Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 25, 2015; 7(7): 720-727
Published online Jun 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i7.720
Published online Jun 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i7.720
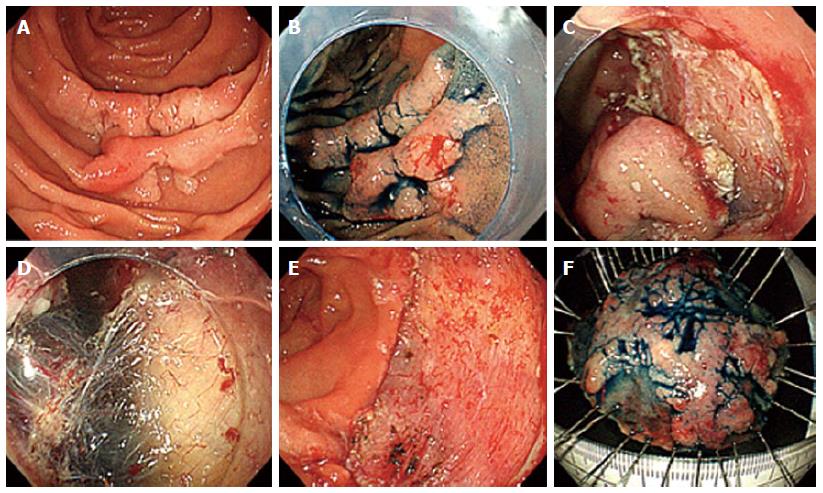
Figure 1 Endoscopic resection of a sporadic neoplastic lesion in the duodenum using endoscopic mucosal resection technique.
A: Sessile lesion in the descending duodenum seen with white light (type 0 - Isp of the Paris classifi-cation); B: Same lesion after chromoendoscopy with indigo carmine; C: Same lesion after subepithelial injection of diluted adrenalin; D: Resected area after endoscopic mucosal resection; E: Closure of the resected area with clips; F: Lesion resected en bloc. Histology revealed a well-differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma limited to the mucosa, with 7 mm × 8 mm, without lymphatic or vascular invasion.
Figure 2 Endoscopic resection of a sporadic neoplastic lesion in the duode-num using endoscopic submucosal dissection technique.
A: Flat lesion in the descending duodenum seen with white light (type 0-IIa of the Paris classi-fication); B: Same lesion after chromoendoscopy with indigo carmine; C: Partial dissection with endoscopic submucosal dissection; D: Dissection plan where the submucosal layer and the partially dissected lesion can be seen; E: Dissected area; F: En bloc dissected lesion. Histology revealed a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma limited to the mucosa, 40 mm × 32 mm, without lymphatic or vascular invasion.
- Citation: Marques J, Baldaque-Silva F, Pereira P, Arnelo U, Yahagi N, Macedo G. Endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection in the treatment of sporadic nonampullary duodenal adenomatous polyps. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(7): 720-727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i7/720.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i7.720