Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2014; 20(21): 6515-6522
Published online Jun 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6515
Published online Jun 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6515
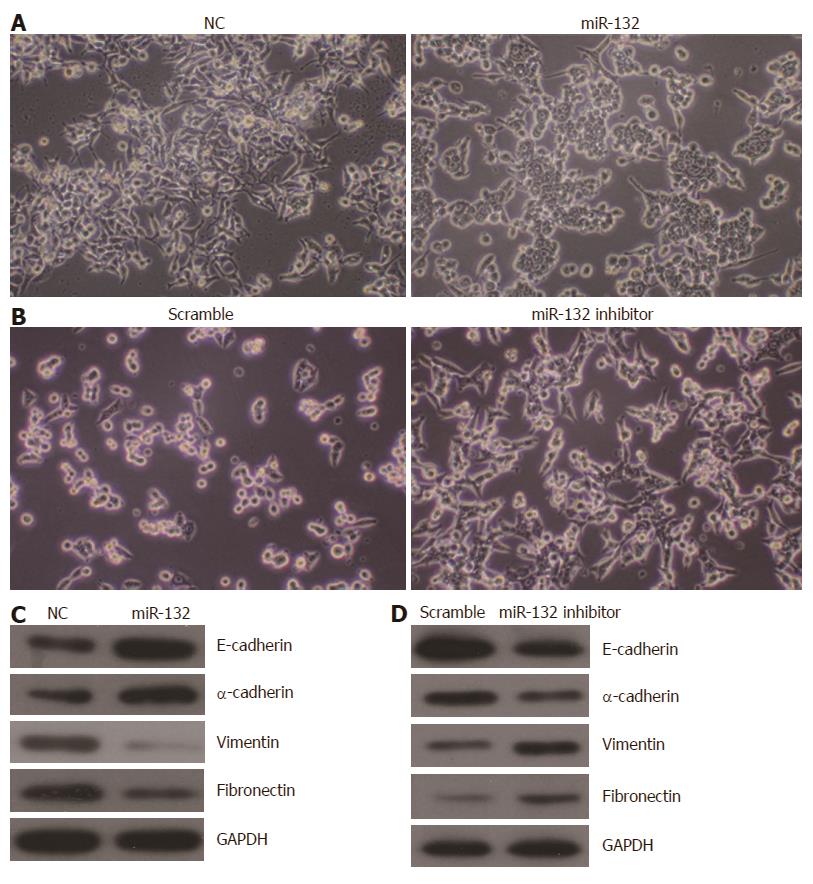
Figure 4 miR-132 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells.
A: Ectopic expression of miR-132 leads to a cobblestone-shaped epithelial-like form in LoVo cells; B: Knockdown of miR-132 leads to spindle-shaped mesenchymal characteristics in HCT116 cells; C, D: Overexpression of miR-132 increased the protein levels of epithelial markers (E-cadherin and α-catenin) but decreased the expression of mesenchymal markers (vimentin and fibronectin) in LoVo cells, whereas knockdown of miR-132 resulted in decreased levels of epithelial markers (E-cadherin and α-catenin) and increased levels of mesenchymal markers (vimentin and fibronectin) in HCT116 cells.
-
Citation: Zheng YB, Luo HP, Shi Q, Hao ZN, Ding Y, Wang QS, Li SB, Xiao GC, Tong SL. miR-132 inhibits colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis
via directly targeting ZEB2. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(21): 6515-6522 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i21/6515.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6515