Published online Jun 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3208
Peer-review started: January 29, 2021
First decision: March 6, 2021
Revised: March 19, 2021
Accepted: May 20, 2021
Article in press: May 20, 2021
Published online: June 21, 2021
Processing time: 133 Days and 13.4 Hours
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) recently emerged as a highly virulent respiratory pathogen that is known as the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Diarrhea is a common early symptom in a significant proportion of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. SARS-CoV-2 can infect and replicate in esophageal cells and enterocytes, leading to direct damage to the intestinal epithelium. The infection decreases the level of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, thereby altering the composition of the gut microbiota. SARS-CoV-2 elicits a cytokine storm, which contributes to gastrointestinal inflammation. The direct cytopathic effects of SARS-CoV-2, gut dysbiosis, and aberrant immune response result in increased intestinal permeability, which may exacerbate existing symptoms and worsen the prognosis. By exploring the elements of pathogenesis, several therapeutic options have emerged for the treatment of COVID-19 patients, such as biologics and biotherapeutic agents. However, the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the feces may facilitate the spread of COVID-19 through fecal-oral transmission and contaminate the environment. Thus gastrointestinal SARS-CoV-2 infection has important epidemiological significance. The development of new therapeutic and preventive options is necessary to treat and restrict the spread of this severe and widespread infection more effectively. Therefore, we summarize the key elements involved in the pathogenesis and the epidemiology of COVID-19-associated diarrhea.
Core Tip: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) replicates in enterocytes, triggers ionic imbalances, activates the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway, induces apoptosis, and exerts a dual effect on the autophagic process. These effects of SARS-CoV-2 lead to the development of leaky gut. Increased permeability triggers the absorption of lipopolysaccharide into the circulation, further exacerbating inflammation induced by viral infection. In addition to drugs that affect the inflammatory response and viral replication, agents targeting autophagy and apoptosis appear to be potentially suitable for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The fecal-oral route of SARS-CoV-2 transmission calls for strict and more consistent adherence to hygiene rules to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
- Citation: Megyeri K, Dernovics Á, Al-Luhaibi ZII, Rosztóczy A. COVID-19-associated diarrhea. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(23): 3208-3222
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i23/3208.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3208
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) recently emerged as a highly virulent respiratory pathogen that is known as the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)[1]. SARS-CoV-2 enters the human body through the airways and multiplies in the lungs. This novel coronavirus causes mild, severe, and critical respiratory disease in 81%, 14%, and 5% of cases, respectively[2]. It may also enter the bloodstream, which results in viremia and systemic spread throughout the body.
In addition to the airways, the virus can multiply in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract (GIT), urinary tract, and central nervous system. The infection elicits an intemperate immune response characterized by a life-threatening cytokine storm and a corrupted interferon (IFN) system, which is unable to eliminate the pathogen effectively. As a result, a systemic inflammatory response syndrome occurs[3,4]. In the severe and critical clinical manifestations of COVID-19, atypical pneumonia leading to pro
As of the 13th of January 2021, about 90 million people have been infected, and nearly 2 million people have died during the COVID-19 pandemic[5]. Although the leading COVID-19 symptoms are due to involvement of the respiratory system, it often causes GI symptoms as well. Thus, we examined the current state of knowledge on the pathogenesis, occurrence rate, clinical significance, and epidemiological consequences of COVID-19-associated diarrhea.
SARS-CoV-2 belongs to the genus Betacoronavirus of the family Coronaviridae, which comprises enveloped viruses with positive-sense single-stranded RNA genomes[1,6,7]. The spherical or elliptical virions are pleomorphic with diameters of 80-160 nm[8,9]. The capsid has helical symmetry, which is built up by the nucleocapsid (N) protein. The spike (S), membrane (M), and envelope (E) proteins are located in the virion envelope[10]. The S protein forms protrusions of 20 nm in length that provide a characteristic crown-like appearance, which is reflected in the name of the viral family. The S-protein is responsible for binding to the cell surface receptor[10].
Besides the S, E, M, and N structural protein genes, the genome of SARS-CoV-2 contains open reading frames (Orfs) that encode nine accessory proteins (3a, 3b, 6, 7a, 7b, 8, 9b, 9c, and 10) and two polyproteins (pp1a and pp1ab)[10-15]. Polyproteins pp1a and pp1ab are cleaved by viral proteases to form unique non-structural proteins (Nsp), which play an important role in viral replication[10]. Although the accessory proteins of SARS-CoV-2 are not essential for viral multiplication, they are implicated in the pathogenesis[10].
As the first step in infection, the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds to its corresponding cell-surface receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2 (ACE2)[16,17]. The S protein has two subunits: S1 and S2. The S1 subunit has a receptor-binding domain and is responsible for receptor engagement, whereas the S2 subunit is involved in the fusion process[17-19]. Following ACE2 binding, cellular proteases such as transmem
Within the endosome, cathepsin-mediated activation of the S protein continues, eventually causing the S2 subunit to gain a fusogenic effect that triggers the fusion of the viral envelope and the endosomal membrane[25]. The nucleocapsid is then released into the cytoplasm, where the translation of Orf1a and Orf1b results in the formation of pp1a and pp1ab, from which Nsp1-16 are generated by proteolysis. Nsp12 functions as an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and associates with Nsp7 and Nsp8 to form the core of the replication and transcription complex (RTC) of SARS-CoV-2[28,29]. The cofactors Nsp7 and Nsp8 form a hexadecameric ring structure that has a primase function and generates RNA primers for the synthesis of the negative-sense RNA[28,29].
RTC synthesizes the genomic RNA and a set of SARS-CoV-2 mRNAs through full-length and subgenomic negative-sense RNA intermediates[28,29]. The replication of the viral genome and transcription of viral genes takes place in double-membraned vesicles[30,31]. The SARS-CoV-2 replication compartment provides a protected environment which inhibits the antiviral effects of IFN and other cellular antiviral defense mechanisms by hiding the viral genome, transcripts, and replicative intermediates from cellular nucleic acid sensors.
The viral mRNAs are translated in the rough endoplasmic reticulum, leading to the formation of accessory proteins and structural proteins (N, M, E, and S). The M, E, and S proteins then become embedded in the endoplasmic reticulum, whereas the N proteins assemble with the newly synthesized full-length positive-sense RNA to form the nucleocapsid[30,31]. After being transported to the ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment), the nucleocapsids bud through the ERGIC membrane into its lumen[30,31]. The mature virions reach the cytoplasm membrane via vesicular transport and are released from the cell[30,31].
During multiplication, SARS-CoV-2 modulates several cellular aspects, including signaling, transcription, translation, cell division, the IFN system, autophagy, and apoptosis, as well as the biogenesis, function, and morphology of mitochondria and intracellular vesicles. Phosphoproteomic profiling has revealed that SARS-CoV-2 infection affects the activity of 97 kinases. The activities of several members of the p38 pathway and the guanosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinases are upregulated, while cell cycle kinases (CDK1/2/5), cell growth-related signaling pathway kinases (AKT1/2), and regulators of the cytoskeleton are down-regulated[32]. The functional changes in the signal transduction pathways have been shown to play an important role in SARS-CoV-2-induced cytoskeletal damage, cytokine production, and slow-down in cell proliferation at the S/G2 transition phase[32].
Transcriptomic profiles of SARS-CoV-2-infected primary human bronchial epithelial cells, lung biopsy, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples of COVID-19 patients have demonstrated upregulated expression of genes implicated in metabolism, immunity, and the stress responses of the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria[33-35]. It has been shown that the M protein, Nsp7, and ORF9c stimulate lipogenesis, while Nsp7, Nsp12, and ORF8 trigger endoplasmic stress response, and Nsp7 induces mitochondrial dysfunction[34]. Moreover, the M and E proteins, along with Nsp3a, Nsp6, Nsp8, Nsp10, and Nsp13, were shown to be able to modify the structure and function of the endomembrane system and vesicle trafficking, thereby facilitating several steps of viral multiplication[36].
Interestingly, the expression of genes involved in the humoral immune response and innate immune response-activating signal transduction are increased, whereas genes implicated in cytokine-mediated signaling pathways are down-regulated[33]. A multiplex gene expression analysis showed that the genes involved in type I IFN signaling were highly up-regulated, whereas the expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) was decreased in severe COVID-19 patients[37]. The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines measured in sera of COVID-19 patients were highly increased in a pattern corresponding to a cytokine storm[38-40].
Consistent with this observation, transcriptional activation of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes was also detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid[41]. The sera and lung tissue samples of patients have shown interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-18, IL-33, transforming growth factor-β, IFN-γ, CSF2/GM-CSF (colony-stimulating factor 2/granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor), CSF3/G-CSF, CC chemokines [CCL2/MCP-1, CCL3/MIP-1A, CCL4/MIP-1B, CCL5/RANTES, CCL8, CCL3L1] and CXC chemokines [CXCL1, CXCL2 and CXCL10/IP10][38,39,41,42]. However, during SARS-CoV-2 infection, the production of type I and III IFNs is decreased[37,43]. Thus, these data clearly demonstrate that SARS-CoV-2 infection alters both the transcriptional and translational patterns in cells profoundly[32-43].
Other observations indicate that SARS-CoV-2 could trigger several cell-death processes, including apoptosis, necrosis, pyroptosis, and anoikis, depending on the type of cell[44-47]. The death of infected cells may contribute to tissue damage and induce an inflammatory reaction[44-47]. It has also been revealed that SARS-CoV-2 Orf 3a stimulates the formation of the autophagic Beclin-1-Vps34-Atg14 complex while simultaneously inhibiting the Beclin-1 complex containing the UVRAG adaptor protein[48]. Orf 3a thereby exerts a dual effect on the autophagic process manifesting in the induction of the initial steps and a block in the fusion of the autophagosomes with lysosomes[48].
GIT involvement is frequent in COVID-19 patients and includes anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain[49-62]. Among the specific GI symptoms, diarrhea is the most common. Based on different studies, the prevalence of diarrhea might range from 2% to 49.5%[50,61,63]. COVID-19-associated diarrhea is characterized by loose or watery stools and is usually mild, self-limiting, and can even be the only symptom of the infection[49,52,58,59,63]. The average frequency of bowel movements is in the range of 3.3-4.3 times per day[53,58], and the average duration of diarrhea is 3-5.4 d[52,53,58,59,63]. In some cases, however, diarrhea is more severe, with patients experiencing more frequent bowel movements of up to 18-30 times per day[58,63].
Rare cases with more severe GI symptoms have also been reported, such as acute hemorrhagic colitis and GI bleeding[53,54,64]. Furthermore, the relationship between GI symptoms and the severity of the disease has been investigated. Statistically significant differences were not observed between COVID-19 patients with and without GI symptoms in clinical severity, length of hospital stay, and mortality rate[49,59,60]. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA could be detected in the stool of COVID-19 patients in 22%-54.5% of cases, and occasionally, the virus is detectable in the stool even after the airway samples become negative[54,57,58,65-69]. Positive results have been obtained from real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (Rrt-PCR) tests of stool even in patients without GI symptoms[58]. In patients with GI symptoms, the total time between the onset of symptoms and viral clearance is significantly longer than in those with only respiratory manifestations[58,70].
The reason why GI symptoms occur in only a subset of COVID-19 patients is currently unknown. There are no significant differences between the two patient groups in terms of demographics and certain coexisting conditions, such as pregnancy, cancer, chronic renal disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or immunosuppression. A study conducted by Jin et al[52] revealed that the rate of chronic liver disease in COVID-19 patients with GI symptoms is much higher than among those without GI symptoms. Moreover, the incidence of COVID-19 with GI symptoms displays familial clustering[52]. Based on these interesting observations, it is reasonable to infer that genetic, immunological, and epidemiological factors are involved in the development of COVID-19-associated diarrhea.
ACE2, the cellular receptor of SARS-CoV-2, is widely expressed in many types of cells and tissues of the GIT, including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, rectum, pancreatic exocrine glands and islets, and gallbladder[71]. The expression level of ACE2 in the GIT is highest in the ileum epithelial cells, especially in the absorptive enterocytes[72]. It has also been demonstrated that ACE2 is co-expressed with TMPRSS2/4 proteases in the GIT, with the highest level in the ileum[73]. These observations indicate that several cell types in the GIT are potentially susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection[71-73].
Studies demonstrating that viral RNA can be detected in the stool samples of COVID-19 patients indicate that SARS-CoV-2 can indeed infect the GIT[54,57-59,66-68]. It is estimated that feces and GI tissues contain 104-108 and 100-104 RNAs per gram, respectively[74,75]. Further studies revealed that SARS-CoV-2 establishes a productive infection in intestinal epithelial cells and human small intestinal organoids, leading to the production of new infectious progeny virions[20,76]. Viral particles within intracytoplasmic vesicles and aggregates of SARS-CoV-2 virions attached to the surface of enterocytes have been detected in intestinal organoids and post-mortem GIT samples from COVID-19 patients by electron microscopy[76,77]. These observations indicate that the GIT can be an entry site and an extra-pulmonary target organ of SARS-CoV-2[20,71-73,76,77].
Further analyses were performed to determine whether infectious viruses are present in the GIT or feces. In most cases, efforts to cultivate infectious SARS-CoV-2 from feces have failed, although Xiao et al[78] recently reported the successful isolation of the virus from stool samples by using the Vero E6 cell line. Simulated large intestinal fluid was shown to reduce the infectivity of the virus significantly[20]. Thus, it is possible that most of the virus that multiplies in the enterocytes may be inactivated in the lumen of intestines within a short time after release.
In vitro cultivation of SARS-CoV-2 has demonstrated that this virus elicits a cytopathic effect (CPE) on some cell lines, whereas in other cell types, no cytomorphological abnormalities could be observed despite efficient viral replication[79]. In human airway epithelial cells, SARS-CoV-2 causes CPE characterized by the formation of multinucleated syncytia and cilium shrinking, and cell death largely occurs by way of apoptosis[45]. In contrast, the colorectal adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cell line proved to be susceptible to infection, but the multiplication of SARS-CoV-2 was not accompanied by a visible CPE[79]. Likewise, intense tissue damage was not observed in the GIT of COVID-19 patients[80].
SARS-CoV-2 can establish a persistent infection in human C2BBe1 intestinal cells expressing a brush border[81]. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 was shown to be more effective in inducing the production of IFN-α, IFN-β, IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2, and IFN-λ3 in human intestinal tissues ex vivo than in lung tissue[80]. Therefore, it is also conceivable that a specific immuno-inflammatory environment develops in the lungs and GIT as a result of infection, which affects the rate of viral replication and cell demise in different ways.
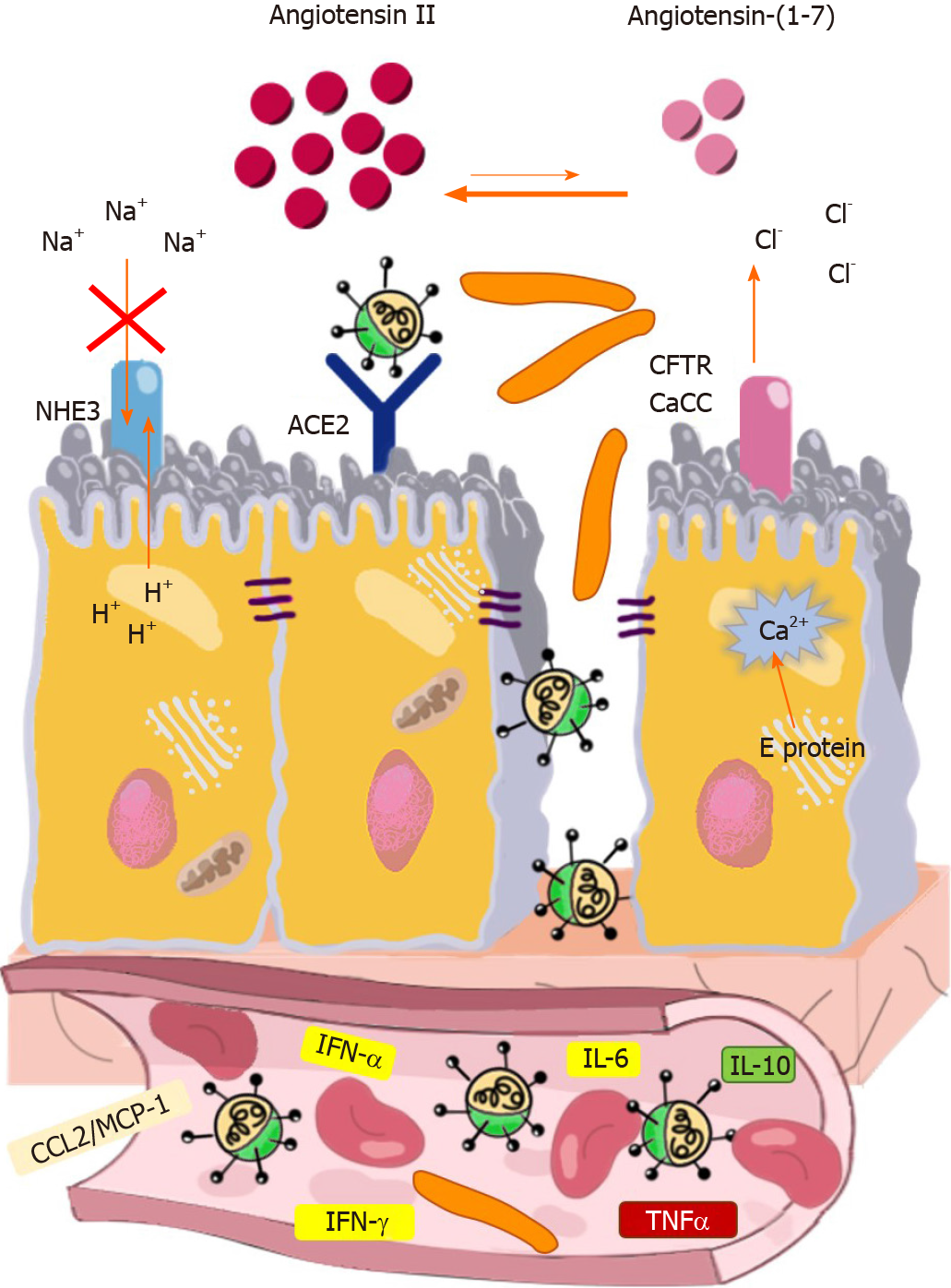
Although SARS-CoV-2 causes no extensive tissue damage in the intestines, the infection seems to harm the enterocytes in a much more sophisticated way. E protein was shown to bind to the tight junction-associated PALS1 (Proteins Associated with Lin Seven 1)[82]. PALS1 interacts with PATJ (PALS1-Associated Tight Junction protein) and CRB3 (Crumbs 3), and the PALS1/PATJ/CRB3 complex that forms is essential for the maintenance of tight junctions connecting epithelial cells[83]. E protein causes functional impairment of PALS1 and interferes with the formation of tight junctions, leading to the disruption of intestinal barrier integrity[82]. By using a biomimetic gut-on-chip system, Guo et. al. elegantly demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 infection destroys tight junctions and adherent junctions in both the endothelium and intestinal epithelium, which in turn may lead to leaky gut syndrome, local and systemic invasion of normal microbiota members, and immune activation[84] (Figure 1).
The E protein of SARS-CoV-2 is a single-spanning membrane protein that forms a homopentameric ion channel, which displays selective permeability for monovalent ions (Na+, K+, and Cl-) and Ca2+[85]. E protein accumulates in the endoplasmic reticulum and ERGIC/Golgi membranes and transports Ca2+ from these compartments to the cytoplasm. Elevated cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration can increase the rate of apical Cl- exit across the Ca2+-activated Cl- channels and cyclic-nucleotide-activated cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator[86].
SARS-CoV-2 also has another ion-channel protein, Orf3a, which is a K+ ion channel viroporin that exhibits plasma membrane and endomembrane localization[46,87]. Orf3a in the cytoplasmic membrane may cause leakage of K+ ions from enterocytes. Moreover, intracellular ionic imbalances triggered by SARS-CoV-2 viroporins (E protein and Orf3a) can lead to the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome (NOD-, LRR-, and Pyrin domain-containing 3). This results in the secretion of IL-1β and cell death in a process called pyroptosis[44,46]. By activating innate immune cells, IL-1β contributes to the development of a local inflammatory environment and a systemic cytokine storm. The direct action of viroporins and the indirect effects of cytokines together can trigger an ionic imbalance of enterocytes, which may contribute to the development of diarrhea (Figure 1).
During its multiplication, SARS-CoV-2 disturbs the function of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). The main components of this system are ACE, angiotensin II, and AT1R. Angiotensin II is known to elicit vasoconstriction, oxidative stress, and inflammation following binding to AT1R[88]. The ACE2/ angiotensin (1-7)/Mas pathway is an important physiological negative regulator of the ACE/angiotensin II/AT1R axis and exerts anti-inflammatory effects[88]. SARS-CoV-2 uses ACE2 for entry as a receptor, which becomes degraded in the endolysosomal compartment after being internalized along with the virion particles[17,19,20].
The viral infection has been shown to increase the expression of ADAM (A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease) metallopeptidase domain 17 enzyme, which is endowed with sheddase activity[89]. ADAM17 functions in the ectodomain shedding of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), EGFR ligands, and ACE2[90,91]. ADAM17-mediated cleavage decreases ACE2 Levels on the cytoplasm membrane and thereby shifts the delicate balance towards the ACE/angiotensin II/AT1R pathway. In turn, this can lead to pro-inflammatory predominance. It has also been demonstrated recently that ACE2 forms dimer-of-heterodimer complexes with the neutral amino acid transporter B0AT1 (Broad neutral Amino acid Transporter 1)[91]. B0AT1 is involved in the Na+-coupled transportation of tryptophan, phenylalanine, glutamine, and leucine[91].
The ADAM17-mediated cleavage of ACE2 ectodomain and attachment of SARS-CoV-2 to the ACE2:B0AT1 complex may potentially compromise the transport of Na+ and neutral amino acids[88]. Impairment of the ACE2:B0AT1 complex and the consequential amino acid starvation can decrease Na+ uptake and affect the activation state of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex, which is an important regulator of autophagy, xenophagy, metabolism, and various immune processes[88,92-95]. Dysregulated RAAS may aggravate ionic imbalance and inflammation, which may affect the metabolic state of cells, the composition of the microbiota, and cell viability, leading to increasingly severe intestinal dysfunction[88,90,91,94,95] (Figure 1).
If diarrhea is not included in the presenting symptoms and develops after admission, it becomes challenging to ascertain the cause of diarrhea. Several confounding variables, such as the hyperinflammatory response, altered gut flora, secondary bacterial infections, antiviral agents, antibiotics, enteral feeding, and the use of proton pump inhibitors can potentially cause diarrhea in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
In approximately 20% of COVID-19 patients, the infection progresses to severe and critical phases in which an extrapulmonary hyperinflammatory state develops due to cytokine release syndrome[96]. Several cytokines may affect the course and clinical manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection by increasing the intestinal and vascular permeability as well as triggering the formation of thrombi in the small blood vessels and the alteration of intestinal microbiota, leading to bacterial translocation towards the bloodstream and the mesenteric lymph node[3,4]. The cytokine-mediated GI damage may thereby further intensify the systemic immunological response and contribute to the deterioration of the patient’s condition. A study conducted by Zhang et al[97] revealed that the pro-inflammatory cytokine patterns are different in COVID-19 patients with and without diarrhea. Moreover, diarrhea patients were more likely to develop cytokine release syndrome and multi-organ damage[97]. Interestingly, the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 were significantly higher in the sera of diarrhea patients than in the non-diarrhea group[97]. TNF-α is known to increase the expression of adhesion molecules on the surface of endothelial cells, platelets, and leukocytes, thereby facilitating the adhesion of thrombocytes to the vessels and initiating the formation of thrombi in the microcirculation of the GIT and other organs. These effects increase vascular permeability and can lead to inflammation and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Furthermore, TNF-α has the ability to disrupt the intestinal tight junction barrier, which in turn contributes to the development of leaky gut[98]. IL-6 exerts dual effects on the intestinal epithelium. It increases gut permeability to small molecules with a radius < 4Å (< 0.4 nm) via activating claudin-2 gene expression[99]. However, by stimulating epithelial proliferation and regeneration, IL-6 plays a beneficial role in the maintenance of intestinal epithelial integrity during acute injury[100]. IL-10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine that restricts uncontrolled immune responses to the intestinal microbiota and defends gut barrier integrity[101,102]. In light of these data, it is reasonable to infer that TNF-α may be an important factor in COVID-19-associated diarrhea, whereas without IL-10, the cytokine storm and intestinal injury would be even more devastating. However, further studies are needed to identify the precise role of each cytokine in the development of COVID-19-associated diarrhea. Such studies could also contribute to a better understanding of the potential adverse effects of anti-cytokine therapies on the GIT.
Interesting observations revealed that the composition of intestinal microbiota is profoundly altered in COVID-19 patients: The diversity is highly reduced, the proportion of beneficial commensal bacteria is decreased and the opportunistic pathogens are enriched compared with that found in healthy controls[103,104]. It has also been demonstrated that some Bacteroides spp., capable of decreasing ACE2 expression in mice, displayed inverse correlation with the fecal SARS-CoV-2 load[104]. The immune system and the intestinal microbiota are in a continuous dialog. The presence of commensal microorganisms shapes host immunity, and alterations in microbiota composition may lead to increased susceptibility to various pathological conditions, including infections, inflammation, and metabolic and autoimmune disorders. Thus, the altered microbiota observed in COVID-19 patients may be an additional factor contributing to the development of diarrhea by weakening colonization resistance, decreasing the production of beneficial bacterial metabolites, and triggering a local immune recalibration.
For clinical improvement and treatment of secondary bacterial infections, COVID-19 patients are treated with antiviral agents, antibiotics, and corticosteroids. Antiviral agents such as the RNA polymerase inhibitors favipiravir and remdesivir may cause diarrhea[105]. Diarrhea is also a common adverse drug reaction to antibiotics such as cephalosporins, macrolides and fluoroquinolones, largely due to destruction of the normal intestinal microbiota. Moreover, treatment of COVID-19 patients with broad-spectrum antibiotics has the potential to increase the risk of Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile) infection, including in survivors even long after recovery. In co-infections with SARS-CoV-2 and C. difficile, intestinal damage is more extensive and diarrhea symptoms are more severe[106]. To counteract the detrimental effects of various proinflammatory cytokines, biological therapy is used in selected patient groups. IL-6 and IL-6 receptor inhibitors, such as tocilizumab, sarilumab and siltuximab, represent another class of drugs that often cause diarrhea[107]. Although enteral feeding has well- established, clear advantages over parenteral nutrition[108], adverse events, like diarrhea, may develop. Tube feeding-related diarrhea can occur for several reasons, mostly related to the circumstances of feeding (adaptation time, perfusion speed, temperature) or the composition of the used enteral formula (osmolarity, fat content, nutrient intolerance), and can be managed easily with careful observation of the patients[109]. Not only is the use of PPIs during the course of COVID-19 infection controversial[110], such drugs may induce diarrhea in general through the alteration of GI microbiota by different mechanisms, including the direct consequences of increased gastric pH itself. This safety issue was evaluated by a number of meta-analyses based on retrospective observational or case-control studies, which suggested an increased risk for enteral infections, especially C. difficile infections, in PPI-treated patients[111-113]. In contrast, a recent long-term prospective study (COMPASS) failed to show an increased risk of C. difficile infection in PPI users and only a slight increase of enteral infections in general[114].
A great body of experimental and clinical evidence demonstrates that SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in the GIT, and the stool contains high copies of viral RNA, although the amount of infectious virus in the stool appears to be low. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the feces may potentially facilitate the spread of COVID-19 through fecal-oral transmission among humans and contaminate the environment[115-117]. Thus, SARS-CoV-2 infection of the GIT has important epidemiological significance.
The feces of COVID-19 patients pose a serious epidemiological risk, which justifies the use of all available methods of prevention, including protective equipment, disinfection procedures, and vaccination. However, further studies are needed to establish the efficiency of the fecal-oral spread of SARS-CoV-2 precisely. It would be very useful if the concentration of infectious virion particles in the stool were determined in asymptomatic individuals and different patient groups under standardized parameters when discharge frequencies and the grade on the Bristol stool scale are precisely recorded. It is possible that the rate of virus inactivation in the intestinal lumen may significantly differ in COVID-19 patients.
SARS-CoV-2 can extensively contaminate the environment, and viral RNA can be detected in sewage and solid waste[118,119]. Measurement of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater is used for local monitoring of the epidemic situation, which facilitates the implementation of preventive measures. Wastewater epidemiology involves using Rrt-PCR to determine SARS-CoV-2 RNA in sewage, but how long the virus survives in this environment has not been measured[118,119]. It would be essential to determine the concentration of infectious virion particles to elucidate the risk of SARS-CoV-2 transmission via wastewater contamination.
Among the specific GI symptoms, diarrhea is the most common in COVID-19 patients. The ACE2 receptor and other elements required for the attachment of this virus to the various cell types are extensively expressed throughout the GIT. SARS-CoV-2 can establish a productive infection in the enterocytes, leading to mild cellular damage. The infection evokes an inflammatory response in the intestines, which is characterized by the production of various pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, many of which are known to increase intestinal permeability. Direct effects of SARS-CoV-2 viroporins and dysregulation of the intestinal RAAS triggering ionic imbalance and inflammation in the intestines seem to play important roles in the development of COVID-19-associated secretory diarrhea and leaky gut.
Infection in the lungs and GIT also seems to display some different tissue-specific features. The production of type I and III IFNs is more efficient in the GIT than in the lungs. The antiviral IFNs may restrict viral replication in the GIT to some extent, which may allow the development of a less cytopathogenic or persistent form of infection in this anatomical region. SARS-CoV-2-mediated dysregulation of the ACE2:B0AT1 complex may modify the biological response of cells to the infection, and in enterocytes, it may contribute to the development of diarrhea by inducing amino acid starvation, which can decrease Na+ uptake. These effects are not seen in the lungs, however, as ACE2 does not form a complex with B0AT1 in this organ. SARS-CoV-2 infection of the GIT is of pivotal epidemiological significance, but further studies are needed to assess the extent of this risk.
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Hungary
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Ding X S-Editor: Gao CC L-Editor: A P-Editor: Liu JH
| 1. | Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: lassifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat Microbiol. 2020;5:536-544. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5202] [Cited by in RCA: 4632] [Article Influence: 926.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19:141-154. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2083] [Cited by in RCA: 3171] [Article Influence: 792.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Tay MZ, Poh CM, Rénia L, MacAry PA, Ng LFP. The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:363-374. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3174] [Cited by in RCA: 2916] [Article Influence: 583.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Vabret N, Britton GJ, Gruber C, Hegde S, Kim J, Kuksin M, Levantovsky R, Malle L, Moreira A, Park MD, Pia L, Risson E, Saffern M, Salomé B, Esai Selvan M, Spindler MP, Tan J, van der Heide V, Gregory JK, Alexandropoulos K, Bhardwaj N, Brown BD, Greenbaum B, Gümüş ZH, Homann D, Horowitz A, Kamphorst AO, Curotto de Lafaille MA, Mehandru S, Merad M, Samstein RM; Sinai Immunology Review Project. Immunology of COVID-19: Current State of the Science. Immunity. 2020;52:910-941. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1336] [Cited by in RCA: 1183] [Article Influence: 236.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. [cited 13 January 2021]. In: World Health Organization [Internet]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int. |
| 6. | Helmy YA, Fawzy M, Elaswad A, Sobieh A, Kenney SP, Shehata AA. The COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comprehensive Review of Taxonomy, Genetics, Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Control. J Clin Med. 2020;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 445] [Cited by in RCA: 382] [Article Influence: 76.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N, Bi Y, Ma X, Zhan F, Wang L, Hu T, Zhou H, Hu Z, Zhou W, Zhao L, Chen J, Meng Y, Wang J, Lin Y, Yuan J, Xie Z, Ma J, Liu WJ, Wang D, Xu W, Holmes EC, Gao GF, Wu G, Chen W, Shi W, Tan W. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 2020;395:565-574. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8473] [Cited by in RCA: 7601] [Article Influence: 1520.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Miller SE, Goldsmith CS. Caution in Identifying Coronaviruses by Electron Microscopy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31:2223-2224. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Caldas LA, Carneiro FA, Higa LM, Monteiro FL, da Silva GP, da Costa LJ, Durigon EL, Tanuri A, de Souza W. Ultrastructural analysis of SARS-CoV-2 interactions with the host cell via high resolution scanning electron microscopy. Sci Rep. 2020;10:16099. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 14.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Naqvi AAT, Fatima K, Mohammad T, Fatima U, Singh IK, Singh A, Atif SM, Hariprasad G, Hasan GM, Hassan MI. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: Structural genomics approach. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866:165878. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 492] [Cited by in RCA: 672] [Article Influence: 134.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 11. | Khailany RA, Safdar M, Ozaslan M. Genomic characterization of a novel SARS-CoV-2. Gene Rep. 2020;19:100682. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 450] [Cited by in RCA: 491] [Article Influence: 98.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Michel CJ, Mayer C, Poch O, Thompson JD. Characterization of accessory genes in coronavirus genomes. Virol J. 2020;17:131. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 128] [Cited by in RCA: 125] [Article Influence: 25.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Finkel Y, Mizrahi O, Nachshon A, Weingarten-Gabbay S, Morgenstern D, Yahalom-Ronen Y, Tamir H, Achdout H, Stein D, Israeli O, Beth-Din A, Melamed S, Weiss S, Israely T, Paran N, Schwartz M, Stern-Ginossar N. The coding capacity of SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 2021;589:125-130. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 286] [Cited by in RCA: 415] [Article Influence: 83.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, Chen YM, Wang W, Song ZG, Hu Y, Tao ZW, Tian JH, Pei YY, Yuan ML, Zhang YL, Dai FH, Liu Y, Wang QM, Zheng JJ, Xu L, Holmes EC, Zhang YZ. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020;579:265-269. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6893] [Cited by in RCA: 7499] [Article Influence: 1499.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Srinivasan S, Cui H, Gao Z, Liu M, Lu S, Mkandawire W, Narykov O, Sun M, Korkin D. Structural Genomics of SARS-CoV-2 Indicates Evolutionary Conserved Functional Regions of Viral Proteins. Viruses. 2020;12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 164] [Cited by in RCA: 165] [Article Influence: 33.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, Chen HD, Chen J, Luo Y, Guo H, Jiang RD, Liu MQ, Chen Y, Shen XR, Wang X, Zheng XS, Zhao K, Chen QJ, Deng F, Liu LL, Yan B, Zhan FX, Wang YY, Xiao GF, Shi ZL. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579:270-273. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15248] [Cited by in RCA: 14131] [Article Influence: 2826.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 17. | Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH, Nitsche A, Müller MA, Drosten C, Pöhlmann S. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020; 181: 271-280. e8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11946] [Cited by in RCA: 14271] [Article Influence: 2854.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Bosch BJ, van der Zee R, de Haan CA, Rottier PJ. The coronavirus spike protein is a class I virus fusion protein: structural and functional characterization of the fusion core complex. J Virol. 2003;77:8801-8811. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1045] [Cited by in RCA: 1084] [Article Influence: 49.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat Microbiol. 2020;5:562-569. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1933] [Cited by in RCA: 2216] [Article Influence: 443.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Zang R, Gomez Castro MF, McCune BT, Zeng Q, Rothlauf PW, Sonnek NM, Liu Z, Brulois KF, Wang X, Greenberg HB, Diamond MS, Ciorba MA, Whelan SPJ, Ding S. TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes. Sci Immunol. 2020;5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 809] [Cited by in RCA: 765] [Article Influence: 153.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Wruck W, Adjaye J. SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 is co-expressed with genes related to transmembrane serine proteases, viral entry, immunity and cellular stress. Sci Rep. 2020;10:21415. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Hussain M, Jabeen N, Amanullah A, Baig AA, Aziz B, Shabbir S, Raza F, Uddin N. Molecular docking between human TMPRSS2 and SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: conformation and intermolecular interactions. AIMS Microbiol. 2020;6:350-360. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 64] [Article Influence: 12.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Wall A, McGuire AT, Veesler D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020; 181: 281-292. e6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4743] [Cited by in RCA: 6156] [Article Influence: 1231.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Belouzard S, Madu I, Whittaker GR. Elastase-mediated activation of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein at discrete sites within the S2 domain. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:22758-22763. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 80] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Ou X, Liu Y, Lei X, Li P, Mi D, Ren L, Guo L, Guo R, Chen T, Hu J, Xiang Z, Mu Z, Chen X, Chen J, Hu K, Jin Q, Wang J, Qian Z. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1620. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2003] [Cited by in RCA: 2291] [Article Influence: 458.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Du L, Kao RY, Zhou Y, He Y, Zhao G, Wong C, Jiang S, Yuen KY, Jin DY, Zheng BJ. Cleavage of spike protein of SARS coronavirus by protease factor Xa is associated with viral infectivity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;359:174-179. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 113] [Cited by in RCA: 106] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Ji HL, Zhao R, Matalon S, Matthay MA. Elevated Plasmin(ogen) as a Common Risk Factor for COVID-19 Susceptibility. Physiol Rev. 2020;100:1065-1075. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 291] [Cited by in RCA: 273] [Article Influence: 54.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Gao Y, Yan L, Huang Y, Liu F, Zhao Y, Cao L, Wang T, Sun Q, Ming Z, Zhang L, Ge J, Zheng L, Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhu Y, Zhu C, Hu T, Hua T, Zhang B, Yang X, Li J, Yang H, Liu Z, Xu W, Guddat LW, Wang Q, Lou Z, Rao Z. Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science. 2020;368:779-782. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 933] [Cited by in RCA: 1082] [Article Influence: 216.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Wang Q, Wu J, Wang H, Gao Y, Liu Q, Mu A, Ji W, Yan L, Zhu Y, Zhu C, Fang X, Yang X, Huang Y, Gao H, Liu F, Ge J, Sun Q, Xu W, Liu Z, Yang H, Lou Z, Jiang B, Guddat LW, Gong P, Rao Z. Structural Basis for RNA Replication by the SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase. Cell 2020; 182: 417-428. e13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 525] [Cited by in RCA: 443] [Article Influence: 88.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Mendonça L, Howe A, Gilchrist JB, Sun D, Knight ML, Zanetti-Domingues LC, Bateman B, Krebs AS, Chen L, Radecke J, Sheng Y, Li VD, Ni T, Kounatidis I, Koronfel MA, Szynkiewicz M, Harkiolaki M, Martin-Fernandez ML, James W, Zhang P. SARS-CoV-2 Assembly and Egress Pathway Revealed by Correlative Multi-modal Multi-scale Cryo-imaging. bioRxiv. 2020;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Klein S, Cortese M, Winter SL, Wachsmuth-Melm M, Neufeldt CJ, Cerikan B, Stanifer ML, Boulant S, Bartenschlager R, Chlanda P. SARS-CoV-2 structure and replication characterized by in situ cryo-electron tomography. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5885. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 287] [Cited by in RCA: 499] [Article Influence: 99.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Bouhaddou M, Memon D, Meyer B, White KM, Rezelj VV, Correa Marrero M, Polacco BJ, Melnyk JE, Ulferts S, Kaake RM, Batra J, Richards AL, Stevenson E, Gordon DE, Rojc A, Obernier K, Fabius JM, Soucheray M, Miorin L, Moreno E, Koh C, Tran QD, Hardy A, Robinot R, Vallet T, Nilsson-Payant BE, Hernandez-Armenta C, Dunham A, Weigang S, Knerr J, Modak M, Quintero D, Zhou Y, Dugourd A, Valdeolivas A, Patil T, Li Q, Hüttenhain R, Cakir M, Muralidharan M, Kim M, Jang G, Tutuncuoglu B, Hiatt J, Guo JZ, Xu J, Bouhaddou S, Mathy CJP, Gaulton A, Manners EJ, Félix E, Shi Y, Goff M, Lim JK, McBride T, O'Neal MC, Cai Y, Chang JCJ, Broadhurst DJ, Klippsten S, De Wit E, Leach AR, Kortemme T, Shoichet B, Ott M, Saez-Rodriguez J, tenOever BR, Mullins RD, Fischer ER, Kochs G, Grosse R, García-Sastre A, Vignuzzi M, Johnson JR, Shokat KM, Swaney DL, Beltrao P, Krogan NJ. The Global Phosphorylation Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell 2020; 182: 685-712. e19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 848] [Cited by in RCA: 791] [Article Influence: 158.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Cavalli E, Petralia MC, Basile MS, Bramanti A, Bramanti P, Nicoletti F, Spandidos DA, Shoenfeld Y, Fagone P. Transcriptomic analysis of COVID19 Lungs and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples reveals predominant B cell activation responses to infection. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46:1266-1273. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Ehrlich A, Uhl S, Ioannidis K, Hofree M. The SARS-CoV-2 transcriptional metabolic signature in lung epithelium. SSRN. 2020;. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Fagone P, Ciurleo R, Lombardo SD, Iacobello C, Palermo CI, Shoenfeld Y, Bendtzen K, Bramanti P, Nicoletti F. Transcriptional landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection dismantles pathogenic pathways activated by the virus, proposes unique sex-specific differences and predicts tailored therapeutic strategies. Autoimmun Rev. 2020;19:102571. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 17.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Gordon DE, Jang GM, Bouhaddou M, Xu J, Obernier K, White KM, O'Meara MJ, Rezelj VV, Guo JZ, Swaney DL, Tummino TA, Hüttenhain R, Kaake RM, Richards AL, Tutuncuoglu B, Foussard H, Batra J, Haas K, Modak M, Kim M, Haas P, Polacco BJ, Braberg H, Fabius JM, Eckhardt M, Soucheray M, Bennett MJ, Cakir M, McGregor MJ, Li Q, Meyer B, Roesch F, Vallet T, Mac Kain A, Miorin L, Moreno E, Naing ZZC, Zhou Y, Peng S, Shi Y, Zhang Z, Shen W, Kirby IT, Melnyk JE, Chorba JS, Lou K, Dai SA, Barrio-Hernandez I, Memon D, Hernandez-Armenta C, Lyu J, Mathy CJP, Perica T, Pilla KB, Ganesan SJ, Saltzberg DJ, Rakesh R, Liu X, Rosenthal SB, Calviello L, Venkataramanan S, Liboy-Lugo J, Lin Y, Huang XP, Liu Y, Wankowicz SA, Bohn M, Safari M, Ugur FS, Koh C, Savar NS, Tran QD, Shengjuler D, Fletcher SJ, O'Neal MC, Cai Y, Chang JCJ, Broadhurst DJ, Klippsten S, Sharp PP, Wenzell NA, Kuzuoglu-Ozturk D, Wang HY, Trenker R, Young JM, Cavero DA, Hiatt J, Roth TL, Rathore U, Subramanian A, Noack J, Hubert M, Stroud RM, Frankel AD, Rosenberg OS, Verba KA, Agard DA, Ott M, Emerman M, Jura N, von Zastrow M, Verdin E, Ashworth A, Schwartz O, d'Enfert C, Mukherjee S, Jacobson M, Malik HS, Fujimori DG, Ideker T, Craik CS, Floor SN, Fraser JS, Gross JD, Sali A, Roth BL, Ruggero D, Taunton J, Kortemme T, Beltrao P, Vignuzzi M, García-Sastre A, Shokat KM, Shoichet BK, Krogan NJ. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature. 2020;583:459-468. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3145] [Cited by in RCA: 3188] [Article Influence: 637.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Hadjadj J, Yatim N, Barnabei L, Corneau A, Boussier J, Smith N, Péré H, Charbit B, Bondet V, Chenevier-Gobeaux C, Breillat P, Carlier N, Gauzit R, Morbieu C, Pène F, Marin N, Roche N, Szwebel TA, Merkling SH, Treluyer JM, Veyer D, Mouthon L, Blanc C, Tharaux PL, Rozenberg F, Fischer A, Duffy D, Rieux-Laucat F, Kernéis S, Terrier B. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science. 2020;369:718-724. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2291] [Cited by in RCA: 2170] [Article Influence: 434.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Wang J, Jiang M, Chen X, Montaner LJ. Cytokine storm and leukocyte changes in mild vs severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: Review of 3939 COVID-19 patients in China and emerging pathogenesis and therapy concepts. J Leukoc Biol. 2020;108:17-41. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 392] [Cited by in RCA: 542] [Article Influence: 108.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497-506. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 35178] [Cited by in RCA: 30116] [Article Influence: 6023.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (3)] |
| 40. | Chen G, Wu D, Guo W, Cao Y, Huang D, Wang H, Wang T, Zhang X, Chen H, Yu H, Zhang M, Wu S, Song J, Chen T, Han M, Li S, Luo X, Zhao J, Ning Q. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:2620-2629. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2835] [Cited by in RCA: 3417] [Article Influence: 683.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Xiong Y, Liu Y, Cao L, Wang D, Guo M, Jiang A, Guo D, Hu W, Yang J, Tang Z, Wu H, Lin Y, Zhang M, Zhang Q, Shi M, Zhou Y, Lan K, Chen Y. Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:761-770. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 877] [Cited by in RCA: 856] [Article Influence: 171.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Blanco-Melo D, Nilsson-Payant BE, Liu WC, Uhl S, Hoagland D, Møller R, Jordan TX, Oishi K, Panis M, Sachs D, Wang TT, Schwartz RE, Lim JK, Albrecht RA, tenOever BR. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020; 181: 1036-1045. e9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3510] [Cited by in RCA: 3167] [Article Influence: 633.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Galani IE, Rovina N, Lampropoulou V, Triantafyllia V, Manioudaki M, Pavlos E, Koukaki E, Fragkou PC, Panou V, Rapti V, Koltsida O, Mentis A, Koulouris N, Tsiodras S, Koutsoukou A, Andreakos E. Untuned antiviral immunity in COVID-19 revealed by temporal type I/III interferon patterns and flu comparison. Nat Immunol. 2021;22:32-40. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 416] [Cited by in RCA: 383] [Article Influence: 95.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Theobald SJ, Simonis A, Kreer C, Zehner M, Fischer J, Albert M-C, Malin JJ, Gräb J, Winter S, Silva US de, Böll B, Köhler P, Gruell H, Suàrez I, Hallek M, Fätkenheuer G, Jung N, Cornely O, Lehmann C, Kashkar H, Klein F, Rybniker J. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein primes inflammasome-mediated interleukin-1-beta secretion in COVID-19 patient-derived macrophages. Res Sq. 2020;. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 45. | Zhu N, Wang W, Liu Z, Liang C, Ye F, Huang B, Zhao L, Wang H, Zhou W, Deng Y, Mao L, Su C, Qiang G, Jiang T, Zhao J, Wu G, Song J, Tan W. Morphogenesis and cytopathic effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection in human airway epithelial cells. Nat Commun. 2020;11:3910. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 290] [Cited by in RCA: 249] [Article Influence: 49.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Xu H, Chitre SA, Akinyemi IA, Loeb JC, Lednicky JA, McIntosh MT, Bhaduri-McIntosh S. SARS-CoV-2 viroporin triggers the NLRP3 inflammatory pathway. 2020 Preprint. Available from: bioRxiv:2020.10.27.357731. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 47. | Li S, Zhang Y, Guan Z, Li H, Ye M, Chen X, Shen J, Zhou Y, Shi ZL, Zhou P, Peng K. SARS-CoV-2 triggers inflammatory responses and cell death through caspase-8 activation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:235. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 153] [Cited by in RCA: 270] [Article Influence: 54.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Qu Y, Wang X, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Yang X, Hu G, Liu C, Li J, Ren S, Xiao Z, Liu Z, Wang W, Li P, Zhang R, Liang Q. ORF3a mediated-incomplete autophagy facilitates SARS-CoV-2 replication. 2020 Preprint. Available from: bioRxiv:2020.11.12.380709. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 49. | Ramachandran P, Onukogu I, Ghanta S, Gajendran M, Perisetti A, Goyal H, Aggarwal A. Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Outcomes in Hospitalized Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients. Dig Dis. 2020;38:373-379. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 14.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DSC, Du B, Li LJ, Zeng G, Yuen KY, Chen RC, Tang CL, Wang T, Chen PY, Xiang J, Li SY, Wang JL, Liang ZJ, Peng YX, Wei L, Liu Y, Hu YH, Peng P, Wang JM, Liu JY, Chen Z, Li G, Zheng ZJ, Qiu SQ, Luo J, Ye CJ, Zhu SY, Zhong NS; China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1708-1720. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19202] [Cited by in RCA: 18877] [Article Influence: 3775.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (7)] |
| 51. | Li LQ, Huang T, Wang YQ, Wang ZP, Liang Y, Huang TB, Zhang HY, Sun W, Wang Y. COVID-19 patients' clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92:577-583. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 886] [Cited by in RCA: 848] [Article Influence: 169.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 52. | Jin X, Lian JS, Hu JH, Gao J, Zheng L, Zhang YM, Hao SR, Jia HY, Cai H, Zhang XL, Yu GD, Xu KJ, Wang XY, Gu JQ, Zhang SY, Ye CY, Jin CL, Lu YF, Yu X, Yu XP, Huang JR, Xu KL, Ni Q, Yu CB, Zhu B, Li YT, Liu J, Zhao H, Zhang X, Yu L, Guo YZ, Su JW, Tao JJ, Lang GJ, Wu XX, Wu WR, Qv TT, Xiang DR, Yi P, Shi D, Chen Y, Ren Y, Qiu YQ, Li LJ, Sheng J, Yang Y. Epidemiological, clinical and virological characteristics of 74 cases of coronavirus-infected disease 2019 (COVID-19) with gastrointestinal symptoms. Gut. 2020;69:1002-1009. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 944] [Cited by in RCA: 870] [Article Influence: 174.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Fang D, Ma J, Guan J, Wang M, Song Y, Tian D, Li P. Manifestations of Digestive system in hospitalized patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-center, descriptive study. Zhonghua Xiaohua Zazhi. 2020;40:E005-E005. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 54. | Xiao F, Tang M, Zheng X, Liu Y, Li X, Shan H. Evidence for Gastrointestinal Infection of SARS-CoV-2. Gastroenterology 2020; 158: 1831-1833. e3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1985] [Cited by in RCA: 1995] [Article Influence: 399.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 55. | Parasa S, Desai M, Thoguluva Chandrasekar V, Patel HK, Kennedy KF, Roesch T, Spadaccini M, Colombo M, Gabbiadini R, Artifon ELA, Repici A, Sharma P. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Fecal Viral Shedding in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e2011335. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 301] [Cited by in RCA: 302] [Article Influence: 60.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | Galanopoulos M, Gkeros F, Doukatas A, Karianakis G, Pontas C, Tsoukalas N, Viazis N, Liatsos C, Mantzaris GJ. COVID-19 pandemic: Pathophysiology and manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26:4579-4588. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 98] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 21.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (5)] |
| 57. | Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, Wang B, Xiang H, Cheng Z, Xiong Y, Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang X, Peng Z. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323:1061-1069. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14113] [Cited by in RCA: 14767] [Article Influence: 2953.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 58. | Han C, Duan C, Zhang S, Spiegel B, Shi H, Wang W, Zhang L, Lin R, Liu J, Ding Z, Hou X. Digestive Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients With Mild Disease Severity: Clinical Presentation, Stool Viral RNA Testing, and Outcomes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:916-923. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 413] [Cited by in RCA: 383] [Article Influence: 76.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 59. | Pan L, Mu M, Yang P, Sun Y, Wang R, Yan J, Li P, Hu B, Wang J, Hu C, Jin Y, Niu X, Ping R, Du Y, Li T, Xu G, Hu Q, Tu L. Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients With Digestive Symptoms in Hubei, China: A Descriptive, Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:766-773. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1160] [Cited by in RCA: 1205] [Article Influence: 241.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 60. | Redd WD, Zhou JC, Hathorn KE, McCarty TR, Bazarbashi AN, Thompson CC, Shen L, Chan WW. Prevalence and Characteristics of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in the United States: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2020; 159: 765-767. e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 241] [Cited by in RCA: 283] [Article Influence: 56.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, Qiu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wei Y, Xia J, Yu T, Zhang X, Zhang L. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395:507-513. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14869] [Cited by in RCA: 12976] [Article Influence: 2595.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 62. | Mo P, Xing Y, Xiao Y, Deng L, Zhao Q, Wang H, Xiong Y, Cheng Z, Gao S, Liang K, Luo M, Chen T, Song S, Ma Z, Chen X, Zheng R, Cao Q, Wang F, Zhang Y. Clinical characteristics of refractory COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 486] [Cited by in RCA: 601] [Article Influence: 120.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 63. | Leung WK, To KF, Chan PK, Chan HL, Wu AK, Lee N, Yuen KY, Sung JJ. Enteric involvement of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus infection. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1011-1017. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 380] [Cited by in RCA: 391] [Article Influence: 17.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 64. | Carvalho A, Alqusairi R, Adams A, Paul M, Kothari N, Peters S, DeBenedet AT. SARS-CoV-2 Gastrointestinal Infection Causing Hemorrhagic Colitis: Implications for Detection and Transmission of COVID-19 Disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:942-946. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 139] [Cited by in RCA: 143] [Article Influence: 28.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 65. | Pan Y, Zhang D, Yang P, Poon LLM, Wang Q. Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20:411-412. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1120] [Cited by in RCA: 1127] [Article Influence: 225.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 66. | Young BE, Ong SWX, Kalimuddin S, Low JG, Tan SY, Loh J, Ng OT, Marimuthu K, Ang LW, Mak TM, Lau SK, Anderson DE, Chan KS, Tan TY, Ng TY, Cui L, Said Z, Kurupatham L, Chen MI, Chan M, Vasoo S, Wang LF, Tan BH, Lin RTP, Lee VJM, Leo YS, Lye DC; Singapore 2019 Novel Coronavirus Outbreak Research Team. Epidemiologic Features and Clinical Course of Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore. JAMA. 2020;323:1488-1494. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1346] [Cited by in RCA: 1366] [Article Influence: 273.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 67. | Peng L, Liu J, Xu W, Luo Q, Chen D, Lei Z, Huang Z, Li X, Deng K, Lin B, Gao Z. SARS-CoV-2 can be detected in urine, blood, anal swabs, and oropharyngeal swabs specimens. J Med Virol. 2020;92:1676-1680. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 207] [Cited by in RCA: 288] [Article Influence: 57.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 68. | Wu Y, Guo C, Tang L, Hong Z, Zhou J, Dong X, Yin H, Xiao Q, Tang Y, Qu X, Kuang L, Fang X, Mishra N, Lu J, Shan H, Jiang G, Huang X. Prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA in faecal samples. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:434-435. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1050] [Cited by in RCA: 1150] [Article Influence: 230.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Chen Y, Chen L, Deng Q, Zhang G, Wu K, Ni L, Yang Y, Liu B, Wang W, Wei C, Yang J, Ye G, Cheng Z. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the feces of COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2020;92:833-840. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 505] [Cited by in RCA: 571] [Article Influence: 114.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 70. | Ling Y, Xu SB, Lin YX, Tian D, Zhu ZQ, Dai FH, Wu F, Song ZG, Huang W, Chen J, Hu BJ, Wang S, Mao EQ, Zhu L, Zhang WH, Lu HZ. Persistence and clearance of viral RNA in 2019 novel coronavirus disease rehabilitation patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133:1039-1043. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 641] [Cited by in RCA: 577] [Article Influence: 115.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Hikmet F, Méar L, Edvinsson Å, Micke P, Uhlén M, Lindskog C. The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues. Mol Syst Biol. 2020;16:e9610. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 631] [Cited by in RCA: 710] [Article Influence: 142.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 72. | Zou X, Chen K, Zou J, Han P, Hao J, Han Z. Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection. Front Med. 2020;14:185-192. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1286] [Cited by in RCA: 1530] [Article Influence: 306.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 73. | Zhang H, Kang Z, Gong H, Xu D, Wang J, Li Z, Cui X, Xiao J, Zhan J, Meng T, Zhou W, Liu J, Xu H. Digestive system is a potential route of COVID-19: an analysis of single-cell coexpression pattern of key proteins in viral entry process. Gut. 2020;69:1010-1018. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 314] [Cited by in RCA: 380] [Article Influence: 76.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 74. | Bar-On YM, Flamholz A, Phillips R, Milo R. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) by the numbers. Elife. 2020;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 750] [Cited by in RCA: 670] [Article Influence: 134.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 75. | Sender R, Bar-On YM, Flamholz A, Gleizer S, Bernsthein B, Phillips R, Milo R. The total number and mass of SARS-CoV-2 virions in an infected person. medRxiv. 2020;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 76. | Lamers MM, Beumer J, van der Vaart J, Knoops K, Puschhof J, Breugem TI, Ravelli RBG, Paul van Schayck J, Mykytyn AZ, Duimel HQ, van Donselaar E, Riesebosch S, Kuijpers HJH, Schipper D, van de Wetering WJ, de Graaf M, Koopmans M, Cuppen E, Peters PJ, Haagmans BL, Clevers H. SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human gut enterocytes. Science. 2020;369:50-54. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1245] [Cited by in RCA: 1312] [Article Influence: 262.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 77. | Bradley BT, Maioli H, Johnston R, Chaudhry I, Fink SL, Xu H, Najafian B, Deutsch G, Lacy JM, Williams T, Yarid N, Marshall DA. Histopathology and ultrastructural findings of fatal COVID-19 infections in Washington State: a case series. Lancet. 2020;396:320-332. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 549] [Cited by in RCA: 622] [Article Influence: 124.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 78. | Xiao F, Sun J, Xu Y, Li F, Huang X, Li H, Zhao J, Huang J. Infectious SARS-CoV-2 in Feces of Patient with Severe COVID-19. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:1920-1922. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 346] [Cited by in RCA: 389] [Article Influence: 77.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 79. | Wurtz N, Penant G, Jardot P, Duclos N, La Scola B. Culture of SARS-CoV-2 in a panel of laboratory cell lines, permissivity, and differences in growth profile. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021;40:477-484. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 19.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 80. | Chu H, Chan JF, Wang Y, Yuen TT, Chai Y, Shuai H, Yang D, Hu B, Huang X, Zhang X, Hou Y, Cai JP, Zhang AJ, Zhou J, Yuan S, To KK, Hung IF, Cheung TT, Ng AT, Hau-Yee Chan I, Wong IY, Law SY, Foo DC, Leung WK, Yuen KY. SARS-CoV-2 Induces a More Robust Innate Immune Response and Replicates Less Efficiently Than SARS-CoV in the Human Intestines: An Ex Vivo Study With Implications on Pathogenesis of COVID-19. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;11:771-781. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 81. | Lee S, Yoon GY, Myoung J, Kim SJ, Ahn DG. Robust and persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection in the human intestinal brush border expressing cells. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:2169-2179. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 9.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 82. | De Maio F, Lo Cascio E, Babini G, Sali M, Della Longa S, Tilocca B, Roncada P, Arcovito A, Sanguinetti M, Scambia G, Urbani A. Improved binding of SARS-CoV-2 Envelope protein to tight junction-associated PALS1 could play a key role in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Microbes Infect. 2020;22:592-597. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 56] [Article Influence: 11.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 83. | Straight SW, Shin K, Fogg VC, Fan S, Liu CJ, Roh M, Margolis B. Loss of PALS1 expression leads to tight junction and polarity defects. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:1981-1990. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 132] [Cited by in RCA: 146] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 84. | Guo Y, Luo R, Wang Y, Deng P, Song T, Zhang M, Wang P, Zhang X, Cui K, Tao T, Li Z, Chen W, Zheng Y, Qin J. SARS-CoV-2 induced intestinal responses with a biomimetic human gut-on-chip. Sci Bull (Beijing). 2021;66:783-793. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 20.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 85. | Cao Y, Yang R, Wang W, Lee I, Zhang R, Zhang W, Sun J, Xu B, Meng X. Computational Study of the Ion and Water Permeation and Transport Mechanisms of the SARS-CoV-2 Pentameric E Protein Channel. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:565797. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 86. | Barrett KE, Keely SJ. Chloride secretion by the intestinal epithelium: molecular basis and regulatory aspects. Annu Rev Physiol. 2000;62:535-572. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 366] [Cited by in RCA: 379] [Article Influence: 15.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 87. | Ren Y, Shu T, Wu D, Mu J, Wang C, Huang M, Han Y, Zhang XY, Zhou W, Qiu Y, Zhou X. The ORF3a protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces apoptosis in cells. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17:881-883. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 264] [Cited by in RCA: 364] [Article Influence: 72.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 88. | Obukhov AG, Stevens BR, Prasad R, Li Calzi S, Boulton ME, Raizada MK, Oudit GY, Grant MB. SARS-CoV-2 Infections and ACE2: Clinical Outcomes Linked With Increased Morbidity and Mortality in Individuals With Diabetes. Diabetes. 2020;69:1875-1886. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 11.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 89. | Xu J, Xu X, Jiang L, Dua K, Hansbro PM, Liu G. SARS-CoV-2 induces transcriptional signatures in human lung epithelial cells that promote lung fibrosis. Respir Res. 2020;21:182. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 139] [Cited by in RCA: 148] [Article Influence: 29.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 90. | Jia HP, Look DC, Tan P, Shi L, Hickey M, Gakhar L, Chappell MC, Wohlford-Lenane C, McCray PB Jr. Ectodomain shedding of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in human airway epithelia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009;297:L84-L96. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 230] [Cited by in RCA: 268] [Article Influence: 16.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 91. | Andring JT, McKenna R, Stevens BR. Amino acid transporter B0AT1 influence on ADAM17 interactions with SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 putatively expressed in intestine, kidney, and cardiomyocytes. 2020 Preprint. Available from: bioRxiv: 2020.10.30.361873. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 92. | Deretic V, Saitoh T, Akira S. Autophagy in infection, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:722-737. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1278] [Cited by in RCA: 1521] [Article Influence: 126.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 93. | Sarkar S. Regulation of autophagy by mTOR-dependent and mTOR-independent pathways: autophagy dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and therapeutic application of autophagy enhancers. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41:1103-1130. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 259] [Cited by in RCA: 286] [Article Influence: 26.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 94. | Delorme-Axford E, Klionsky DJ. Highlights in the fight against COVID-19: does autophagy play a role in SARS-CoV-2 infection? Autophagy. 2020;16:2123-2127. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 95. | Shojaei S, Suresh M, Klionsky DJ, Labouta HI, Ghavami S. Autophagy and SARS-CoV-2 infection: Apossible smart targeting of the autophagy pathway. Virulence. 2020;11:805-810. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 14.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 96. | Siddiqi HK, Mehra MR. COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: A clinical-therapeutic staging proposal. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020;39:405-407. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1169] [Cited by in RCA: 1122] [Article Influence: 224.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 97. | Zhang L, Han C, Zhang S, Duan C, Shang H, Bai T, Hou X. Diarrhea and altered inflammatory cytokine pattern in severe coronavirus disease 2019: Impact on disease course and in-hospital mortality. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36:421-429. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 11.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 98. | Ma TY, Iwamoto GK, Hoa NT, Akotia V, Pedram A, Boivin MA, Said HM. TNF-alpha-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability requires NF-kappa B activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;286:G367-G376. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 613] [Cited by in RCA: 714] [Article Influence: 34.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 99. | Al-Sadi R, Ye D, Boivin M, Guo S, Hashimi M, Ereifej L, Ma TY. Interleukin-6 modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability is mediated by JNK pathway activation of claudin-2 gene. PLoS One. 2014;9:e85345. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 145] [Cited by in RCA: 211] [Article Influence: 19.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 100. | Kuhn KA, Manieri NA, Liu TC, Stappenbeck TS. IL-6 stimulates intestinal epithelial proliferation and repair after injury. PLoS One. 2014;9:e114195. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 158] [Cited by in RCA: 200] [Article Influence: 18.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 101. | Kühn R, Löhler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Müller W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell. 1993;75:263-274. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3189] [Cited by in RCA: 3226] [Article Influence: 100.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 102. | Lorén V, Cabré E, Ojanguren I, Domènech E, Pedrosa E, García-Jaraquemada A, Mañosa M, Manyé J. Interleukin-10 Enhances the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier in the Presence of Corticosteroids through p38 MAPK Activity in Caco-2 Monolayers: A Possible Mechanism for Steroid Responsiveness in Ulcerative Colitis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0130921. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 103. | Gu S, Chen Y, Wu Z, Gao H, Lv L, Guo F, Zhang X, Luo R, Huang C, Lu H, Zheng B, Zhang J, Yan R, Zhang H, Jiang H, Xu Q, Guo J, Gong Y, Tang L, Li L. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 or H1N1 Influenza. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:2669-2678. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 324] [Cited by in RCA: 569] [Article Influence: 142.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 104. | Zuo T, Zhang F, Lui GCY, Yeoh YK, Li AYL, Zhan H, Wan Y, Chung ACK, Cheung CP, Chen N, Lai CKC, Chen Z, Tso EYK, Fung KSC, Chan V, Ling L, Joynt G, Hui DSC, Chan FKL, Chan PKS, Ng SC. Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients With COVID-19 During Time of Hospitalization. Gastroenterology 2020; 159: 944-955. e8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 739] [Cited by in RCA: 1066] [Article Influence: 213.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 105. | Mifsud EJ, Hayden FG, Hurt AC. Antivirals targeting the polymerase complex of influenza viruses. Antiviral Res. 2019;169:104545. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 89] [Cited by in RCA: 109] [Article Influence: 18.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 106. | Granata G, Bartoloni A, Codeluppi M, Contadini I, Cristini F, Fantoni M, Ferraresi A, Fornabaio C, Grasselli S, Lagi F, Masucci L, Puoti M, Raimondi A, Taddei E, Trapani FF, Viale P, Johnson S, Petrosillo N; On Behalf Of The CloVid Study Group. The Burden of Clostridioides Difficile Infection during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Retrospective Case-Control Study in Italian Hospitals (CloVid). J Clin Med. 2020;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 9.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 107. | Hanna R, Dalvi S, Sălăgean T, Pop ID, Bordea IR, Benedicenti S. Understanding COVID-19 Pandemic: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. An Evidence-Based Review. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:13-56. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 108. | Gramlich L, Kichian K, Pinilla J, Rodych NJ, Dhaliwal R, Heyland DK. Does enteral nutrition compared to parenteral nutrition result in better outcomes in critically ill adult patients? Nutrition. 2004;20:843-848. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 422] [Cited by in RCA: 365] [Article Influence: 18.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 109. | Blumenstein I, Shastri YM, Stein J. Gastroenteric tube feeding: techniques, problems and solutions. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:8505-8524. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 325] [Cited by in RCA: 269] [Article Influence: 24.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (10)] |
| 110. | Li GF, An XX, Yu Y, Jiao LR, Canarutto D, Yu G, Wang G, Wu DN, Xiao Y. Do proton pump inhibitors influence SARS-CoV-2 related outcomes? Gut. 2020;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 8.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 111. | Leonard J, Marshall JK, Moayyedi P. Systematic review of the risk of enteric infection in patients taking acid suppression. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2047-56; quiz 2057. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 423] [Cited by in RCA: 423] [Article Influence: 23.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 112. | Tariq R, Singh S, Gupta A, Pardi DS, Khanna S. Association of Gastric Acid Suppression With Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177:784-791. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 119] [Cited by in RCA: 115] [Article Influence: 14.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 113. | Hafiz RA, Wong C, Paynter S, David M, Peeters G. The Risk of Community-Acquired Enteric Infection in Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Pharmacother. 2018;52:613-622. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 114. | Moayyedi P, Eikelboom JW, Bosch J, Connolly SJ, Dyal L, Shestakovska O, Leong D, Anand SS, Störk S, Branch KRH, Bhatt DL, Verhamme PB, O'Donnell M, Maggioni AP, Lonn EM, Piegas LS, Ertl G, Keltai M, Bruns NC, Muehlhofer E, Dagenais GR, Kim JH, Hori M, Steg PG, Hart RG, Diaz R, Alings M, Widimsky P, Avezum A, Probstfield J, Zhu J, Liang Y, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Kakkar AK, Parkhomenko AN, Ryden L, Pogosova N, Dans AL, Lanas F, Commerford PJ, Torp-Pedersen C, Guzik TJ, Vinereanu D, Tonkin AM, Lewis BS, Felix C, Yusoff K, Metsarinne KP, Fox KAA, Yusuf S; COMPASS Investigators. Safety of Proton Pump Inhibitors Based on a Large, Multi-Year, Randomized Trial of Patients Receiving Rivaroxaban or Aspirin. Gastroenterology 2019; 157: 682-691. e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 221] [Cited by in RCA: 340] [Article Influence: 56.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 115. | Amirian ES. Potential fecal transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Current evidence and implications for public health. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;95:363-370. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 218] [Cited by in RCA: 197] [Article Influence: 39.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 116. | Arslan M, Xu B, Gamal El-Din M. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via fecal-oral and aerosols-borne routes: Environmental dynamics and implications for wastewater management in underprivileged societies. Sci Total Environ. 2020;743:140709. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 123] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 20.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 117. | Hindson J. COVID-19: faecal-oral transmission? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17:259. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 233] [Cited by in RCA: 227] [Article Influence: 45.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 118. | Ahmed W, Angel N, Edson J, Bibby K, Bivins A, O'Brien JW, Choi PM, Kitajima M, Simpson SL, Li J, Tscharke B, Verhagen R, Smith WJM, Zaugg J, Dierens L, Hugenholtz P, Thomas KV, Mueller JF. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: A proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci Total Environ. 2020;728:138764. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1259] [Cited by in RCA: 1260] [Article Influence: 252.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 119. | Medema G, Heijnen L, Elsinga G, Italiaander R, Brouwer A. Presence of SARS-Coronavirus-2 RNA in sewage and correlation with reported COVID-19 prevalence in the early stage of the epidemic in the Netherlands. Environ Sci Technol Lett. 2020;7:511-516. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1010] [Cited by in RCA: 1029] [Article Influence: 205.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |