Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Sep 16, 2016; 8(17): 628-634
Published online Sep 16, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i17.628
Published online Sep 16, 2016. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i17.628
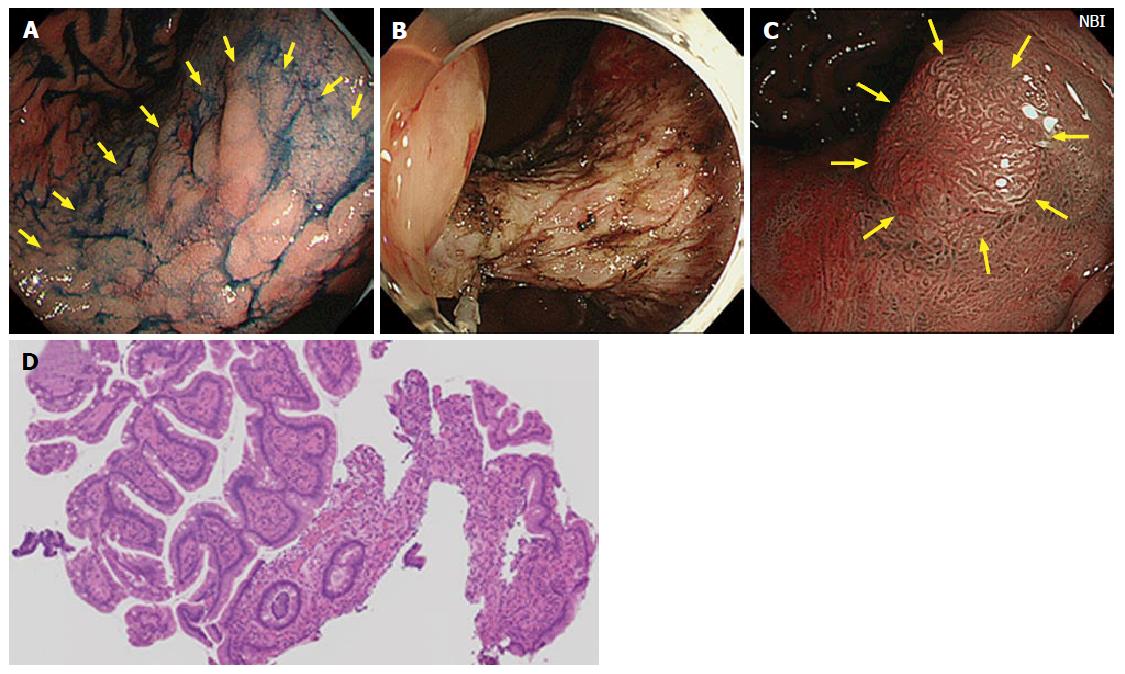
Figure 1 Case from Japan.
A: A large superficial elevated lesion was found at the lesser curvature of the gastric angle (yellow arrows); B: The lesion was removed by endoscopic submucosal dissection technique. The lesion was diagnosed as well differentiated adenocarcinoma confined to the mucosa and resection margin was free from the tumor; C: One year later, a polypoid nodule was noted at the center of the scar (yellow arrows). Narrow band image suspected irregular surface structure on the surface of the nodule; D: Biopsy specimens were taken from the polypoid nodule. Histological examination showed hyperplastic change of the foveolar epithelium and increased capillaries and inflammatory cell infiltration in the lamina propria.
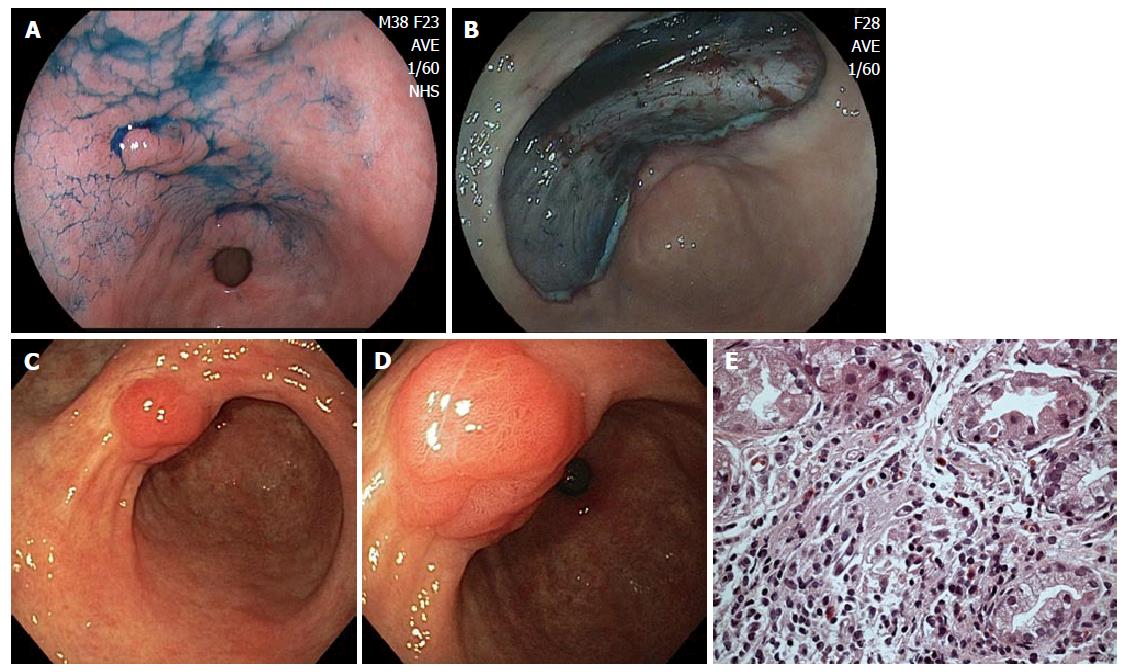
Figure 2 Case from Brazil.
A: A depressed lesion (0IIc) was found at the lesser curvature of antrum; B: The lesion was removed by endoscopic submucosal dissection technique. The lesion was diagnosed as well differentiated adenocarcinoma confined to the muscularis mucosae and resection margins were free of tumor; C: Patient developed a polypoid nodule at the center of the scar. Three years later, polypoid nodule scar (PNS) with convergence of folds is still present; D: Closer view of PNS, demonstrating irregular surface and suspicious appearance on white-light image; E: Biopsy specimens were taken from the polypoid nodule. Histological examination showed similar findings to case illustrated in Figure 1: Regenerative hyperplastic tissue with inflammatory cell infiltration.
- Citation: Arantes V, Uedo N, Pedrosa MS, Tomita Y. Clinical relevance of aberrant polypoid nodule scar after endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2016; 8(17): 628-634
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v8/i17/628.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v8.i17.628