Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2011; 17(43): 4772-4778
Published online Nov 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4772
Published online Nov 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4772
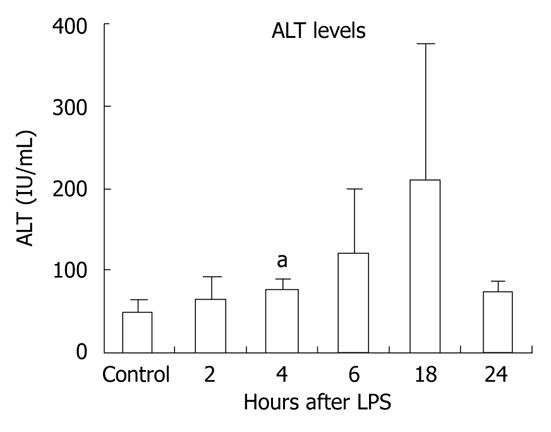
Figure 1 Lipopolysaccharide stimulation results in liver damage.
C57BL/6 wild-type chow-fed mice (three per group) were injected intraperitoneally with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 2, 4, 6, 18 or 24 h. Serum was separated from whole blood and analyzed for alanine aminotransferase (ALT), which was significantly increased after 4 h of LPS stimulation. Mean ± SD are shown. aP < 0.01.
- Citation: Ganz M, Csak T, Nath B, Szabo G. Lipopolysaccharide induces and activates the Nalp3 inflammasome in the liver. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(43): 4772-4778
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i43/4772.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4772