Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2020; 12(11): 949-964
Published online Nov 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i11.949
Published online Nov 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i11.949
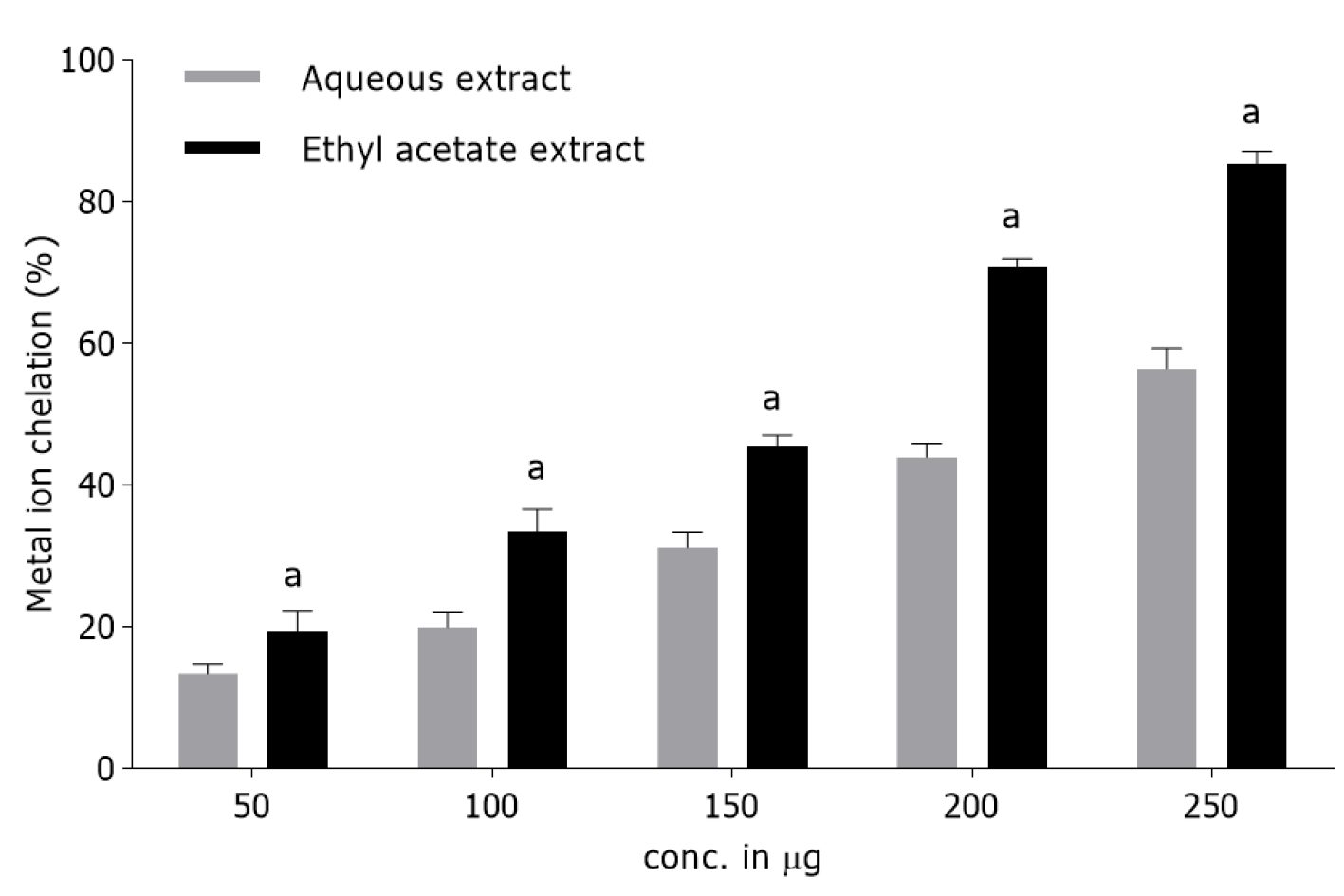
Figure 1 In vitro metal ion chelating activity of Terminaliabellirica fruit aqueous and ethyl acetate extracts.
The chelating activity was measured at different concentrations (50-250 μg/ml). Butylated hydroxytoluene was included for comparison and absorbance was measured at 562 nm. Results are presented as mean ± SD of triplicates. aP < 0.05 as compared to butylated hydroxytoluene.
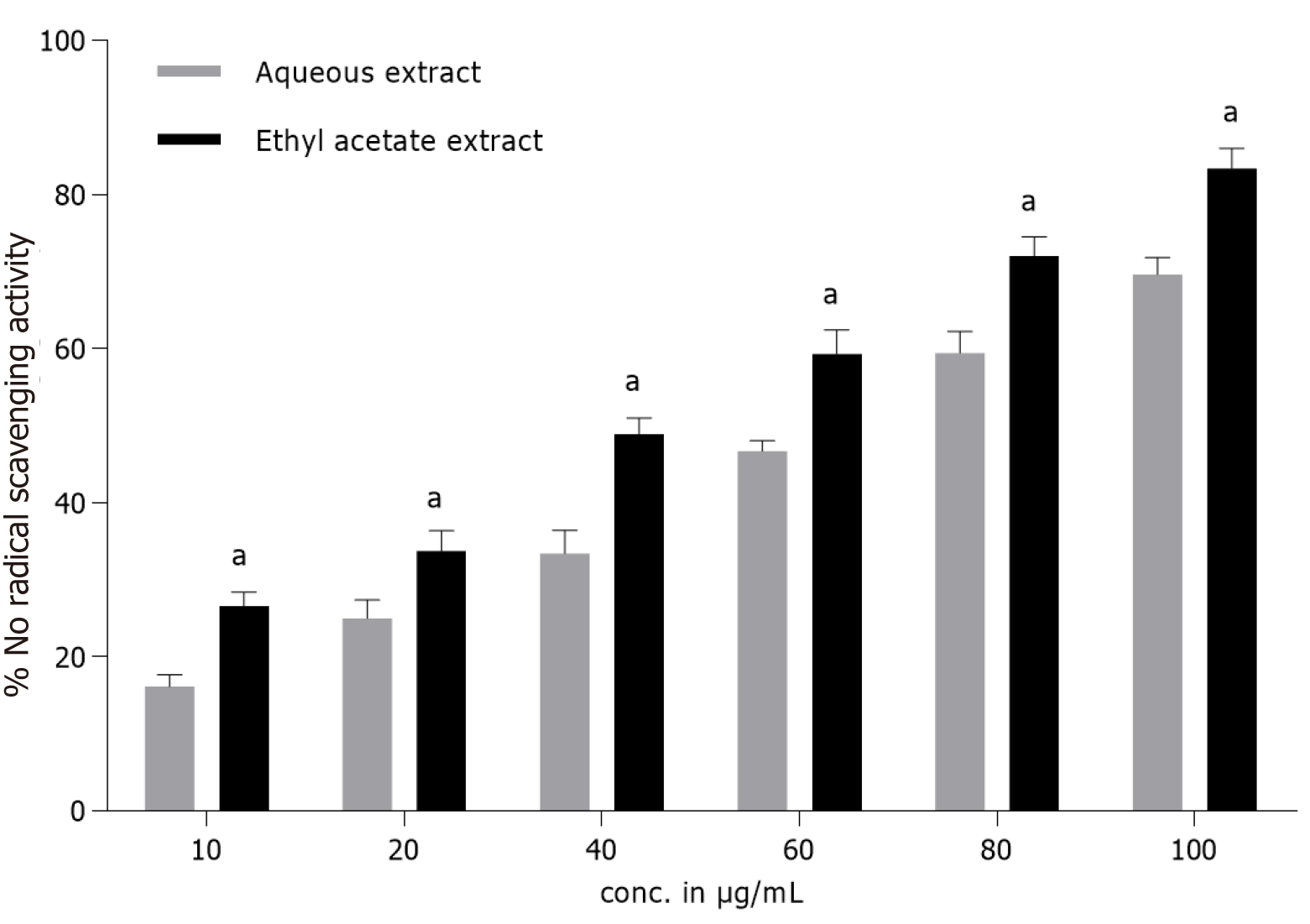
Figure 2 In vitro nitric oxide radical scavenging activity of Terminaliabellirica fruit aqueous and ethyl acetate extracts at different concentrations.
Butylated hydroxytoluene was included as a standard and absorbance was measured at 546 nm. Results are presented as mean ± SD of triplicates. aP < 0.05 as compared to butylated hydroxytoluene.
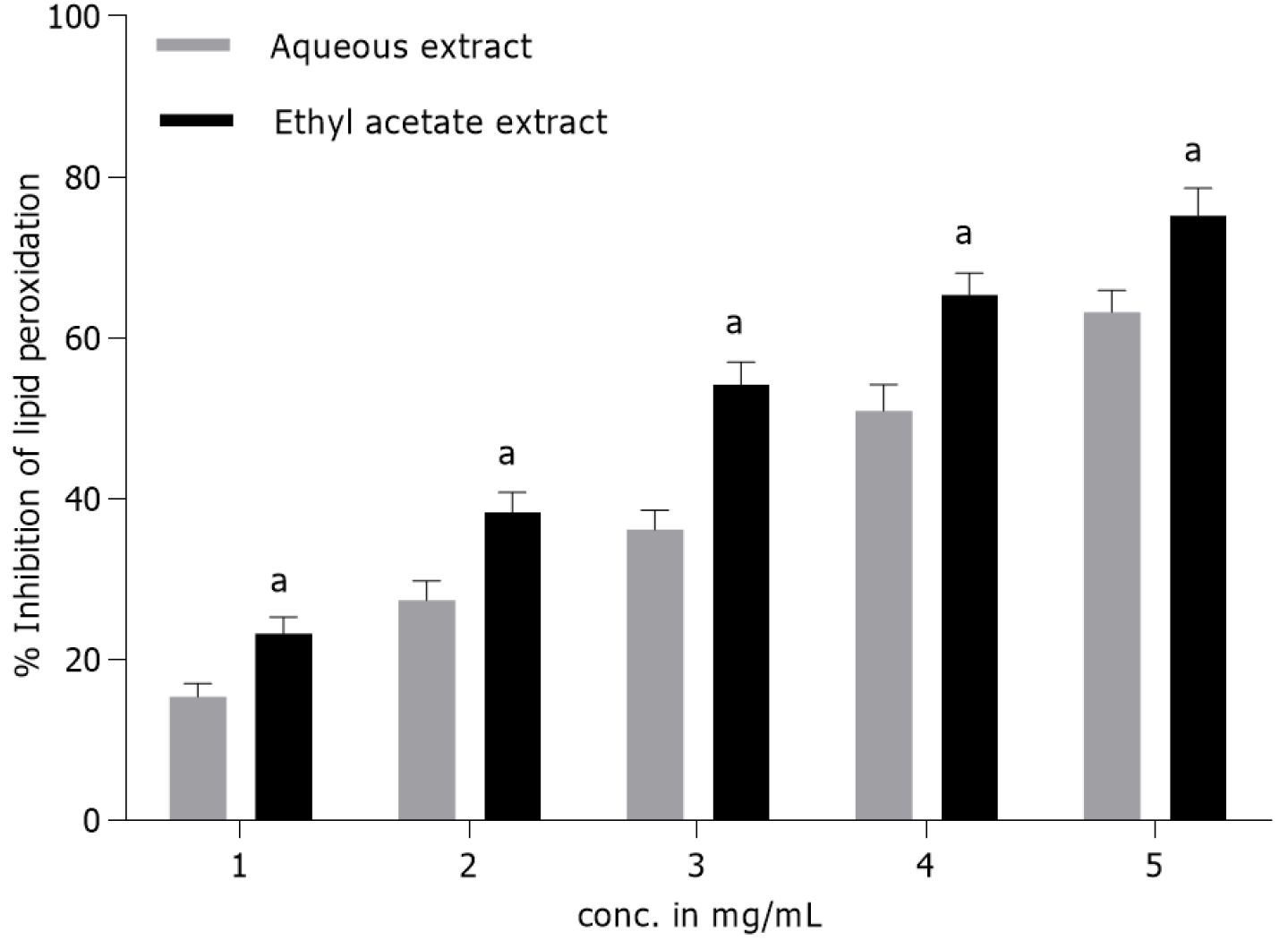
Figure 3 Percentage inhibition of lipid peroxidation in rat liver homogenate by Terminaliabellirica fruit extracts at different concentrations.
Butylated hydroxytoluene (2 mg/mL) was included for comparison and accounted for approximately 85% lipid peroxidation inhibition. The results are shown as mean ± SD of triplicates (aP < 0.05).
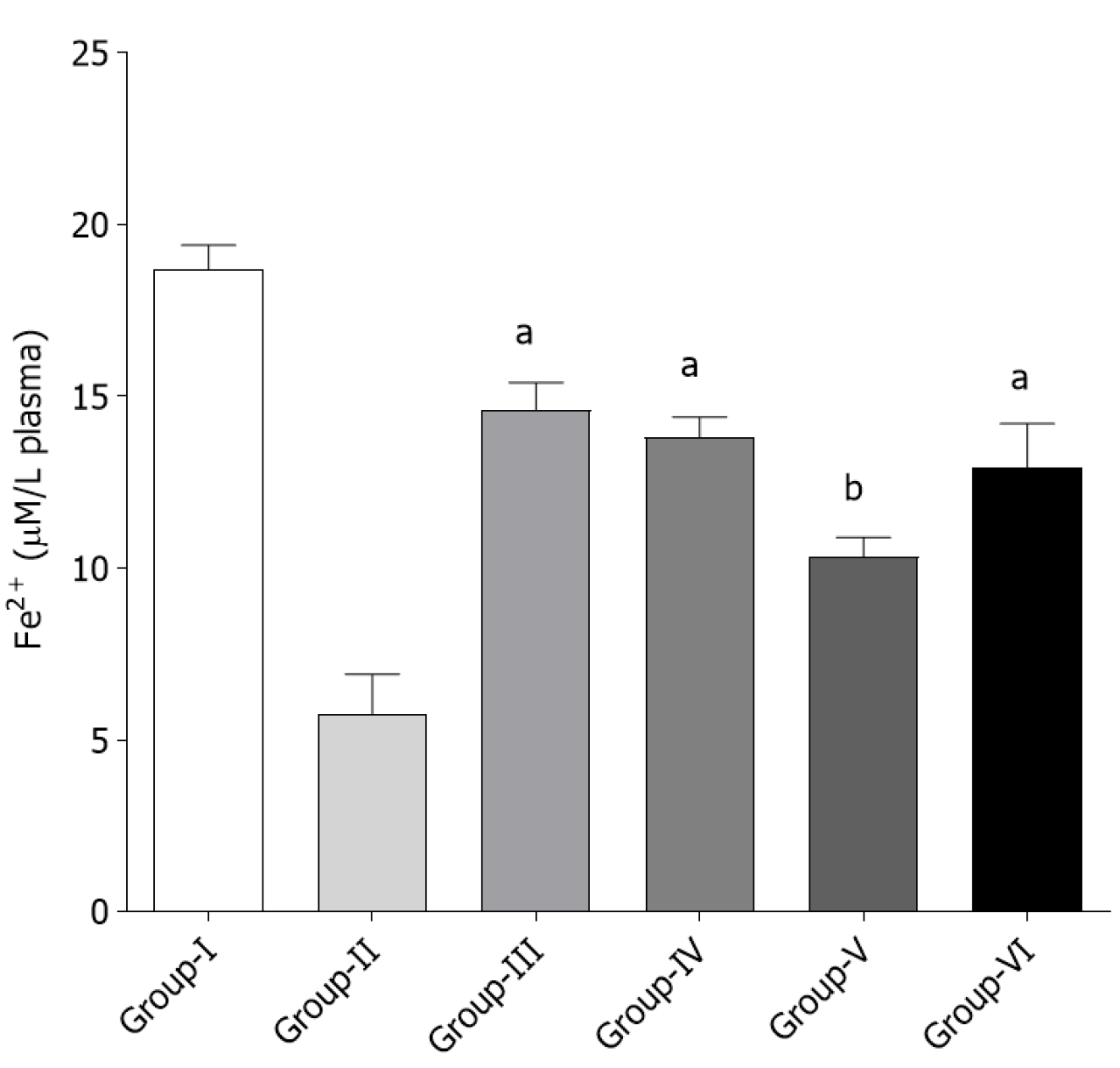
Figure 4 Effect of Terminaliabellirica fruit extracts and ellagic acid on the ferric reducing ability of plasma in aceclofenac-treated rats.
Group I-normal control; Group II-Aceclofenac (ACF) treated rats; Group III-ACF + Silymarin treated rats; Group IV-ACF + Ellagic acid treated rats; Group V- ACF + Aqueous extract treated rats; Group VI: ACF + Ethyl acetate extract treated rats. Silymarin was used as a positive control. The data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 5, aP < 0.01; bP < 0.05 as compared to group II).
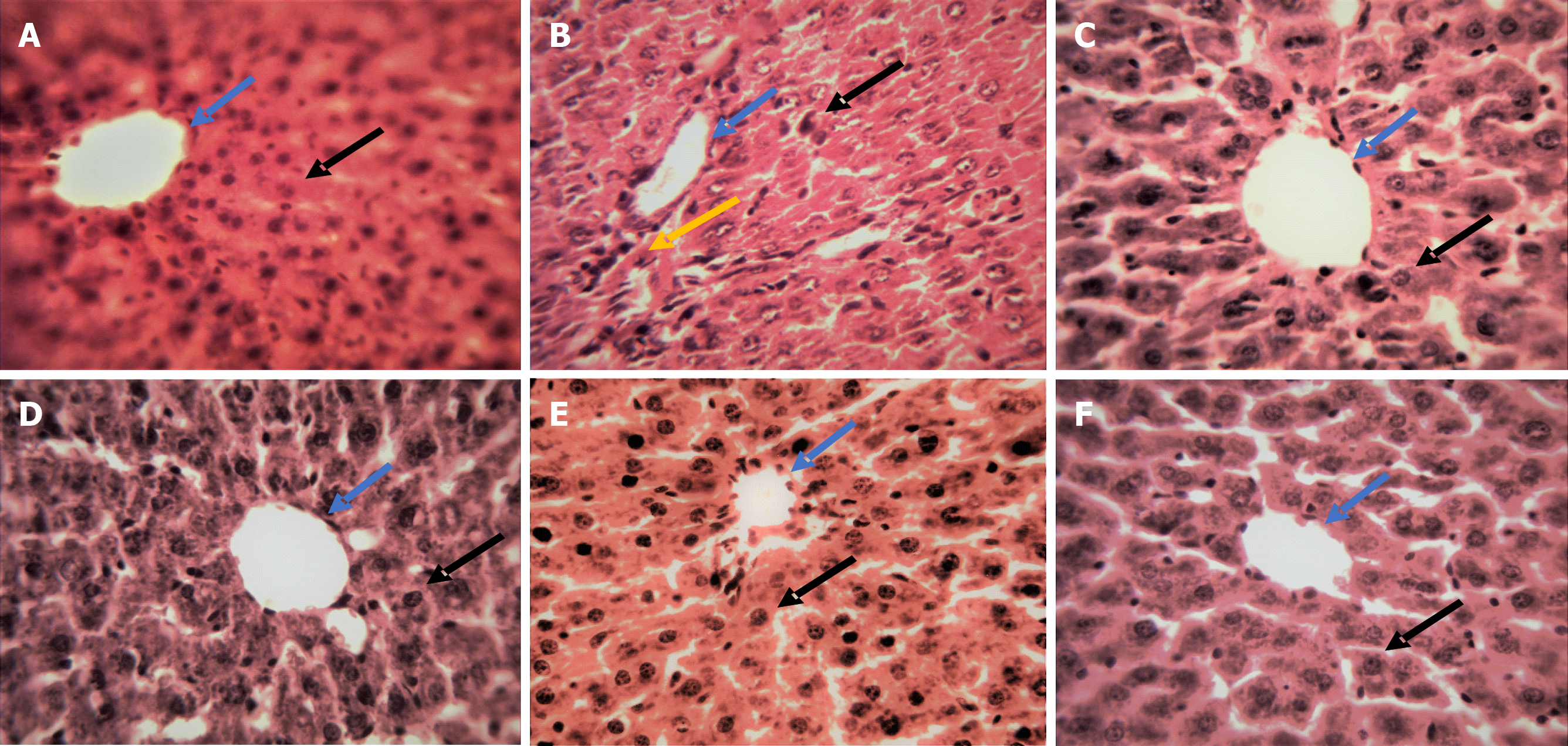
Figure 5 Histopathological changes in liver slices after oral administration of Terminaliabellirica fruit extracts, ellagic acid and Silymarin in Aceclofenac-treated rats.
A: Control; B: Aceclofenac (ACF) treated rats; C: ACF + Silymarin treated rats; D: ACF + Ellagic acid treated rats; E: ACF + Aqueous extract treated rats; and F: ACF + Ethyl acetate extract treated rats. The blue color arrow represents central vain, black arrow represents a nucleus and the yellow arrow represents inflammatory cells.
- Citation: Gupta A, Pandey A. Aceclofenac-induced hepatotoxicity: An ameliorative effect of Terminalia bellirica fruit and ellagic acid. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(11): 949-964
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i11/949.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i11.949