SJ, Hopper A, Metz A. The target sign: an endoscopic marker for the resection of the muscularis propria and potential perforation during colonic endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:79-85. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 114] [Cited by in RCA: 103] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 140. | Kim JS, Kim BW, Kim JI, Kim JH, Kim SW, Ji JS, Lee BI, Choi H. Endoscopic clip closure versus surgery for the treatment of iatrogenic colon perforations developed during diagnostic colonoscopy: a review of 115,285 patients. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:501-504. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 64] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 141. | Nanda KS, and Bourke MJ. Endoscopic mucosal resection and complications. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;15 (2):88-95. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 142. | Albéniz E, Álvarez MA, Espinós JC, Nogales O, Guarner C, Alonso P, Rodríguez-Téllez M, Herreros de Tejada A, Santiago J, Bustamante-Balén M, Rodríguez Sánchez J, Ramos-Zabala F, Valdivielso E, Martínez-Alcalá F, Fraile M, Elosua A, Guerra Veloz MF, Ibáñez Beroiz B, Capdevila F, Enguita-Germán M. Clip Closure After Resection of Large Colorectal Lesions With Substantial Risk of Bleeding. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:1213-1221.e4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 108] [Article Influence: 18.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 143. | Metz AJ, Bourke MJ, Moss A, Williams SJ, Swan MP, Byth K. Factors that predict bleeding following endoscopic mucosal resection of large colonic lesions. Endoscopy. 2011;43 (6):506-511. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 141] [Cited by in RCA: 147] [Article Influence: 10.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 144. | Kim HS, Kim TI, Kim WH, Kim YH, Kim HJ, Yang SK, Myung SJ, Byeon JS, Lee MS, Chung IK, Jung SA, Jeen YT, Choi JH, Choi KY, Choi H, Han DS, Song JS. Risk factors for immediate postpolypectomy bleeding of the colon: a multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1333-1341. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 188] [Cited by in RCA: 189] [Article Influence: 9.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 145. | Chino A, Karasawa T, Uragami N, Endo Y, Takahashi H, Fujita R. A comparison of depth of tissue injury caused by different modes of electrosurgical current in a pig colon model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:374-379. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 146. | Nishizawa T, Suzuki H, Goto O, Ogata H, Kanai T, Yahagi N. Effect of prophylactic clipping in colorectal endoscopic resection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. United European Gastroenterol J. 2017;5:859-867. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 147. | Pohl H, Grimm IS, Moyer MT, Hasan MK, Pleskow D, Elmunzer BJ, Khashab MA, Sanaei O, Al-Kawas FH, Gordon SR, Mathew A, Levenick JM, Aslanian HR, Antaki F, von Renteln D, Crockett SD, Rastogi A, Gill JA, Law RJ, Elias PA, Pellise M, Wallace MB, Mackenzie TA, Rex DK. Clip Closure Prevents Bleeding After Endoscopic Resection of Large Colon Polyps in a Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:977-984.e3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 176] [Cited by in RCA: 169] [Article Influence: 28.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 148. | Gupta S, Sidhu M, Shahidi N, Vosko S, McKay O, Bahin FF, Zahid S, Whitfield A, Byth K, Brown G, Lee EYT, Williams SJ, Burgess NG, Bourke MJ. Effect of prophylactic endoscopic clip placement on clinically significant post-endoscopic mucosal resection bleeding in the right colon: a single-centre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:152-160. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 13.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 149. | Pohl H. The Cost of Clipping-How Much Does Price Matter? Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116:276-277. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 150. | Bahin FF, Rasouli KN, Byth K, Hourigan LF, Singh R, Brown GJ, Zanati SA, Moss A, Raftopoulos S, Williams SJ, Bourke MJ. Prediction of Clinically Significant Bleeding Following Wide-Field Endoscopic Resection of Large Sessile and Laterally Spreading Colorectal Lesions: A Clinical Risk Score. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111:1115-1122. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 8.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 151. | Singh H, Penfold RB, DeCoster C, Kaita L, Proulx C, Taylor G, Bernstein CN, Moffatt M. Colonoscopy and its complications across a Canadian regional health authority. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:665-671. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 152. | Chukmaitov A, Bradley CJ, Dahman B, Siangphoe U, Warren JL, Klabunde CN. Association of polypectomy techniques, endoscopist volume, and facility type with colonoscopy complications. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:436-446. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 64] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 153. | Lamb CA, Barbour JA. Developing an endoscopic mucosal resection service in a district general hospital. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2012;3:272-277. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 154. | Gupta S, Miskovic D, Bhandari P, Dolwani S, McKaig B, Pullan R, Rembacken B, Riley S, Rutter MD, Suzuki N, Tsiamoulos Z, Valori R, Vance ME, Faiz OD, Saunders BP, Thomas-Gibson S. A novel method for determining the difficulty of colonoscopic polypectomy. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2013;4:244-248. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 155. | Sidhu M, Tate DJ, Desomer L, Brown G, Hourigan LF, Lee EYT, Moss A, Raftopoulos S, Singh R, Williams SJ, Zanati S, Burgess N, Bourke MJ. The size, morphology, site, and access score predicts critical outcomes of endoscopic mucosal resection in the colon. Endoscopy. 2018;50:684-692. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 8.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 156. | Chandan S, Facciorusso A, Ramai D, Deliwala S, Mohan BP, Kassab LL, Draganov PV, Othman MO, Kochhar GS. Snare tip soft coagulation (STSC) after endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of large (> 20 mm) non pedunculated colorectal polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc Int Open. 2022;10:E74-E81. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 157. | Moon N, Aryan M, Khan W, Jiang P, Madhok I, Wilson J, Ruiz N, Ponniah SA, Westerveld DR, Gupte A, Pooran N, Qumseya B, Forsmark CE, Draganov PV, Yang D. Effect of referral pattern and histopathology grade on surgery for nonmalignant colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;92:702-711.e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 158. | Rex DK, Bond JH, Winawer S, Levin TR, Burt RW, Johnson DA, Kirk LM, Litlin S, Lieberman DA, Waye JD, Church J, Marshall JB, Riddell RH; U. S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Quality in the technical performance of colonoscopy and the continuous quality improvement process for colonoscopy: recommendations of the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:1296-1308. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 691] [Cited by in RCA: 723] [Article Influence: 31.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 159. | Rembacken B, Hassan C, Riemann JF, Chilton A, Rutter M, Dumonceau JM, Omar M, Ponchon T. Quality in screening colonoscopy: position statement of the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE). Endoscopy. 2012;44:957-968. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 195] [Cited by in RCA: 232] [Article Influence: 17.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 160. | Zagari RM, Frazzoni L, Fuccio L, Bertani H, Crinò SF, Magarotto A, Dajti E, Tringali A, Da Massa Carrara P, Cengia G, Ciliberto E, Conigliaro R, Germanà B, Lamazza A, Pisani A, Spinzi G, Capelli M, Bazzoli F, Pasquale L. Adherence to European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Quality Performance Measures for Upper and Lower Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: A Nationwide Survey From the Italian Society of Digestive Endoscopy. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:868449. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 161. | Beg S, Ragunath K, Wyman A, Banks M, Trudgill N, Pritchard DM, Riley S, Anderson J, Griffiths H, Bhandari P, Kaye P, Veitch A. Quality standards in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a position statement of the British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons of Great Britain and Ireland (AUGIS). Gut. 2017;66:1886-1899. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 243] [Cited by in RCA: 224] [Article Influence: 28.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |