Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2019; 11(2): 55-72
Published online Feb 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i2.55
Published online Feb 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i2.55
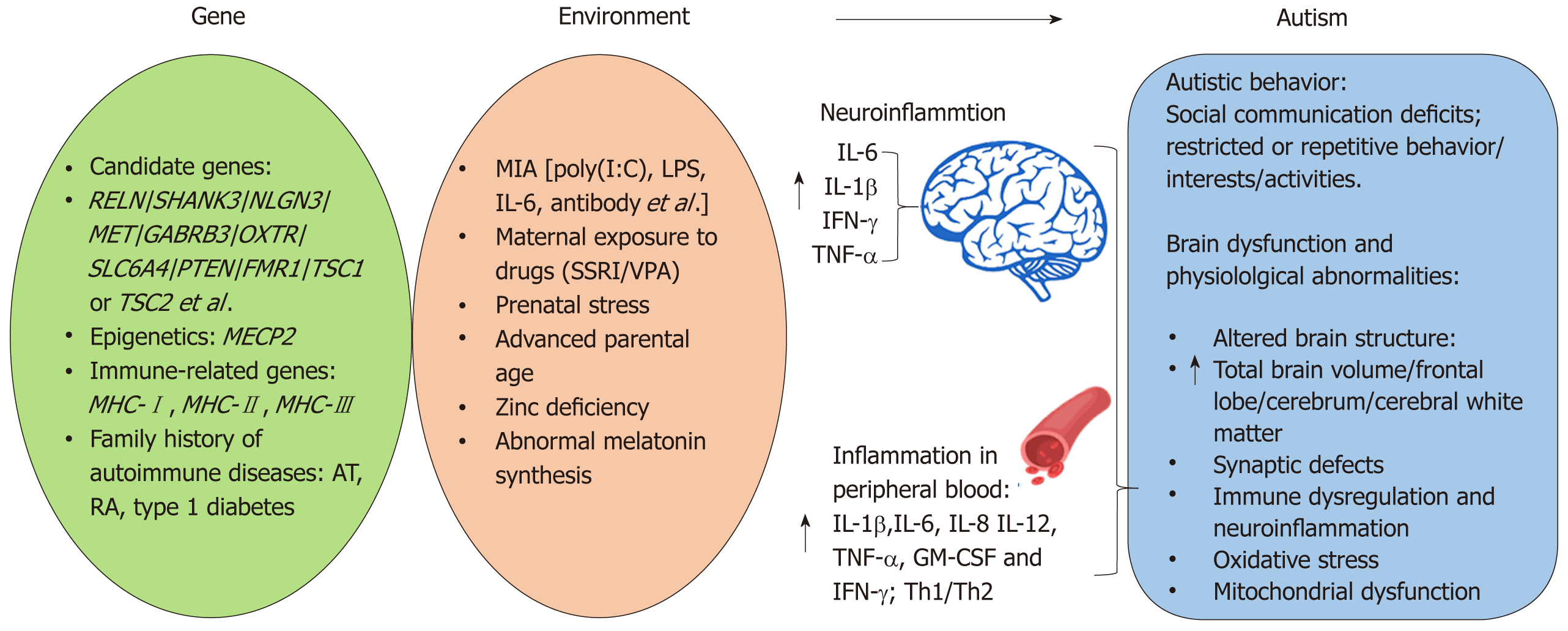
Figure 1 Genetic and environmental risk factors for autism spectrum disorders.
Genetic risk factors for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) including: important candidate genes, immune-related genes (such as MHC), epigenetics, and family history of autoimmune disease. Prenatal infection, maternal exposure to drugs, prenatal stress, advanced parental age, zinc deficiency, and abnormal melatonin synthesis are important environmental risk factors for ASD. ASD children exhibit social communication deficits and repetitive behavior. Brain dysfunction and physiological abnormalities are observed in ASD patients and animal models. RELN: Reelin; GABRB3: Gamma-aminobutyric acid type-A receptor beta3 subunit; OXTR: Oxytocin receptor; SLC6A: PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; FMR1: Fragile X mental retardation 1; TSC1/2: Tuberous sclerosis 1/2; MECP2: Methyl CpG binding protein 2; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; AT: Autoimmune thyroiditis; RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; MIA: Maternal immune activation; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; SSRI: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; VPA: Valproic acid.
- Citation: Liu Q, Chen MX, Sun L, Wallis CU, Zhou JS, Ao LJ, Li Q, Sham PC. Rational use of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of autism spectrum disorders. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(2): 55-72
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i2/55.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i2.55