Published online Sep 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i36.5527
Peer-review started: May 23, 2020
First decision: June 20, 2020
Revised: July 28, 2020
Accepted: September 4, 2020
Article in press: September 4, 2020
Published online: September 28, 2020
Processing time: 124 Days and 0.3 Hours
A gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is a mesenchymal tumor of the gastrointestinal tract that is most commonly found in the stomach. Recurrence of GISTs mostly occurs in the liver or peritoneum, and in most cases, multiple metastases occur. As a solitary peritoneal metastasis is rare, an appropriate treatment strategy has not been established. Here, we report a case of solitary peritoneal metastasis after complete resection of gastric GIST.
A 76-year-old woman was diagnosed with stomach GIST and underwent laparoscopic local resection using the CLEAN-NET method. As the recurrence risk was intermediate, adjuvant imatinib therapy was not administered. Two years after surgery, routine computed tomography revealed an abdominal mass between the dorsal side of the right hepatic lobe and right kidney. Other imaging tests did not reveal any abnormalities. Laparoscopic observation showed that the tumor was located at the retroperitoneum, and intraperitoneal dissemination was not found. Therefore, we performed laparoscopic tumor resection. Immunohistochemically, the tumor was positive for c-kit and CD34 and had a relatively high mitotic index and MIB-1 Labeling index. We administered adjuvant imatinib therapy. There was no evidence of recurrence 3 years after the operation.
This is the first reported case of a solitary recurrence of GIST in the peritoneum treated with complete laparoscopic resection.
Core Tip: Solitary peritoneal metastasis from a gastrointestinal stromal tumor is rare, and thus, there are no appropriate treatment strategies available. We report a rare case of solitary peritoneal metastasis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor in a 76-year-old woman. Complete laparoscopic resection of the tumor was performed. Moreover, adjuvant imatinib therapy was administered. There was no recurrence in the 3 years of follow-up.
- Citation: Sugiyama Y, Shimbara K, Sasaki M, Kouyama M, Tazaki T, Takahashi S, Nakamitsu A. Solitary peritoneal metastasis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(36): 5527-5533
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i36/5527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i36.5527
Most metastases from gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) occur locally in the liver and peritoneum. Moreover, peritoneal metastasis is generally found as multiple peritoneal dissemination. Administration of imatinib for the treatment of recurrent GIST has resulted in improved survival. However, long-term imatinib therapy for recurrent GIST seldom results in complete response and eventually leads to the progression of disease and death. Contrarily, surgical resection of metastases is an effective and well-established treatment for colorectal and neuroendocrine cancer[1,2]. Moreover, several single-center analyses have shown that metastasectomy for recurrent GIST was safe, and in some cases, prolonged overall survival[3]. However, few cases of solitary recurrences in the peritoneum have been reported, and the effects of surgical treatment in these cases have not been clarified.
Here, we report a case of solitary peritoneal recurrence of GIST that was successfully resected with laparoscopy.
A 76-year-old woman was undergoing a routine follow-up outpatient visit after surgery. She had no complaint and routine computed tomography (CT) revealed an abdominal mass.
Two years prior to the routine outpatient visit, the patient had been admitted to our hospital complaining of melena. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy revealed a submucosal tumor (SMT) with ulceration located at the greater curvature of the gastric body. CT revealed inhomogeneous density and an extramural mass measuring 4.5 cm. She underwent laparoscopic local resection of the gastric SMT with a non-touch lesion-lifting method called CLEAN-NET. Immunohistochemical examination showed c-kit- and CD34-positive cells. The tumor was 4.5 cm × 4.0 cm in size, and the mitotic count was under 5 mitoses per 50 high-power fields (HPF). The patient was diagnosed with gastric GIST with intermediate recurrence risk. Therefore, adjuvant imatinib therapy was not administered. After surgery, she underwent regular outpatient visits and routine periodic examinations. Two years after the operation, periodic CT revealed an abdominal mass.
The patient’s medical history included hypertension for more than 5 years.
The patient had no subjective symptoms, such as abdominal pain or bloating. Physical examination revealed normal abdominal findings, and the intra-abdominal mass could not be palpated.
A laboratory examination showed a decreased level of hemoglobin (Hb = 11.5 g/dL). Blood tests for liver and kidney function and electrolyte levels showed results within the normal range.
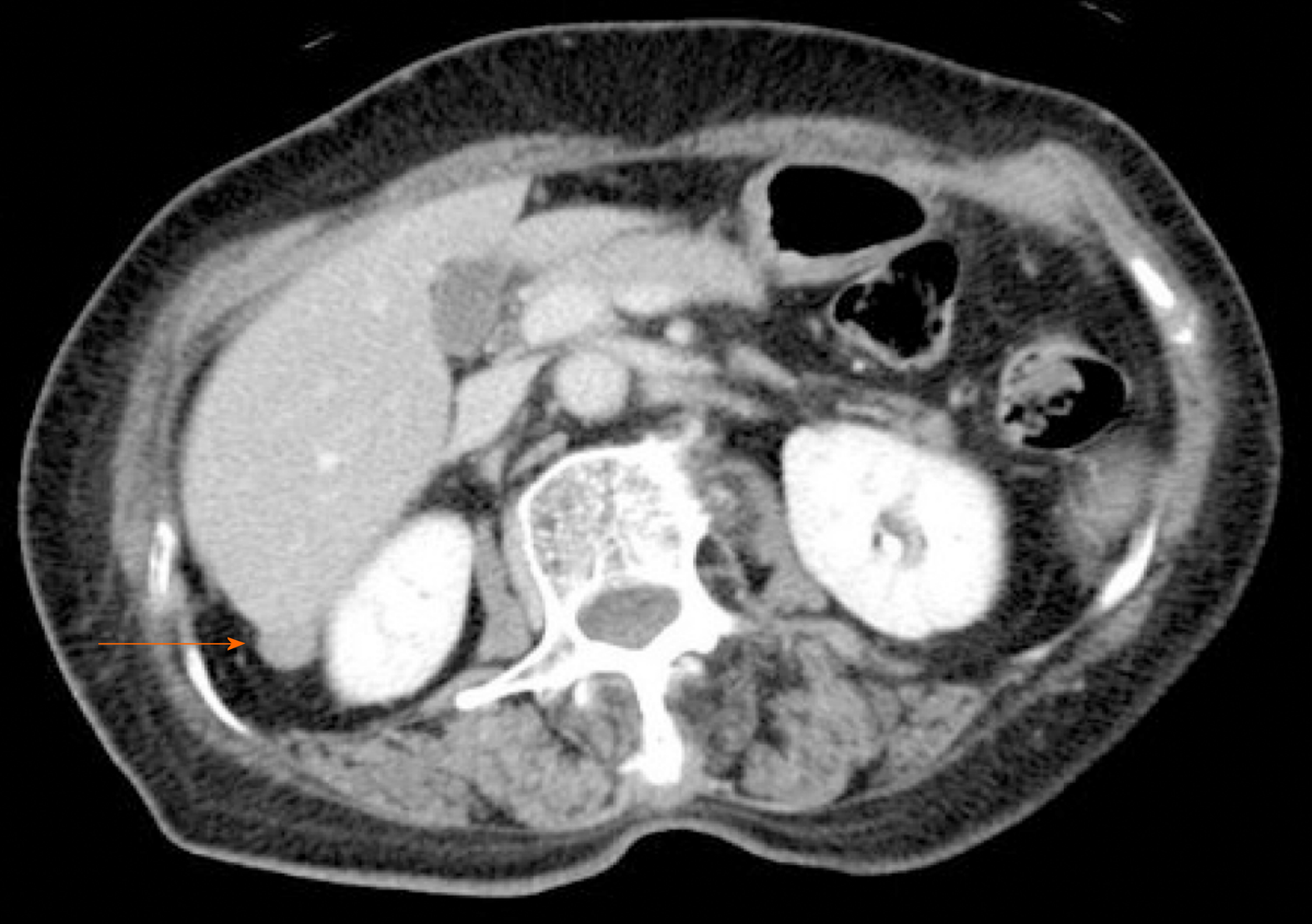
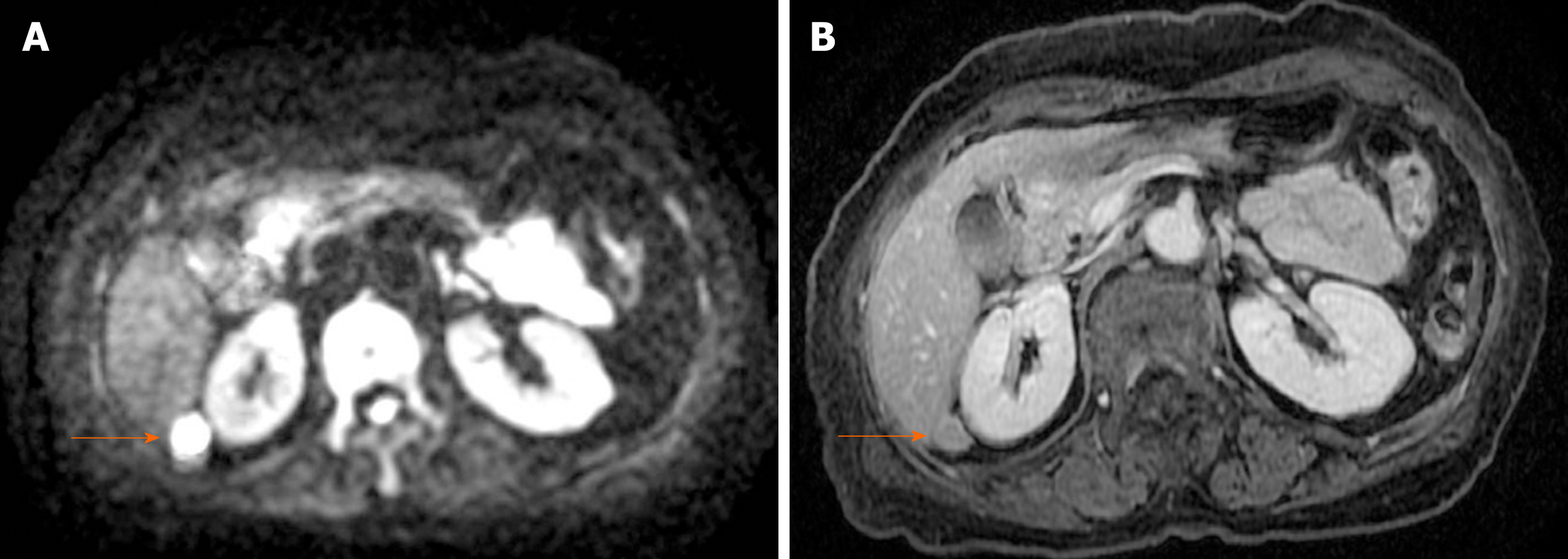
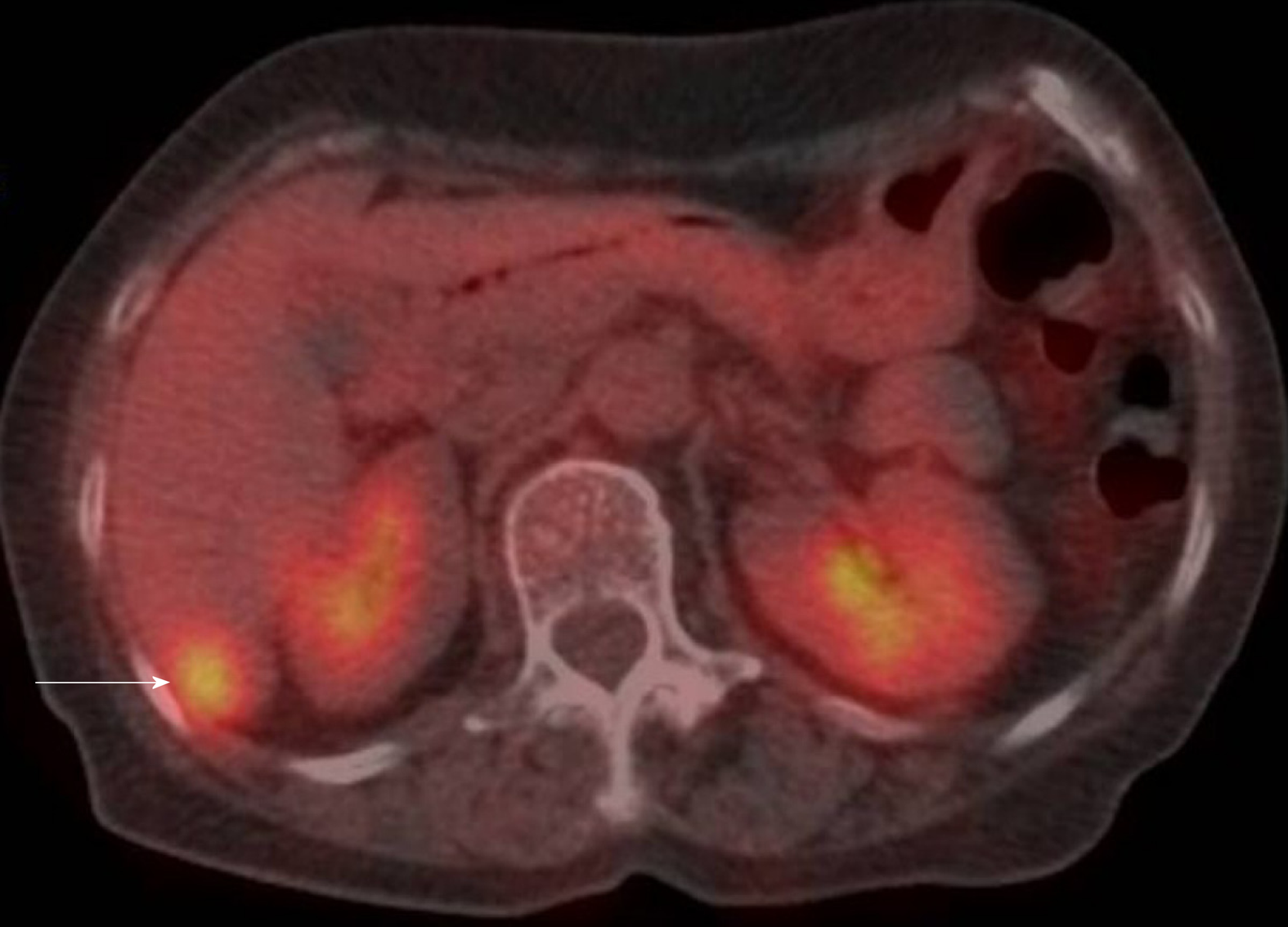
CT revealed an abdominal mass between the dorsal side of the right hepatic lobe and the right kidney (Figure 1). The tumor size was 12 mm with uniform enhancement. CT did not show any other intraperitoneal masses or ascites. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a tumor with high signal intensity with uniform contrast (Figure 2). Positron emission tomography/CT (PET/CT) showed the accumulation of fluorine-18 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose (FDG) in the tumor, with a standardized uptake value of 5.5; no other definitive intra-abdominal lesions were noted (Figure 3). Other imaging tests did not reveal any additional abnormalities.
Based on the clinical course, we suspected a solitary recurrence of gastric GIST but could not distinguish whether the source of the suspected metastases was from the liver or retroperitoneum.
The final diagnosis was a solitary peritoneal recurrence of gastric GIST.
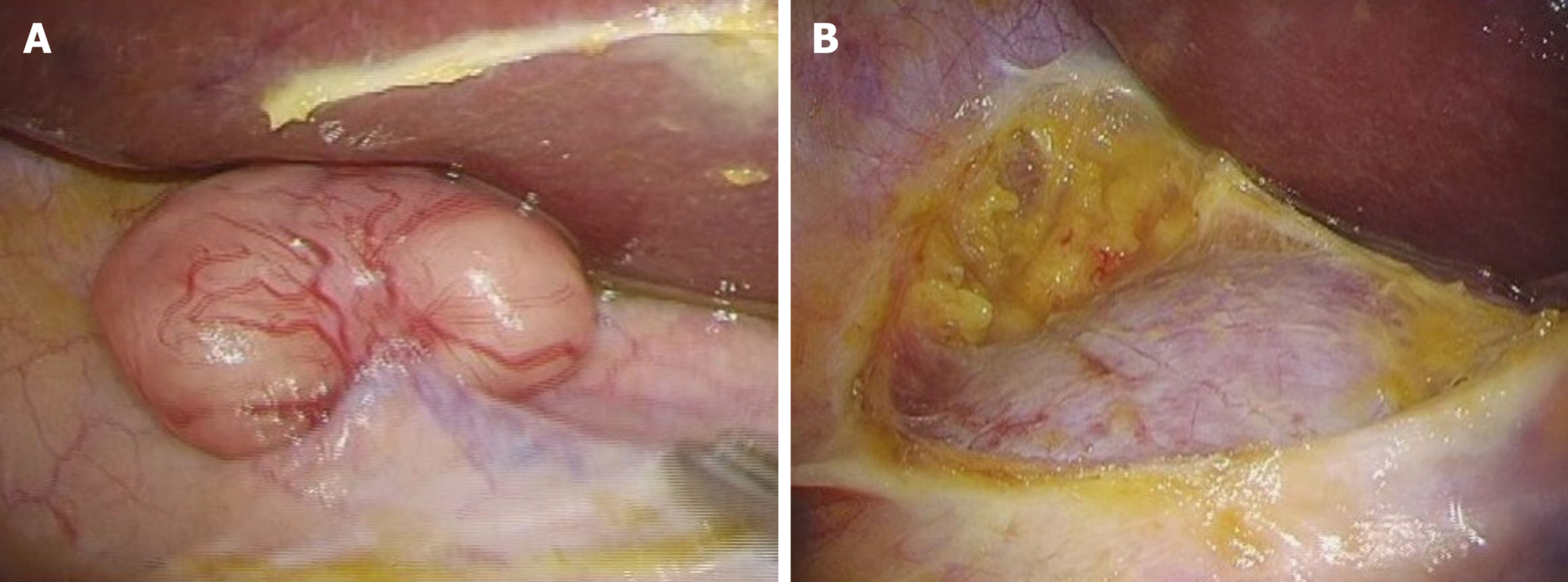
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the proper treatment strategy, we performed laparoscopic surgery. We found that the tumor did not disseminate from either the retroperitoneum and or intraperitoneally. Since malignant cells were not detected in the rapid peritoneal washing cytology, we performed laparoscopic resection of the tumor (Figure 4). The operation time was 54 min, and only 5 mL of blood-loss occurred.
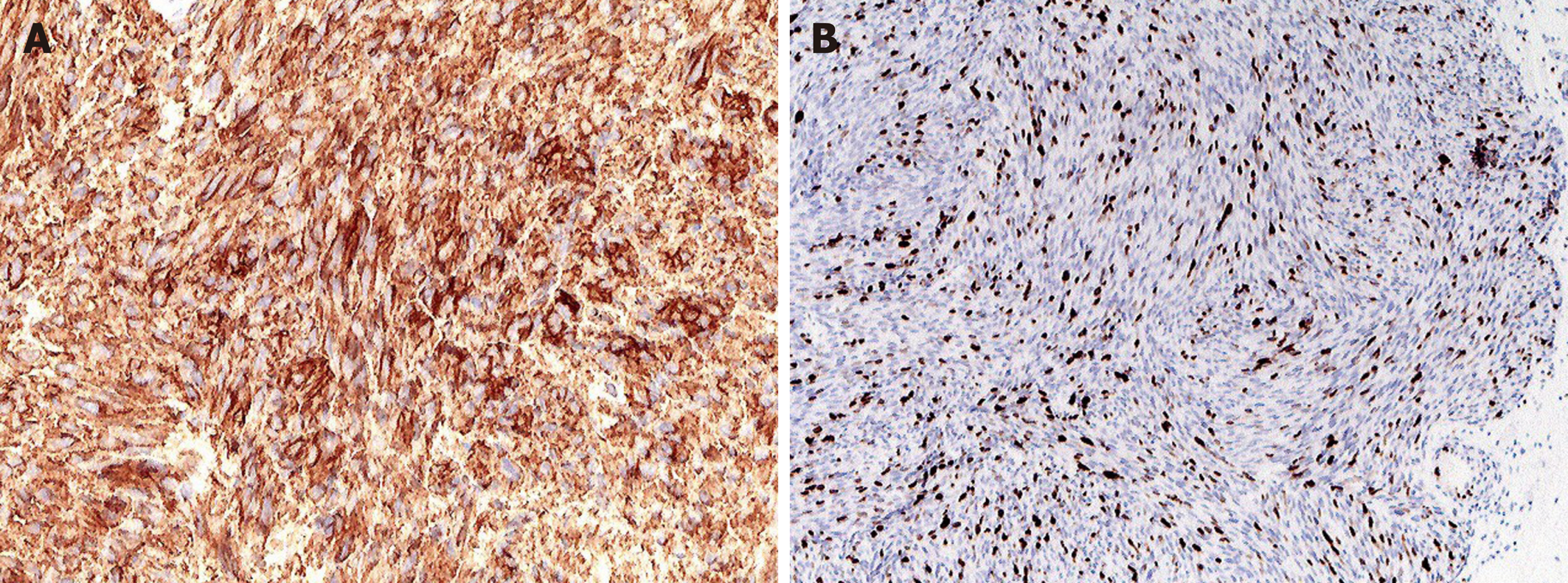
The resected tumor was round and 15 mm in size. Histopathological examination revealed a hypercellular spindle-cell neoplasm with a relatively high mitotic index and an MIB-1 Labeling index of 15%–20% (Figure 5). Immunohistochemically, the tumor was positive for c-kit and CD34 but negative for S-100, α-SMA, and desmin. Genetic analysis of c-kit mutations revealed a kit exon 11 mutation that resulted in the deletion of codons W557 to K558 and 1669 to 1674.
The postoperative course was uneventful, with no complications in the perioperative period. The patient was discharged 7 d after surgery. Subsequently, imatinib administration was initiated at a dosage of 400 mg daily. However, due to the development of grade 3 general fatigue and appetite loss, the imatinib dose was reduced to 300 mg. The patient was followed-up regularly for 3 years post-operation, and there was no evidence of recurrence.
The main site of metastasis after curative resection for GIST is the abdominal cavity. Dematteo et al[4] investigated the recurrence pattern of GIST and found that it was predominantly found in the liver (63%) or the peritoneum (21%). In many cases, subcutaneous and intraperitoneal recurrence of GIST had multiple concurrent or subsequent abdominal and/or hepatic metastases. There have been a few case reports of abdominal wall metastases; mainly, port-site recurrence is documented in the literature. However, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first documented case of GIST with a solitary peritoneal metastasis involving laparoscopic radical resection.
The cause for solitary peritoneal recurrence is unknown; however, several mechanisms may be considered[5]. First, excessive manipulation of the tumor during surgery can be considered[6]; especially in laparoscopic surgery, careless handling of hard forceps during an operation is thought to be the main cause of peritoneal recurrence. To prevent the exposure of the tumor during the operation and to resect safely, several techniques have been developed, such as laparoscopic and endoscopic cooperative surgery and the eversion method. Second, dissemination when removing the tumor may cause solitary intraperitoneal recurrence due to the lack of protection of the abdominal wall. The wound protector protects the wound edges from the contamination of bacteria and tumor cells. Edwards et al[7] reported that the use of a wound protector in gastrointestinal surgery halved infection at the surgical site. Moreover, the use of a tumor retrieval bag prevents tumor cells from leaking into the abdominal cavity. Third, the high pressure of CO2 insufflation may lead to the seeding of tumor cells. Clumps of whole cells are collected in the smoke produced by electrocoagulation at laparoscopy that might be seeded in the peritoneal cavity. Additionally, prolonged exposure of the pneumoperitoneum to high-pressure CO2 (15 mmHg) can promote the migration ability of GIST cells in vitro[8]. In this case, to prevent migration of tumor cells, we performed the CLEAN-NET method[9], used a wound protector and tumor retrieval bag, and maintained low pressure (6 mmHg) CO2 pneumoperitoneum at the time of the first surgery. Moreover, at the time of the second surgery, ascites cytology was negative, and the recurrence was not near the primary tumor, the abdominal wall, or the port site. Therefore, we believe that peritoneal recurrence could be prevented based on the implemented measures.
The treatment of recurrent GIST consisted of the administration of imatinib, which is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, as the first-line therapy[10]. However, reports of a complete response with imatinib therapy alone are rare, and withdrawal of imatinib led to early recurrence in some cases. On the contrary, in some cases of metastasis from GIST, surgical intervention in combination with imatinib was more effective than imatinib alone[11]. Only single or multiple resectable liver metastases or local recurrences are eligible for surgical treatment and are considered optional in Japanese GIST guidelines[12]. However, even in cases of peritoneal dissemination, there are some reports that resection is worthwhile unless there are multiple disseminations. Further, long-term survival has also been observed with treatment for GIST with disseminated foci[13]. Moreover, complete resection of metastatic GIST had a significant positive prognostic value in the multivariate analysis compared to patients in whom complete resection could not be achieved[14]. Therefore, gross resection is at minimum a useful treatment option and should be aimed at R0 resection. In our case, metastatic GIST was a solitary tumor, and a preoperative diagnosis was unclear; therefore, surgical resection was meaningful. Furthermore, it was useful to perform the surgery laparoscopically, which is minimally invasive.
The SSGXVIII/AIO trial, which was an open-label, multicenter, randomized, phase III study, showed that 3 years of adjuvant imatinib improved the recurrence rate and overall survival of GIST patients who were at a high risk of recurrence. Therefore, adjuvant therapy with imatinib for at least 3 years is the standard treatment for patients with high-risk GIST[15]. Our patient initially had a 4.5 cm GIST located in the stomach, with a mitotic rate of 5 mitoses per HPF, and therefore, the patient was classified into the intermediate-risk group; thus, adjuvant imatinib therapy was not administered. However, adjuvant therapy after R0 resection of recurrent GIST has not been studied. In this case, metastatic GIST had a relatively high mitotic index and had an exon 11 mutation with deletion of codons 557 and 558, which have a poorer prognosis than other single nucleotide substitution mutations[16,17]; therefore, the patient was considered to be at a high risk of recurrence. Importantly, Sato et al[18] reported that continuous imatinib administration appears to be important for the prognostic improvement of patients who undergo complete resection of recurrent/metastatic GIST; thus, we administered adjuvant therapy with imatinib after resection of the solitary peritoneal GIST and had no recurrence.
We report a rare case of solitary intraperitoneal metastasis after laparoscopic curative resection of primary gastric GIST. Although the treatment effect of metastasectomy was unclear, laparoscopic resection was useful in confirming the diagnosis of a solitary intra-abdominal metastasis and was minimally invasive.
We thank Dr. Y Daimaru, Department of Pathology, JA Hiroshima General Hospital for his pathological diagnosis.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Surgery
Country/Territory of origin: Japan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A, A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Coco D, Katuchova J S-Editor: Ma YJ L-Editor: A P-Editor: Zhang YL
| 1. | Brown KGM, Koh CE. Surgical management of recurrent colon cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020;11:513-525. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Rashidian N, Alseidi A, Kirks RC. Cancers Metastatic to the Liver. Surg Clin North Am. 2020;100:551-563. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 3. | Zaydfudim V, Okuno SH, Que FG, Nagorney DM, Donohue JH. Role of operative therapy in treatment of metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Surg Res. 2012;177:248-254. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | DeMatteo RP, Lewis JJ, Leung D, Mudan SS, Woodruff JM, Brennan MF. Two hundred gastrointestinal stromal tumors: recurrence patterns and prognostic factors for survival. Ann Surg. 2000;231:51-58. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Schaeff B, Paolucci V, Thomopoulos J. Port site recurrences after laparoscopic surgery. A review. Dig Surg. 1998;15:124-134. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 132] [Cited by in RCA: 115] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Hachim H, Majbar AM, Alaoui M, Raiss M, Sabbah F, Hrora A, Ahallat M. Abdominal wall recurrence of a gastrointestinal stromal tumor: case report. Springerplus. 2015;4:429. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Edwards JP, Ho AL, Tee MC, Dixon E, Ball CG. Wound protectors reduce surgical site infection: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Surg. 2012;256:53-59. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 105] [Cited by in RCA: 106] [Article Influence: 8.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Zheng L, Zhou D, Lu L, Liu Z, Fang L. Effects of CO2 pneumoperitoneum on proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells. Surg Endosc. 2019;33:3384-3395. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Inoue H, Ikeda H, Hosoya T, Yoshida A, Onimaru M, Suzuki M, Kudo SE. Endoscopic mucosal resection, endoscopic submucosal dissection, and beyond: full-layer resection for gastric cancer with nonexposure technique (CLEAN-NET). Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2012;21:129-140. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 116] [Cited by in RCA: 142] [Article Influence: 10.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Blanke CD, Van den Abbeele AD, Eisenberg B, Roberts PJ, Heinrich MC, Tuveson DA, Singer S, Janicek M, Fletcher JA, Silverman SG, Silberman SL, Capdeville R, Kiese B, Peng B, Dimitrijevic S, Druker BJ, Corless C, Fletcher CD, Joensuu H. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:472-480. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3203] [Cited by in RCA: 3107] [Article Influence: 135.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Xia L, Zhang MM, Ji L, Li X, Wu XT. Resection combined with imatinib therapy for liver metastases of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Surg Today. 2010;40:936-942. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Nishida T, Hirota S, Yanagisawa A, Sugino Y, Minami M, Yamamura Y, Otani Y, Shimada Y, Takahashi F, Kubota T; GIST Guideline Subcommittee. Clinical practice guidelines for gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) in Japan: English version. Int J Clin Oncol. 2008;13:416-430. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 219] [Cited by in RCA: 320] [Article Influence: 18.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Katayanagi S, Katsumata K, Murakoshi Y, Ogata T, Serizawa H, Tsuchida A, Aoki T, Shimazu M. [More than 20 years of long-term survival case of intraabdominal GIST by combined therapies with frequent surgeries]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2010;37:2322-2324. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Bauer S, Rutkowski P, Hohenberger P, Miceli R, Fumagalli E, Siedlecki JA, Nguyen BP, Kerst M, Fiore M, Nyckowski P, Hoiczyk M, Cats A, Casali PG, Treckmann J, van Coevorden F, Gronchi A. Long-term follow-up of patients with GIST undergoing metastasectomy in the era of imatinib -- analysis of prognostic factors (EORTC-STBSG collaborative study). Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014;40:412-419. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 92] [Cited by in RCA: 108] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Joensuu H, Eriksson M, Sundby Hall K, Reichardt A, Hermes B, Schütte J, Cameron S, Hohenberger P, Jost PJ, Al-Batran SE, Lindner LH, Bauer S, Wardelmann E, Nilsson B, Kallio R, Jaakkola P, Junnila J, Alvegård T, Reichardt P. Survival Outcomes Associated With 3 Years vs 1 Year of Adjuvant Imatinib for Patients With High-Risk Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: An Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial After 10-Year Follow-up. JAMA Oncol. 2020;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 32.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors--definition, clinical, histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and differential diagnosis. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:1-12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1185] [Cited by in RCA: 1177] [Article Influence: 49.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Zhang H, Liu Q. Prognostic Indicators for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: A Review. Transl Oncol. 2020;13:100812. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 12.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Sato S, Tsujinaka T, Masuzawa T, Yamamoto K, Takahashi T, Yamashita Y, Fujita J, Takagi M, Hirota S, Nishida T. Role of metastasectomy for recurrent/metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors based on an analysis of the Kinki GIST registry. Surg Today. 2017;47:58-64. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |