Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2020; 12(12): 1623-1639
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1623
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1623
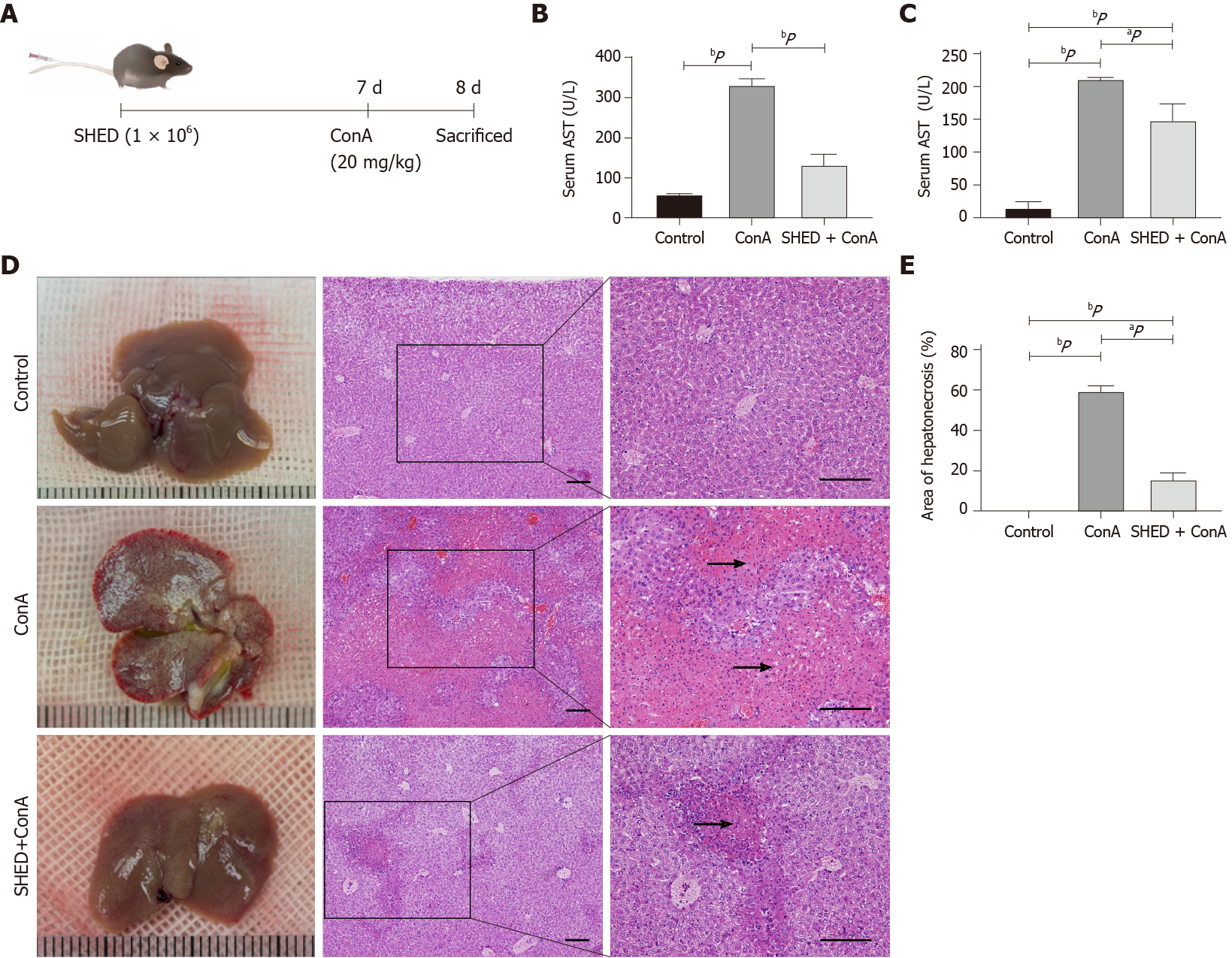
Figure 1 Pretreatment with stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth alleviates concanavalin A-induced acute liver injury in mice.
A: Mice were subjected to intravenous injections with stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth cells (1 × 106) 7 d prior to a concanavalin A (20 mg/kg) challenge. Mice were sacrificed 1 d after injection; B: Levels of serum alanine aminotransferase; C: Levels of serum aspartate aminotransferase; D: Anatomical examination and hematoxylin-eosin staining showing necrotic area in the three groups. Arrows indicate massive cell death in the liver section; E: Percentage of liver tissue necrotic areas. Scale bars = 200 μm. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; n ≥ 3.
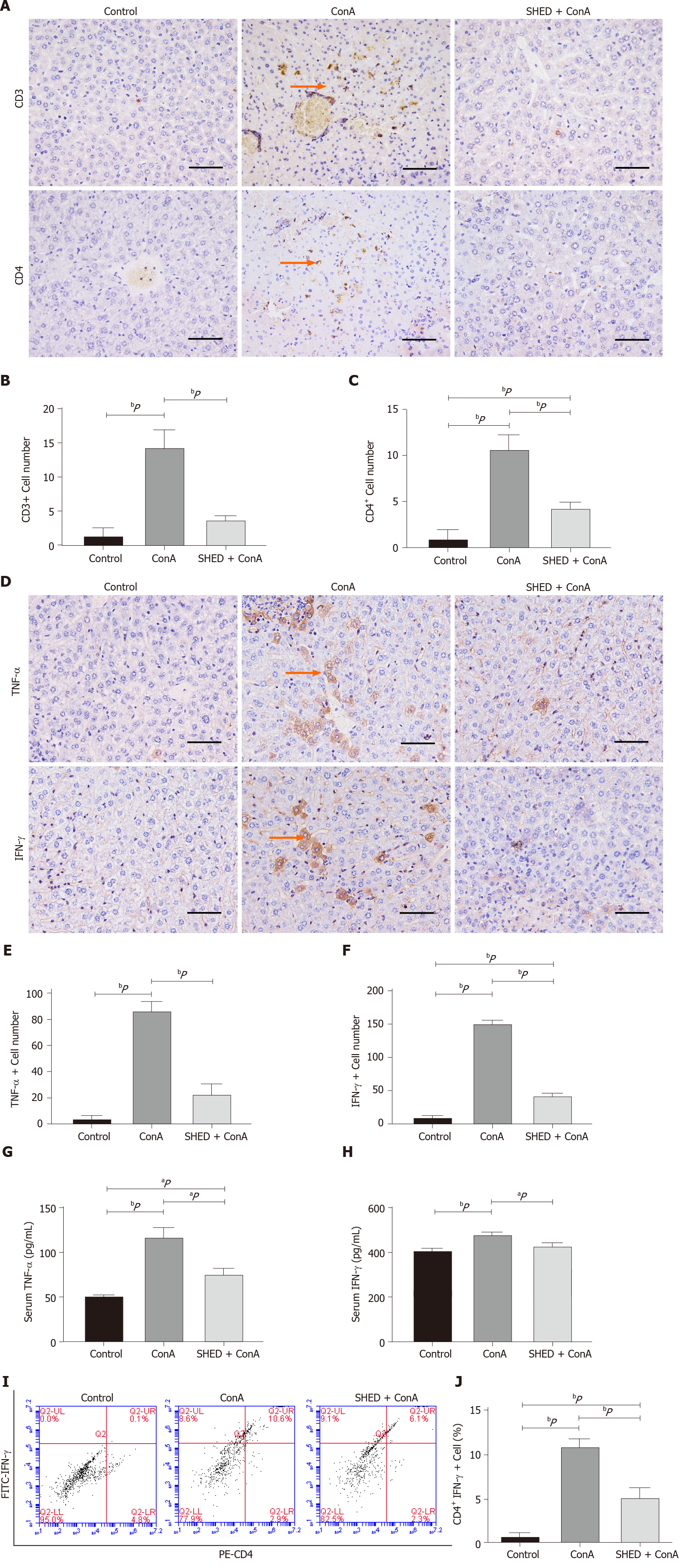
Figure 2 Pretreatment with stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth reduces inflammation in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis.
A: CD3+ and CD4+ T cell expression in liver tissues; B: Quantitative analysis of the number of CD3+ T cells; C: Quantitative analysis of the number of CD4+ T cells; D: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) expression in liver tissues; E: Quantitative analysis of the number of TNF-α+ cells; F: Quantitative analysis of the number of IFN-γ+ cells; G: Serum TNF-α levels; H: Serum IFN-γ levels. Arrows indicate positive cells in the liver section; I: Th1 cells detected by flow cytometry; J: Quantitative analysis of the percentage of CD4+ IFN-γ+ T cells; Scale bars = 100 μm. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; n ≥ 3.
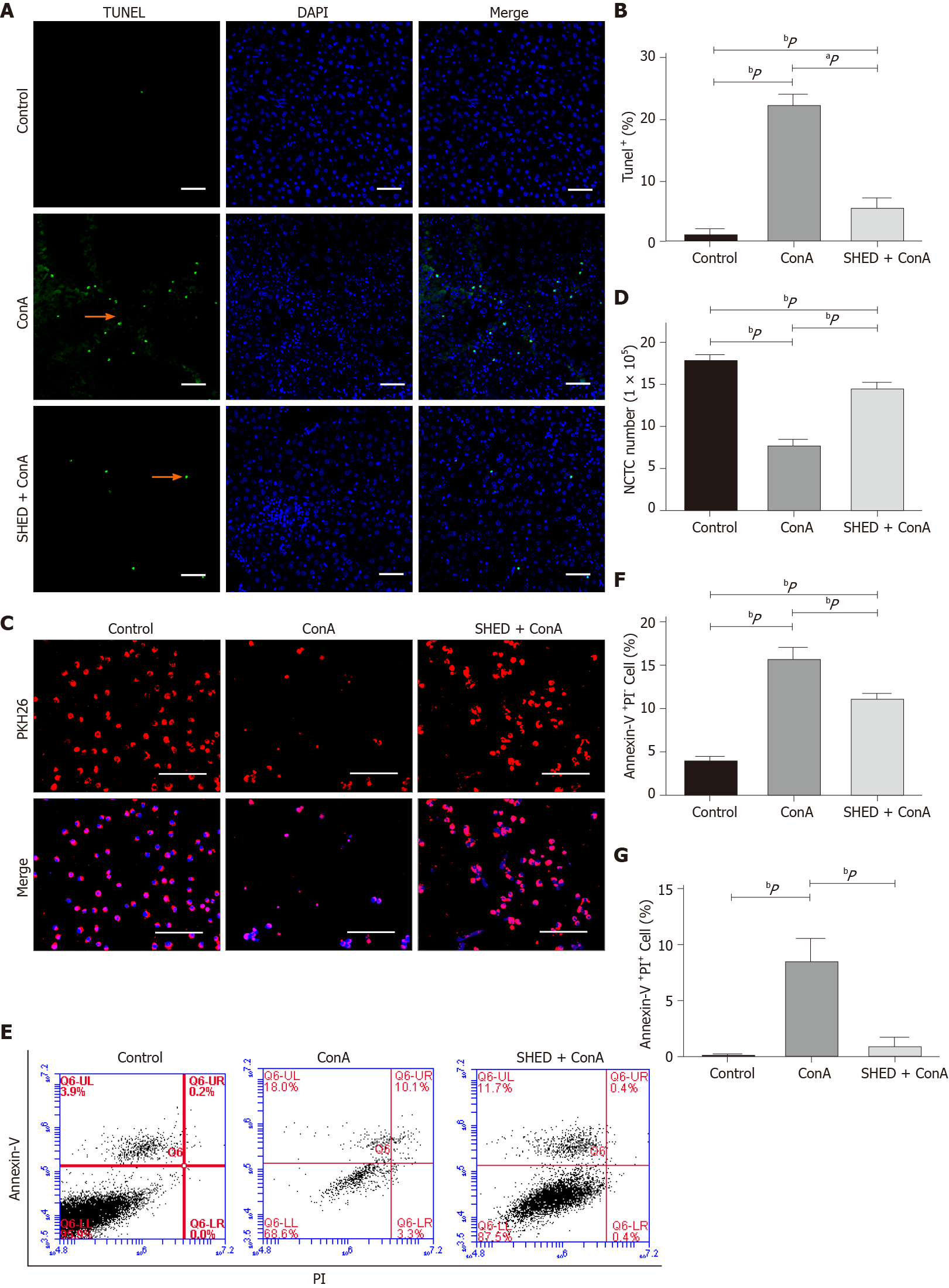
Figure 3 Pretreatment with stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth pretreatment inhibits concanavalin A-induced hepatocyte apoptosis.
A: Terminal dUTP nick-end labeling staining of apoptotic cells; B: Semi-quantitative analysis of the percentage of terminal dUTP nick-end labeling+ area in liver tissues. Arrows indicate positive cell death in the liver section; C: NCTC-1469 liver cells in the indicated treatment groups. NCTC cells are labeled with PKH26; D: Quantitative analysis of NCTC-1469 liver cell number; E: NCTC cell apoptosis detected by flow cytometry; F: Quantitative analysis of Annexin V+PI- rate; G: Quantitative analysis of Annexin V+PI+ rate. Scale bars = 100 μm. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, n ≥ 3.
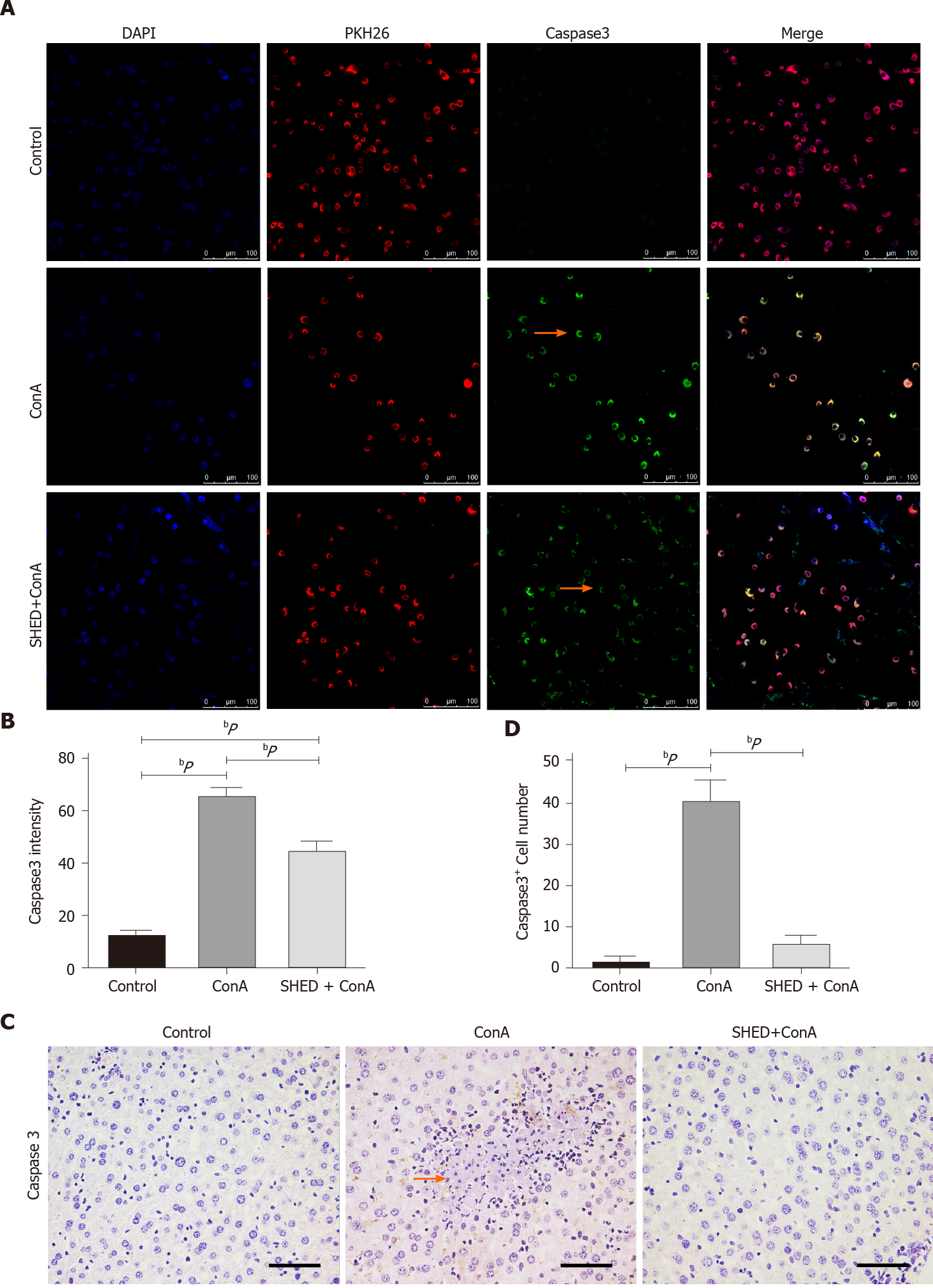
Figure 4 Pretreatment with stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth reduces Caspase3 in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis.
A: Caspase3 protein expression in NCTC cells; B: Semi-quantitative analysis of caspase3 protein fluorescence intensity; C: Caspase3 protein expression in liver tissues; D: Quantitative analysis of the number of caspase3+ cells. Arrows indicate positive cells in the liver section. Scale bars = 100 μm. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, n ≥ 3.
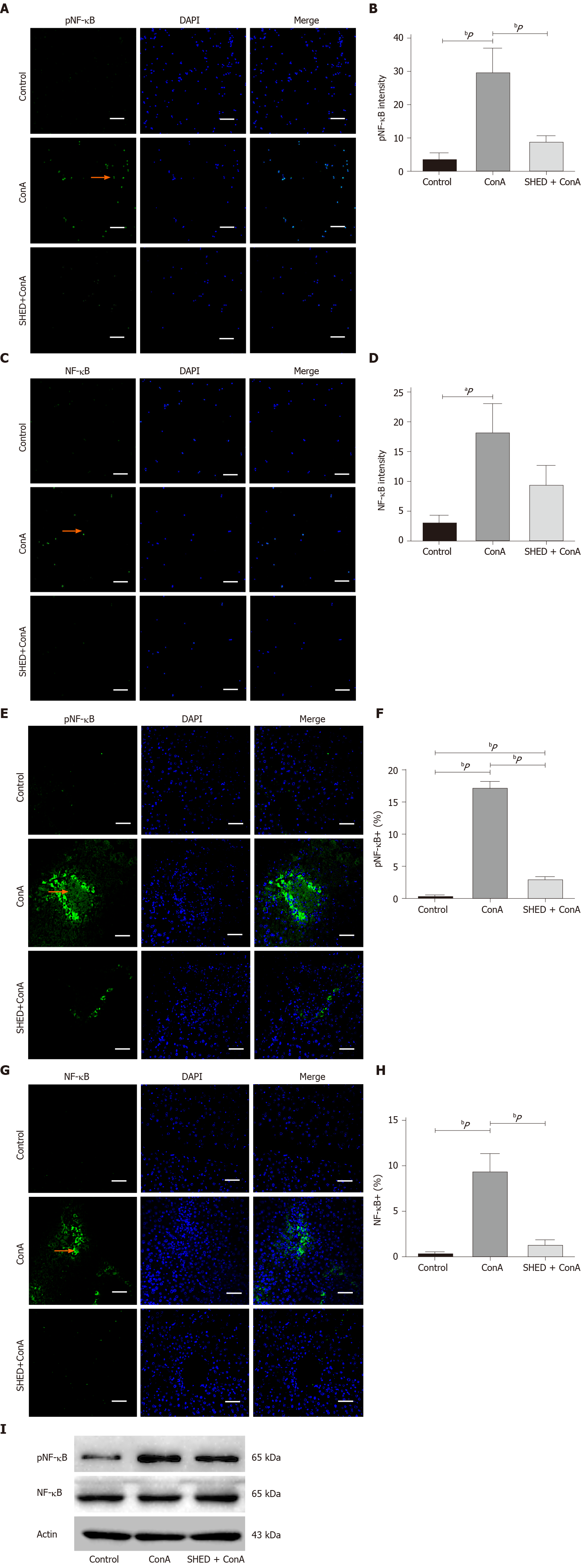
Figure 5 Pretreatment with stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth reduces nuclear factor-kappa B activation in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis.
A: Phosphorylated nuclear factor-kappa B [(p)NF-κB] protein expression in NCTC cells; B: Semi-quantitative analysis of (p)NF-κB protein fluorescence intensity; C: NF-κB protein expression NCTC cells; D: Semi-quantitative analysis of NF-κB protein fluorescence intensity; E: Phosphorylated (p)nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) protein expression in liver tissues; F: Quantitative analysis of the number of NF-κB+ cells; G: NF-κB protein expression in liver tissues; H: Quantitative analysis of the number of pNF-κB+ cells; I: Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analysis of (p)NF-κB and NF-κB levels in different groups. Arrows indicate positive cells in the liver section. Scale bars = 100 μm. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, n ≥ 3.
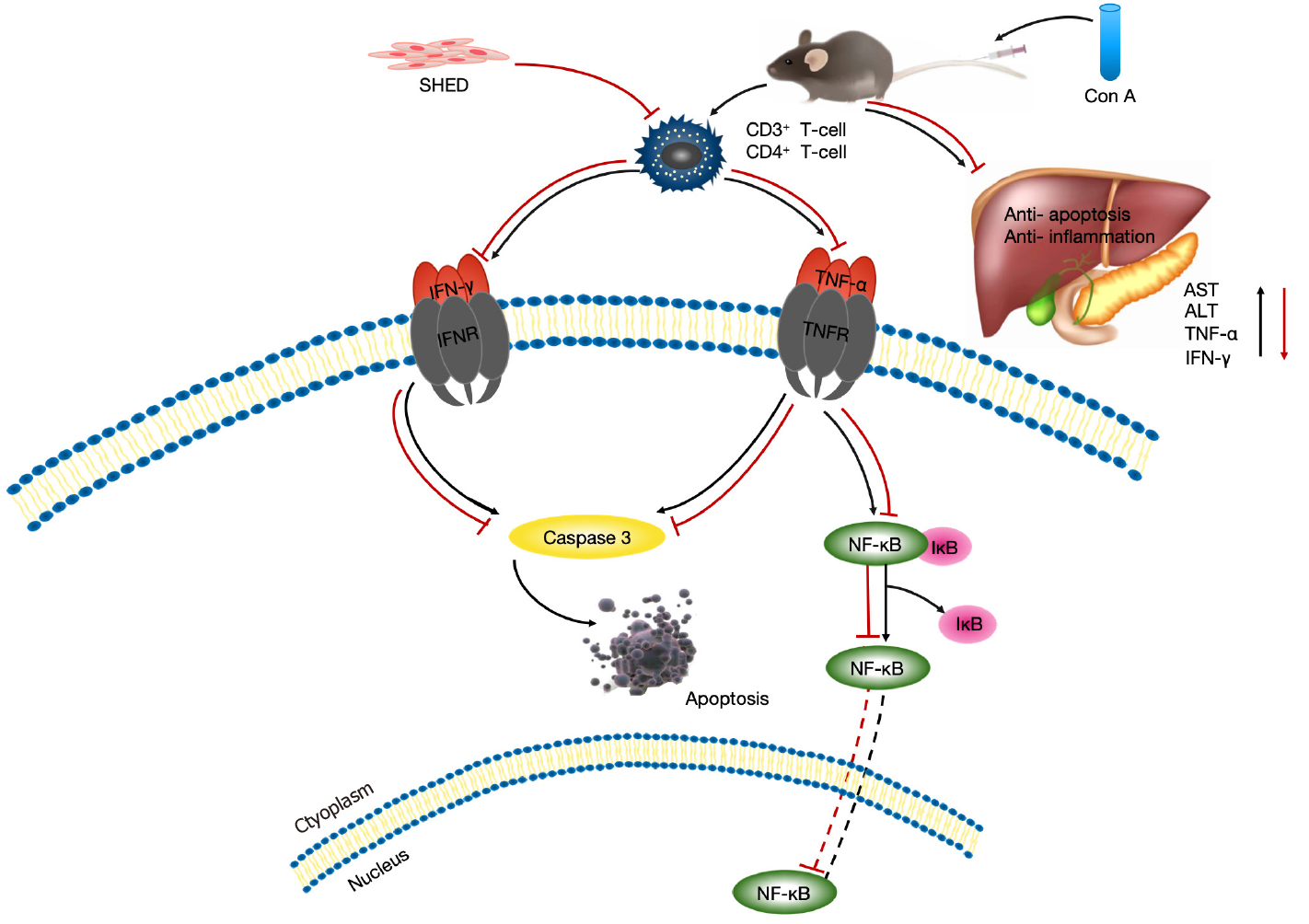
Figure 6 Schematic of treatment with stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth for concanavalin A-induced hepatitis.
In concanavalin A-induced acute liver injury, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma activate nuclear factor-kappa B and caspase3 to induce hepatocyte apoptosis. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth alleviate concanavalin A-induced acute liver injury via hepatocyte apoptotic inhibition, which is mediated by the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway.
- Citation: Zhou YK, Zhu LS, Huang HM, Cui SJ, Zhang T, Zhou YH, Yang RL. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorate concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis by protecting hepatocytes from apoptosis. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(12): 1623-1639
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i12/1623.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1623