Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2015; 7(7): 1054-1063
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i7.1054
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i7.1054
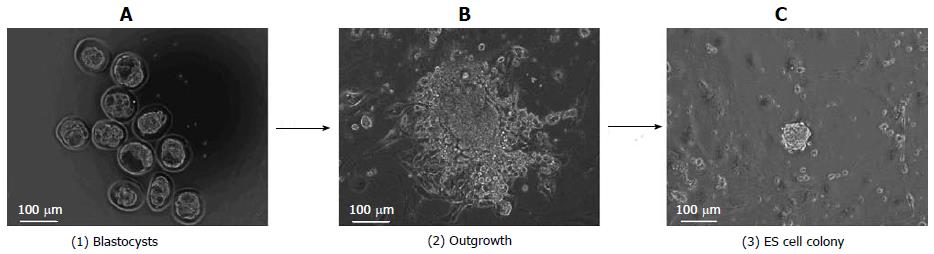
Figure 1 Establishment of rat embryonic stem cells.
A: E4.5 Blastocysts are isolated from Sprague-Dawley rats, and the blastocysts dissolved zona pellucida are put on mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) feeders; B: After 7-10 d, the outgrowth formed from the blastocysts are dispersed, and transferred on MEF feeders; C: Approximately 7 d after culture, rat embryonic stem (ES) cells are appeared (our unpublished data).
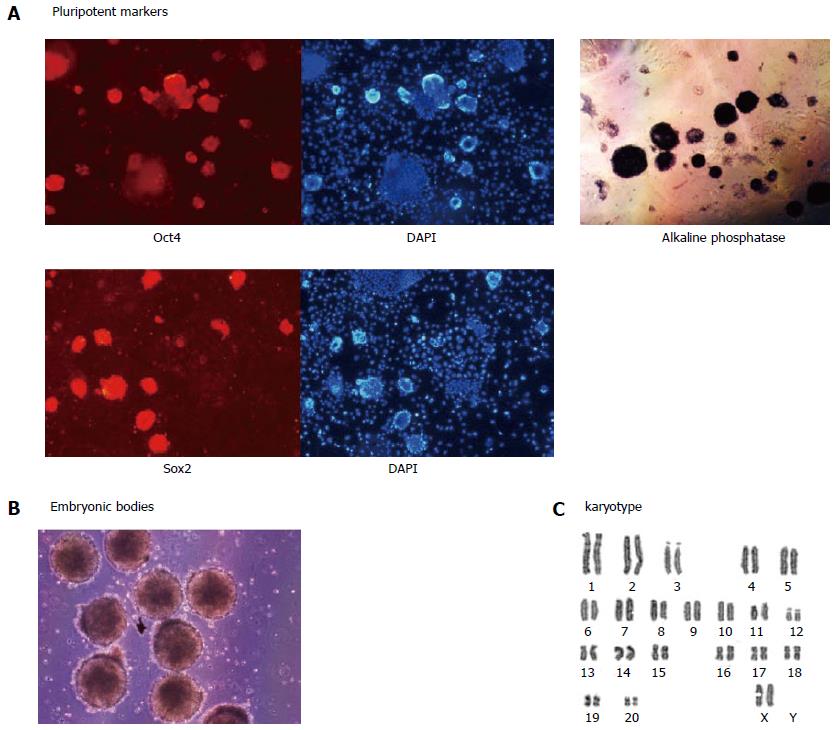
Figure 2 Properties of the rat embryonic stem cells.
The rat embryonic stem cells are established using the combination of four inhibitors and serum: mitogen-associated protein kinase/extracellular signal-related kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitor, glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitor, activin receptor-like kinase (ALK5) inhibitor, Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase inhibitor and FBS. A: Expression of the pluripotent markers Oct4 and Sox2, and alkaline phosphatase staining; B: Embryonic body formation; C: Karyotype analysis by G-band staining (our unpublished data). DAPI: 4',6 -diamidino-2-phenylindole; FBS: Fetal bovine serum.
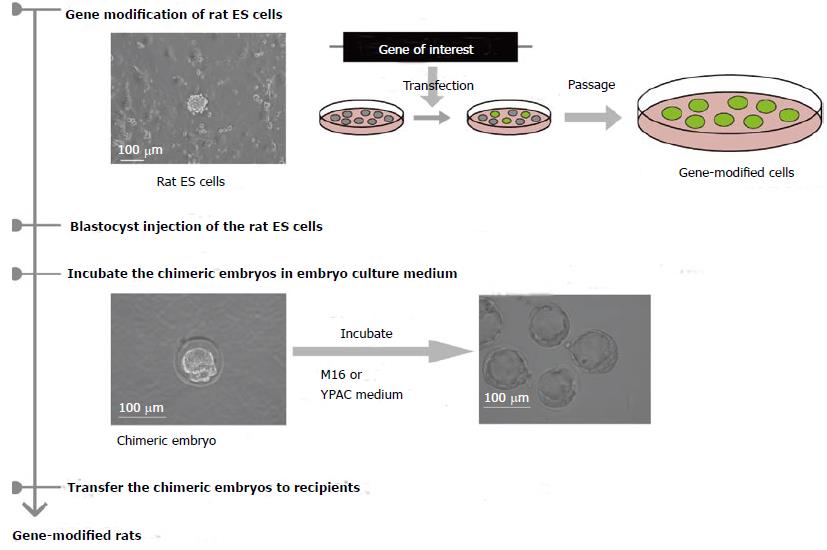
Figure 3 Generation of embryonic stem cell-derived gene-modified rats.
First, a gene of interest is introduced into rat embryonic stem (ES) cells. Next, the gene-targeted rat ES cells are injected into blastocysts and are incubated in embryo culture medium or YPAC medium. Then, the chimeric rat embryos are transferred into recipient rats. After that, gene-modified rats will be generated following breeding of the chimeric rats obtained from chimeric embryos.
- Citation: Kawaharada K, Kawamata M, Ochiya T. Rat embryonic stem cells create new era in development of genetically manipulated rat models. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(7): 1054-1063
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i7/1054.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i7.1054