Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2025; 17(6): 108096
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.108096
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.108096
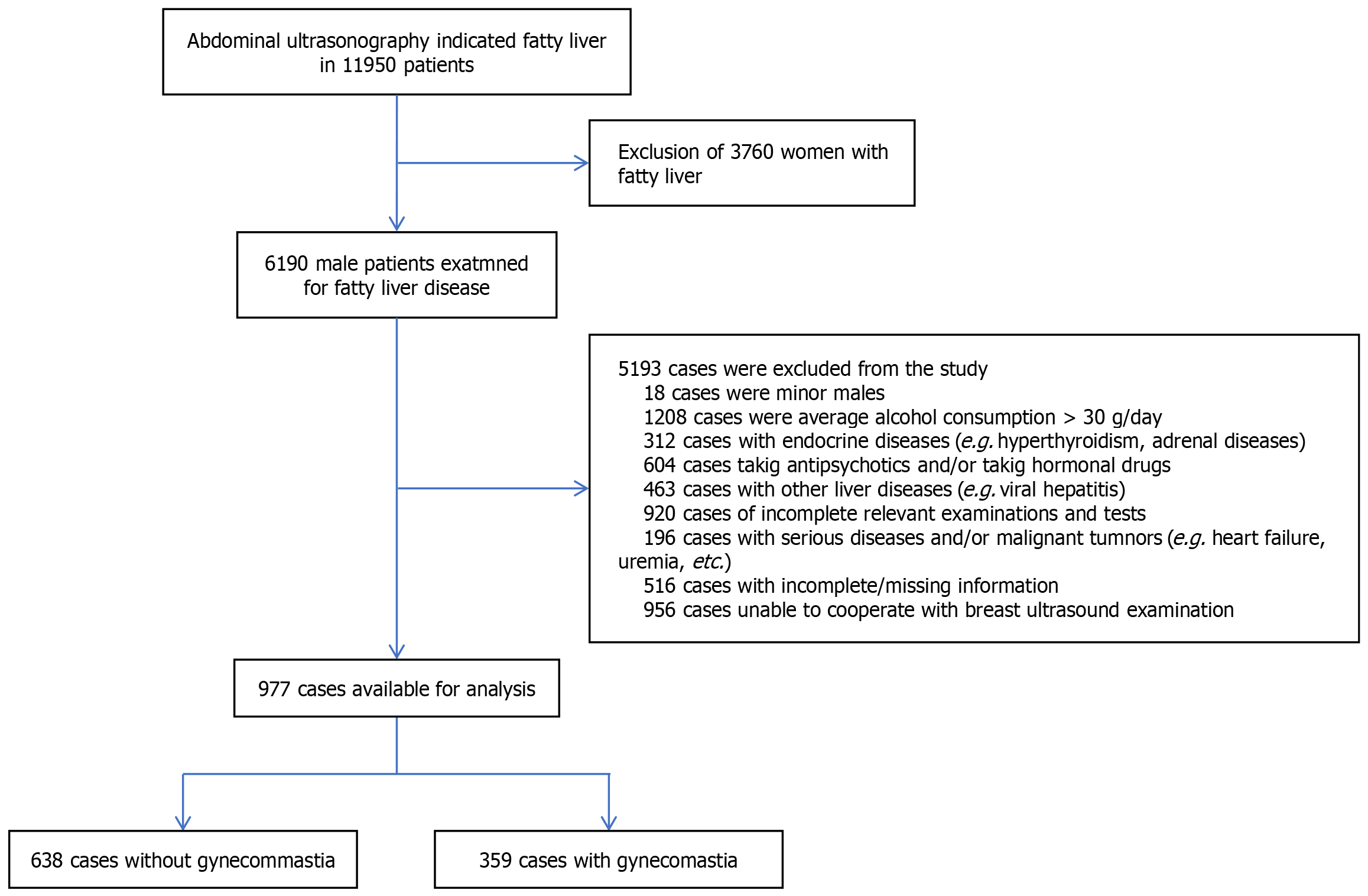
Figure 1
Detailed process of personnel screening.
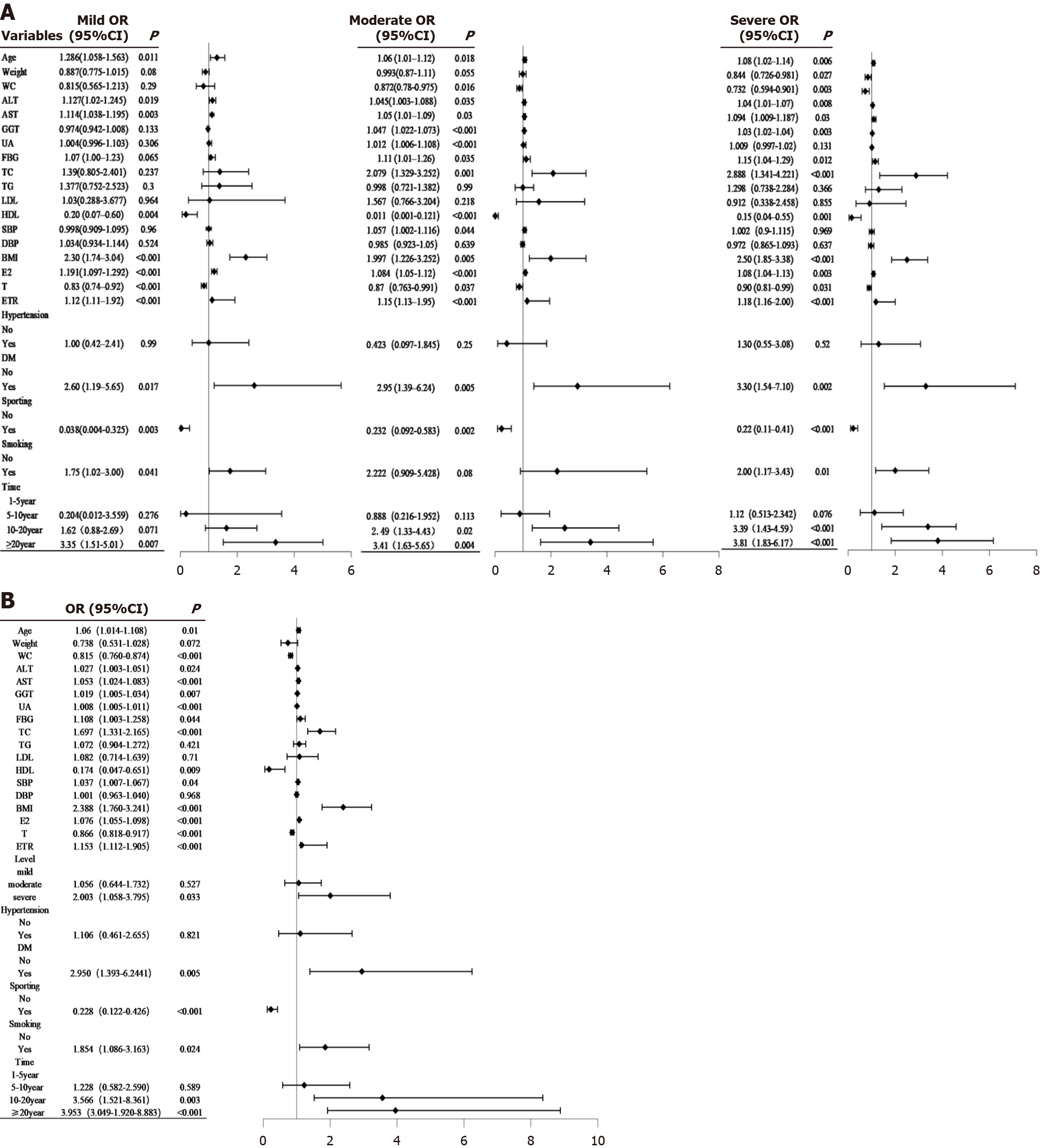
Figure 2 Forest plot.
A: Forest plot of effect values of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MASLD) on gynecomastia (GYN) by subgroups; B: Forest plot of MASLD on the overall impact value of GYN. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; BMI: Body mass index; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; DM: Diabetes mellitus; ETR: Estrogen to androgen ratio; E2: Estradiol; FBG: Fasting blood glucose; GGT: Gamma-glutamyltransferase; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; OR: Odds ratio; SBP: Systolic blood pressure; T: Testosterone; TC: Total cholesterol; TG: Triglycerides; UA: Uric acid; WC: Waist circumference.
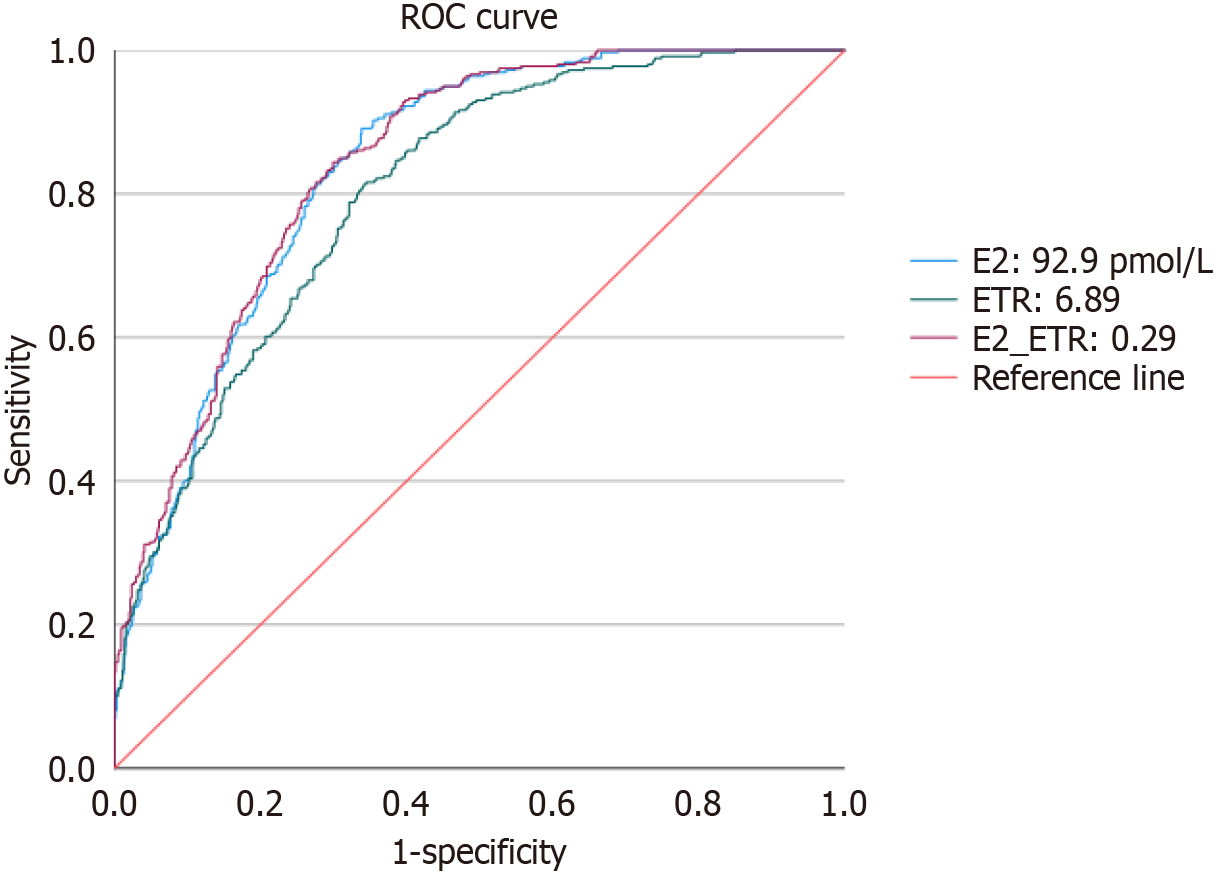
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curves for the occurrence of gynecomastia in patients with sex hormone-diagnosed metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease.
ETR: Estrogen to androgen ratio; E2: Estradiol; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic.
- Citation: Zhang MH, Meng N, Zhang KH, Yu JK, Huang CH, Yang S, Zhu DY. Correlation between gynecomastia and endocrine regulation in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(6): 108096
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i6/108096.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.108096