Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jan 16, 2015; 7(1): 13-36
Published online Jan 16, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i1.13
Published online Jan 16, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i1.13
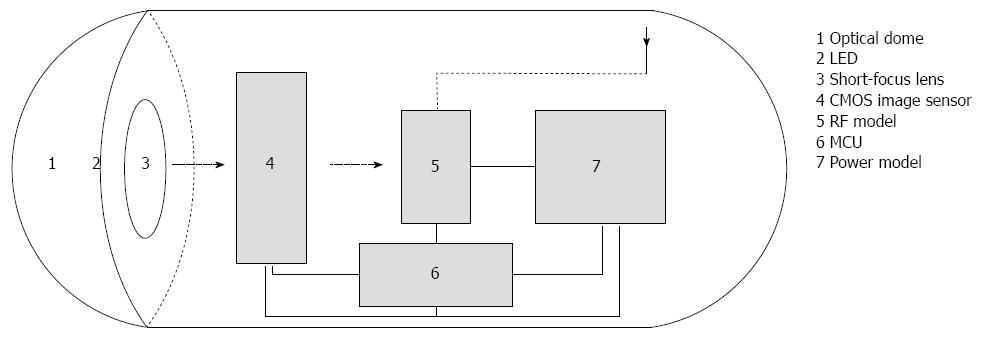
Figure 1 Main parts of the wireless capsule endoscope.
Figure 2 Types of small bowel capsule endoscopes.
A: PillCam SB 3 (Given Imaging, Yoqneam, Israel); B: MiroCam (IntroMedic, Seoul, South Korea); C: Endo Capsule (Olympus America, Center Valley, PA); D: OMOM (Jinshan Science and Technology, Chongqing, China).
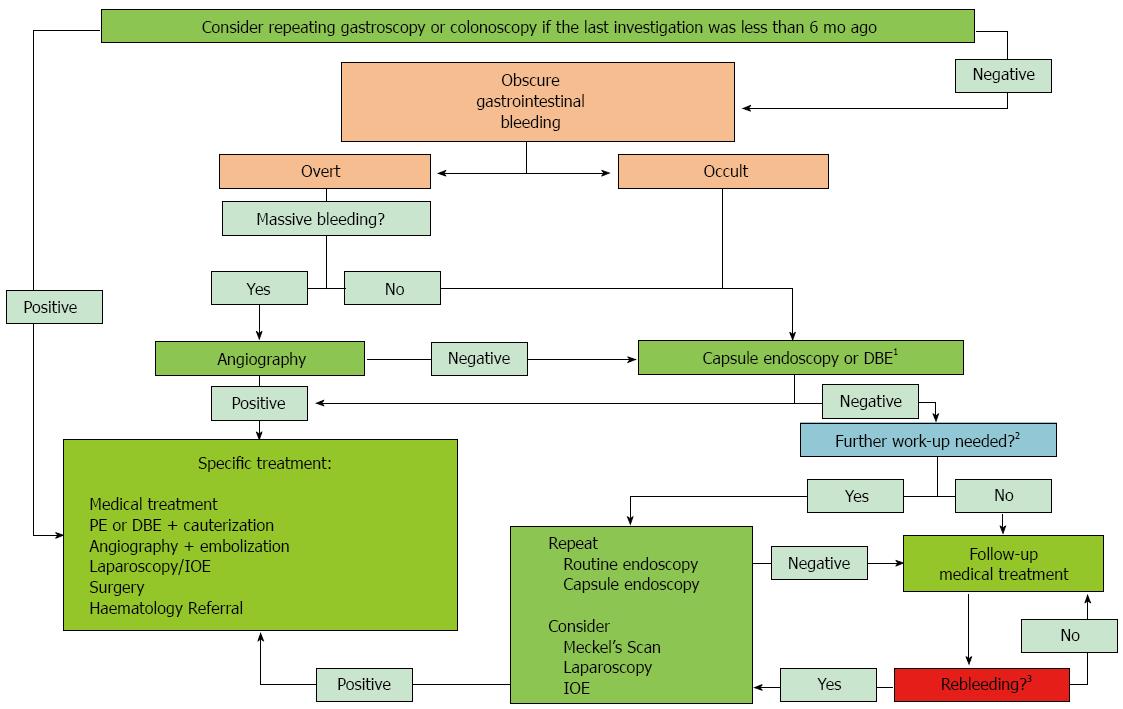
Figure 3 Recommended approaches for diagnosis and treatment of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding.
1DBE is recommended in (1) patients requiring a biopsy or a therapeutic intervention (2) patients with an initial negative CE and suspicion of a small bowel lesion (3) large scale hospitals or (4) hospitals where CE is not available; 2If a lesion is suspected, further work-up is needed; 3Rebleeding was defined as a change from occult to overt bleeding or a hemoglobin level drop more than 4 g/dL. DBE: Double balloon enteroscopy; PE: Push enteroscopy; IOE: Intraoperative enteroscopy; Routine endoscopy: Uni/bidirectional endoscopy.
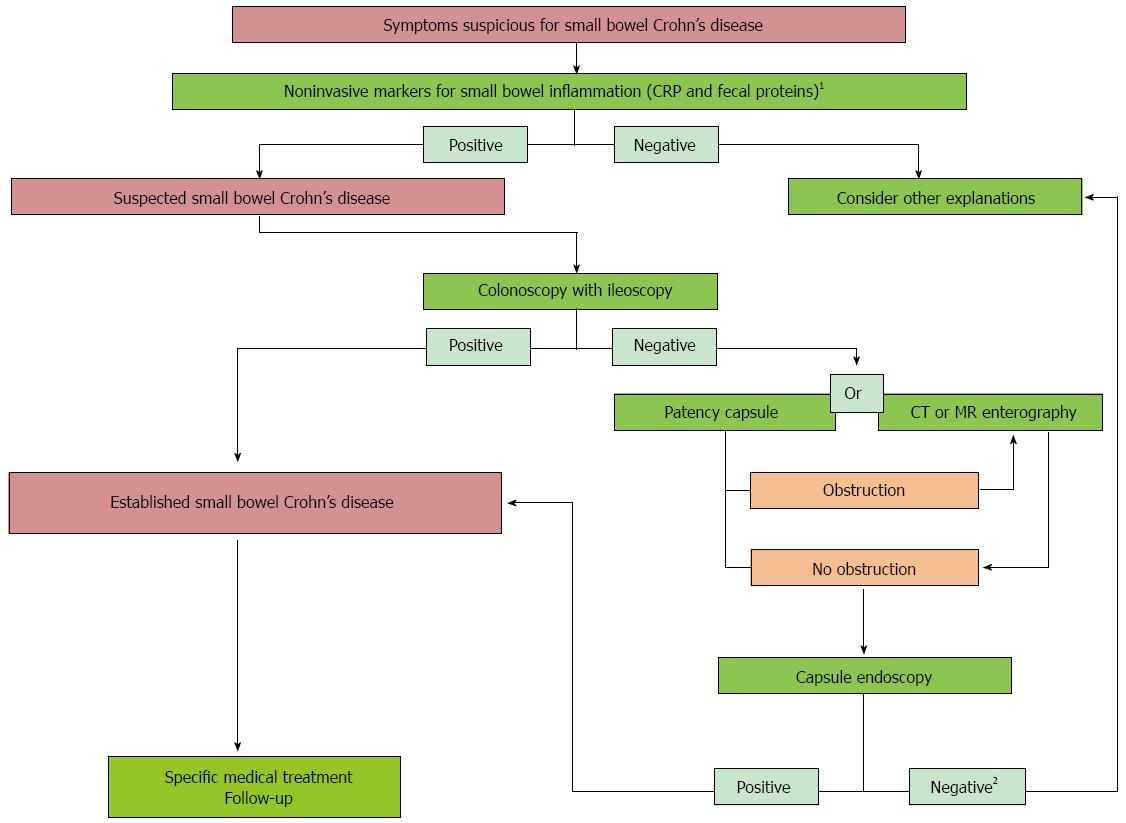
Figure 4 Recommended approaches for diagnosis and treatment of Crohn’s disease.
1Non-invasive markers have proven to be useful in giving baseline information about the presence of small bowel inflammation; 2If capsule endoscopy (CE) is negative, Crohn’s disease can be ruled out due to the high negative predictive value of CE. In that case, other explanations should be considered. CRP: C reactive protein.
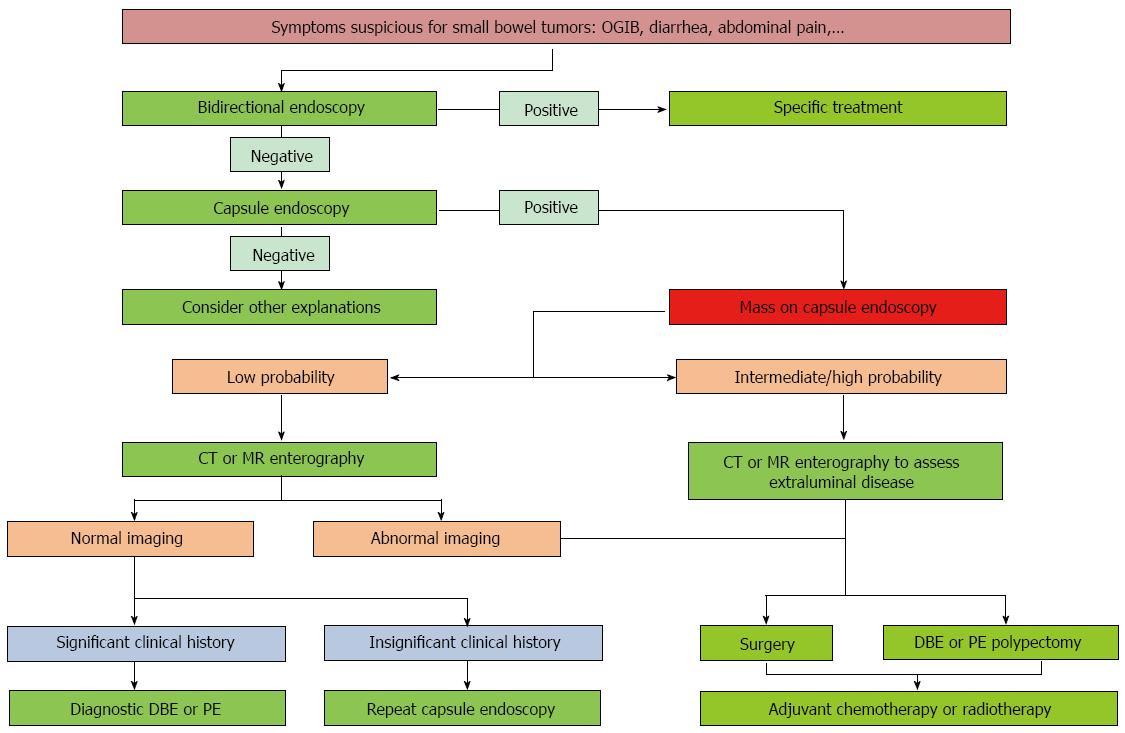
Figure 5 Recommended approaches for diagnosis and treatment of small bowel tumors.
DBE: Double balloon enteroscopy; PE: Push enteroscopy; OGIB: Obscure gastrointestinal bleeding.
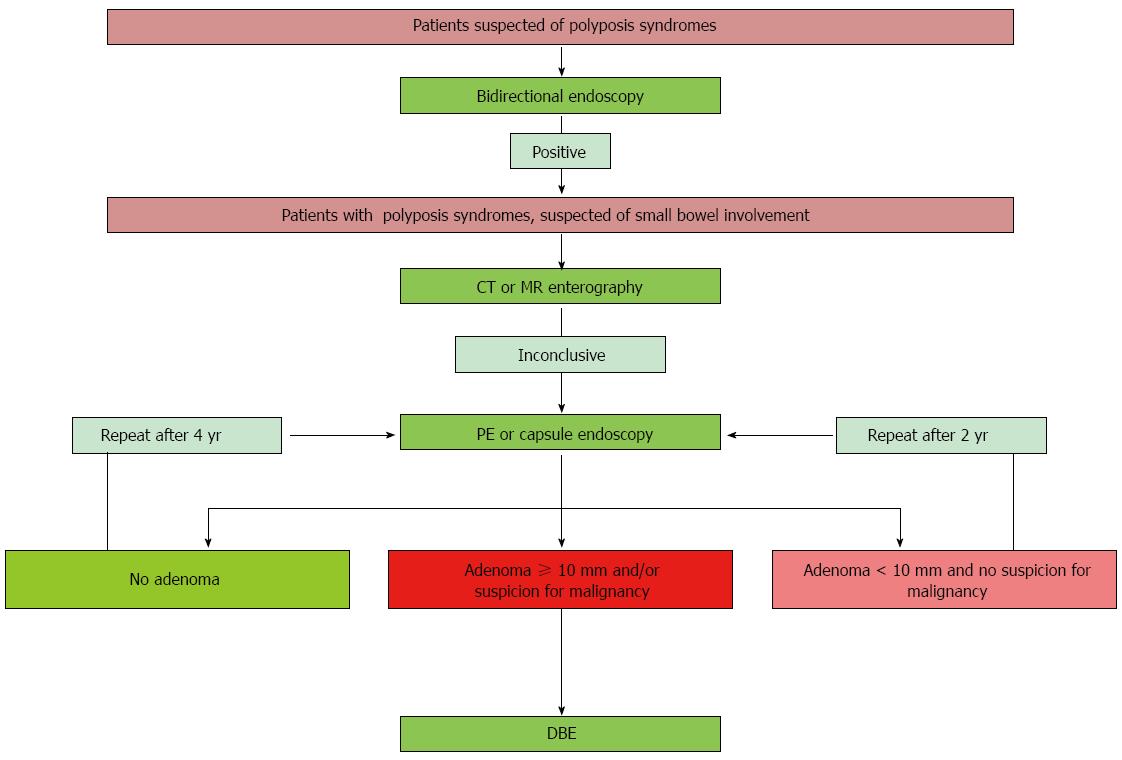
Figure 6 Recommended approaches or diagnosis of small bowel hereditary polyposis.
DBE: Double balloon enteroscopy; PE: Push enteroscopy.
- Citation: Van de Bruaene C, De Looze D, Hindryckx P. Small bowel capsule endoscopy: Where are we after almost 15 years of use? World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(1): 13-36
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i1/13.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i1.13