Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. May 16, 2019; 11(5): 373-382
Published online May 16, 2019. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i5.373
Published online May 16, 2019. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i5.373
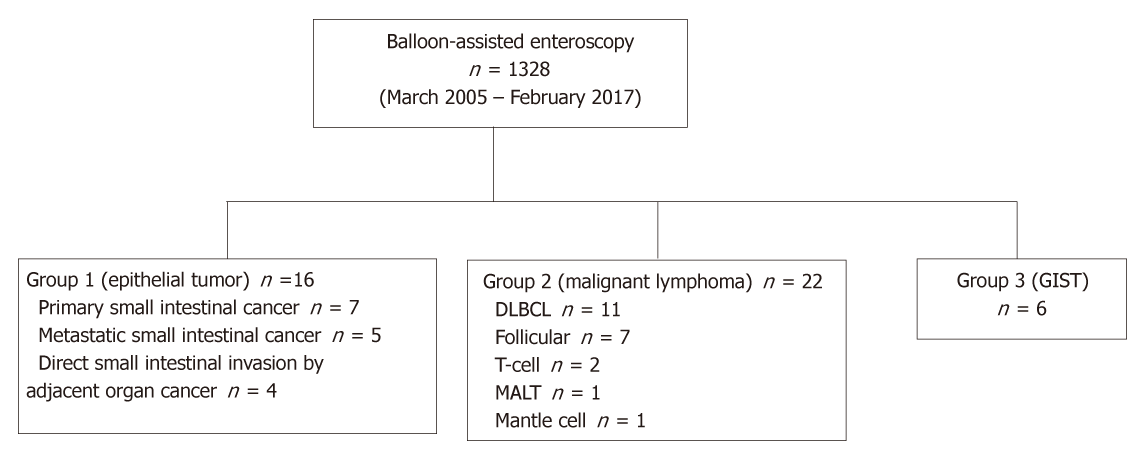
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the patient enrollment.
DLBCL: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; GIST: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor; MALT: Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue.
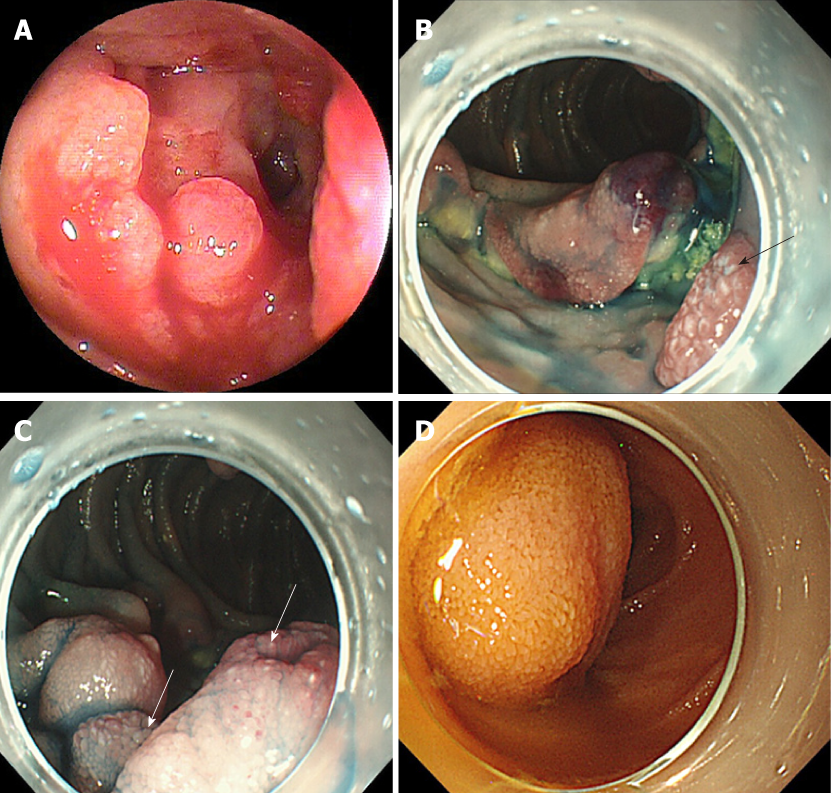
Figure 2 Endoscopic findings for each small intestinal tumor.
A: Representative image of an epithelial tumor (Group 1: primary small intestinal cancer). This tumor was solitary and located in the jejunum. The type was infiltrative ulcerated type. This tumor was also associated with stenosis and bleeding; B and C: Representative images of malignant lymphoma (Group 2: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). These tumors were multiple and located in the jejunum and ileum and appeared as ulcerated masses with raised margins. These tumors also had white villi (arrows) and were not associated with stenosis or bleeding; D: Representative image of a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (Group 3). This tumor was solitary and located in the jejunum and appeared as a protruded mass. This tumor was not associated with stenosis or bleeding.
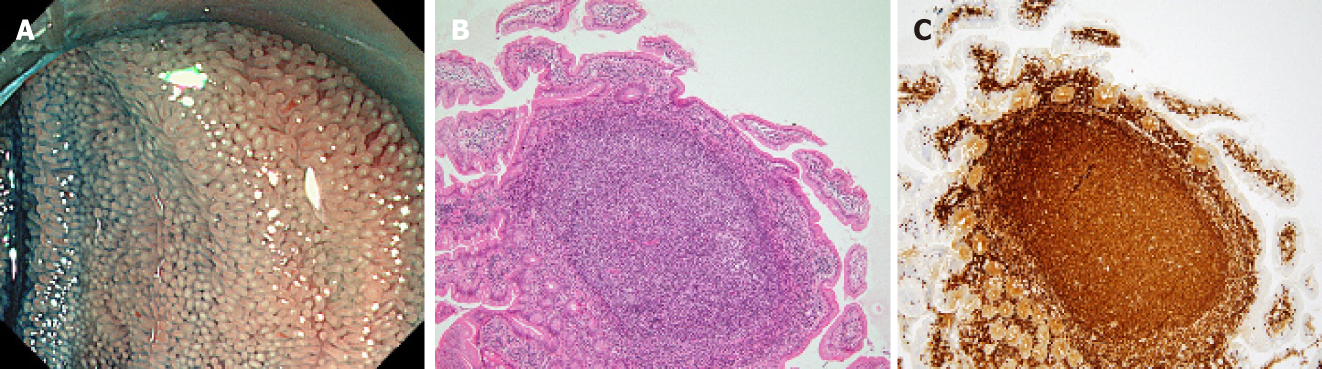
Figure 3 Endoscopic and pathological findings of the white villi.
Representative endoscopic and pathological images of the white villi (Follicular lymphoma). A: White light image with indigo carmine staining shows diffuse white villi in the ileum; B, C: Pathological images are showing the lymphoma cells infiltrating the villi with an intact epithelium. Most of the villi are filled with lymphoma cells, which formed lymphoid follicles (B: Hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 10; C: Immunohistochemical staining for bcl-2 was positive, ×10).
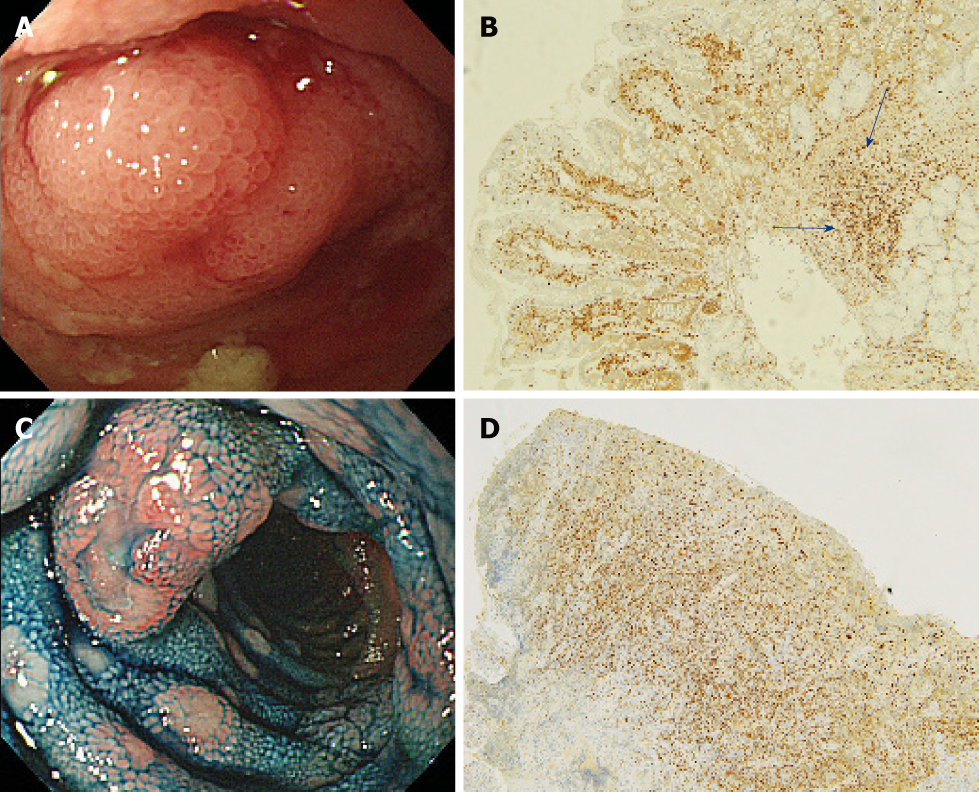
Figure 4 Endoscopic and pathological images of malignant lymphoma without white villi appearance.
A, B: Representative endoscopic and pathological images of malignant lymphoma without white villi appearance (Follicular lymphoma) [A: White light image shows enlarged villi with stenosis, without white villi appearance in the ileum (with stenosis); B: Pathological image is showing the lymphoma cells sparsely infiltrating the villi, some lymphoma cells present in the deep mucosa (blue arrow), immunohistochemical staining for bcl-2, ×10]; C, D: Representative endoscopic and pathological images of malignant lymphoma without white villi appearance (Mantle cell lymphoma) (C: White light image with indigo carmine staining shows multiple polyposis with ulceration, without white villi appearance in the ileum; D: Pathological image is showing the lymphoma cells infiltrating the mucosa without an intact epithelium, immunohistochemical staining for cyclin D1, ×10).
- Citation: Horie T, Hosoe N, Takabayashi K, Hayashi Y, Kamiya KJL, Miyanaga R, Mizuno S, Fukuhara K, Fukuhara S, Naganuma M, Shimoda M, Ogata H, Kanai T. Endoscopic characteristics of small intestinal malignant tumors observed by balloon-assisted enteroscopy. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2019; 11(5): 373-382
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v11/i5/373.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v11.i5.373